Current protection — MTZ and power failure
All consumers of electricity are connected to the generator end with a power switch. When the load is at or below the rated value, there is no reason to trip, and the overcurrent protections scan the circuit continuously.
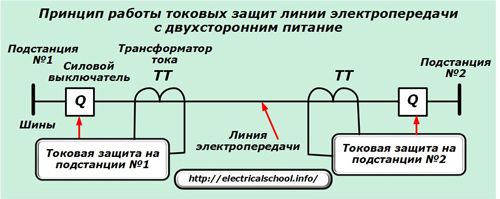
The circuit breaker can be tripped by overcurrent protection when:
1. The size of the load as a result of a short circuit sharply exceeds the nominal value, and short circuit currents are created that can burn out the equipment. The deactivation of such an accident must be done as quickly as possible;
2. due to the connection of additional consumers (or for other reasons), an overload occurred in the circuit — the current slightly exceeded the setting. As a result, there is a gradual heating of the equipment and live parts, when the balance between heat removal to the atmosphere and the heating effect of the current is disturbed.In this case, it is advisable to turn off the switch after a short interval of time, which creates a delay in the supply of the circuit, during which unnecessary loads can be eliminated independently;
3. the direction of the current through the power switch abruptly changed to the opposite — the phase of the current shifted.
For these three emergency situations, the following types of overcurrent protection have been created:
-
cut off;
-
maximum protection;
-
differential phase.
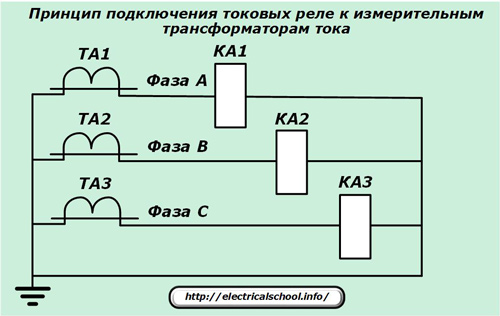
For the operation of current protection, measuring complexes are created, consisting of:
-
measuring current transformers (CT)conversion of the primary current into a secondary value with a given class of metrological error;
-
current relays adjustable to pickup setting;
-
commutation circuit which transmits the secondary current from the CT to the relay with minimum permissible losses.
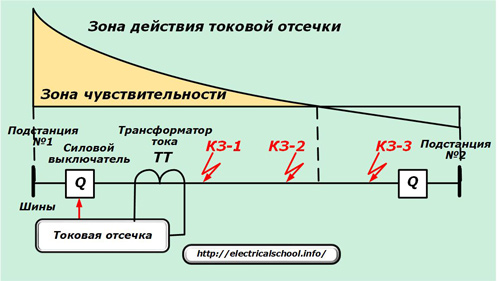
Breaking current (TO)
Its purpose: the fastest removal of short circuits that occurred at the beginning (at least about 20% of the length) of the working area, although in some cases it can be applied to the entire line.
Defense team
This exclusive bundle includes:
-
a measuring device made of a current relay set to operate at the minimum possible load when a metal short circuit (or sensitivity) occurs at the end of the protected zone;
-
intermediate relay, to the coil of which voltage is supplied from the activated contact of the measuring device. The output contact of the intermediate element acts directly on the cut-off solenoid of the power switch, turning it off.
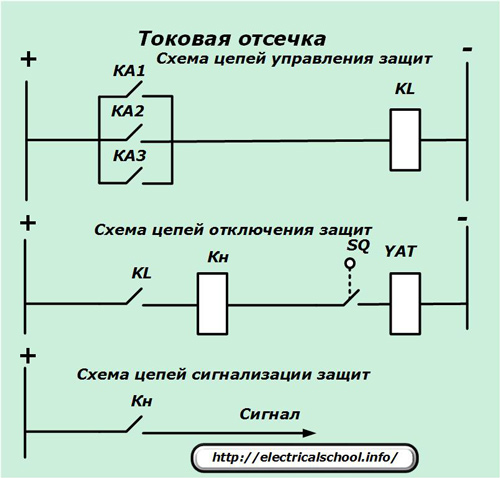
Usually these two relays are enough.Exceptionally, the time relay can be introduced in the current interruption, which is included in a logic circuit between the measuring and executive bodies, in order to create a time delay in the operation of several protections to ensure their selectivity.
To ensure control of the operation of the control and shutdown circuits, signal circuits are introduced into the circuit based on direction indicators Kn, which help the service personnel to analyze the state of the circuit and the operation of the protections.
The technical characteristic of the current interruption is the sensitivity factor, which determines the ratio of the three-phase short-circuit currents at the beginning of the line to the actual tripping of the interruption. ≥1.2 is chosen for the current cutoff.
Overcurrent protection (MTZ)
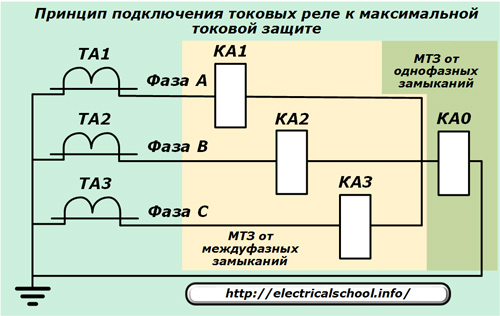
Purpose: protection of objects from currents exceeding the nominal values, taking into account the coefficients:
-
reliability of operation and return of the relay;
-
self-starting circuit.
This offset is designed to eliminate the possibility of false alarms under nominal conditions.
Defense team
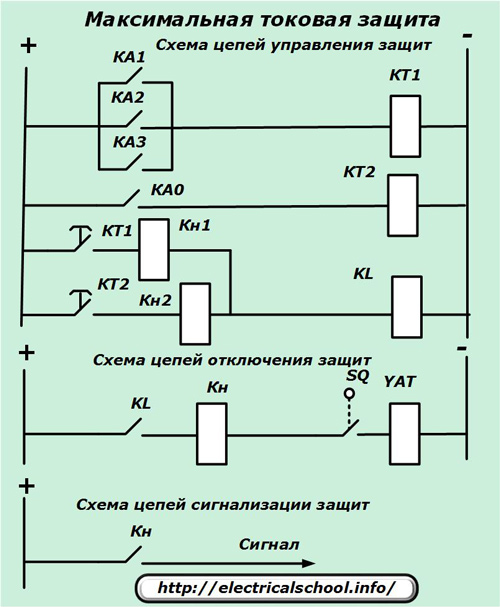
The overcurrent circuit breaker kit includes the same components as in the current breaker, but these must be supplemented with a time relay that creates a delay for the breaker operation to provide selectivity stages.
The technical characteristic of overcurrent protection is the sensitivity coefficient, which determines the ratio of the short-circuit phase currents at the end of the line to the actual operation of the maximum protection. For overcurrent protection, it is selected ≥1.5 for long distance backup and ≥1.2 — within its own area.
Current protection in relay protection and automation also includes differential protection.
