The main types of relay protection
 Electricity in electricity is produced in generating stations, transmitted over long distances by power lines. Overhead and cable transmission lines are located between transformer substations and consumers supplying electricity to the latter.
Electricity in electricity is produced in generating stations, transmitted over long distances by power lines. Overhead and cable transmission lines are located between transformer substations and consumers supplying electricity to the latter.
At all technological stages of production, transmission and distribution of electrical energy, emergency situations can occur that can destroy technical equipment or lead to the death of service personnel in a very short time, calculated in fractions of a second.
The human body is simply not able to react to such short-term events. Therefore, only special technical devices operating in automatic mode according to previously prepared algorithms can control deviations in the nominal parameters of electrical installations, identify the initial stage of an accident and take effective measures to eliminate it.
Historically, the tradition has developed to call protections.And since they worked on a relay basis for a very long time, this additional definition was firmly embedded in them.
How relay protections are formed
The quality of electricity is strictly regulated by technical standards:
-
voltage and current amplitude;
-
network frequency;
-
the form of a sinusoidal harmonic and the presence of external noise in it;
-
direction, magnitude and quality of power;
-
signal phase and some other parameters.
For each of these characteristics, certain types of relay protection have been created. They are, after commissioning:
-
is constantly monitored by the measuring body — transmits the status of one or more network parameters. For example, current, voltage, frequency, phase, power and continuously compare its value with a predetermined range called set point;
-
in the event of a controlled value exceeding the normalized limit, the measuring element is triggered and by switching the position of its contacts switches the circuits of the connected logic part;
-
depending on the tasks to be solved, the logic of the circuit is adjusted to certain algorithms. It performs them by acting on the switching device, for example, the cut-off solenoid of the switch of the primary equipment of the electrical circuit;
-
the power switch eliminates the fault in the circuit by disconnecting the power from it.
According to the types of controlled parameter, protection is divided into:
-
current,
-
voltage;
-
distance (line resistance);
-
frequency;
-
power;
-
phases and others.
Classification by principle of action
The measuring body of each protection is set to a certain setting that limits the coverage area of the protection operation. It can include several sections (primary and backup) or just one.
The protection can react to all possible types of damage occurring in the protected area, or only to any individual, specific manifestations of them.
In the responsible protected area of the power circuit, usually not one protection is installed, but several of its varieties, which complement and preserve mutual action. They are classified into:
1. basic;
2. backup copy.
There are 3 requirements for basic protection:
1. Action on all possible malfunctions in the working area or on most of them;
2. covering the entire controlled area with protection, not a part of it;
3. the fastest response to an emerging malfunction than other protections.
Protection that does not fit these conditions is called fallback, and they perform fallback:
1. near;
2. distant.
In the first case, a backup of the main protections acting on the specified zone is implemented. For the second option, in addition to the neighbor, a reservation of neighboring work zones is created in case their own protection refuses to work in them.
Types of current protection:
Overcurrent and power failure protection
Types of surge protection:

Protections that control the electrical resistance of the supply circuit
Every power line is created from metal current conductors that have a minimal but very real resistance. It constantly increases with the increase in the length of the highway — distance.
When a short circuit occurs at a certain distance from the end of the line at one of the substations, then, according to the principle of measuring the magnitude of the electrical resistance to the place of the resulting damage, protections are used, which are called remote , work.

The following complexes are included in the resistance assessment process:
-
measuring systems of current and voltage transformers designed for self-protection;
-
resistive relays (RS) that process signals from VT and CT to them to calculate the impedance according to Ohm's law to the point of occurrence of a short circuit Z = U / i.
Resistive relays constantly monitor the distance, the length of the power line connected to its zone. When a short circuit occurs on it, the resistance / distance due to metal short circuit decreases sharply, which affects the set point and causes the relay to operate.
Distance protections are usually divided into several sections according to tripping zones, which are used to back up the main protections of power lines, power transformers, generators, busbars and other equipment.
They are used to protect against phase-to-phase and in some cases single-phase faults occurring in power equipment.
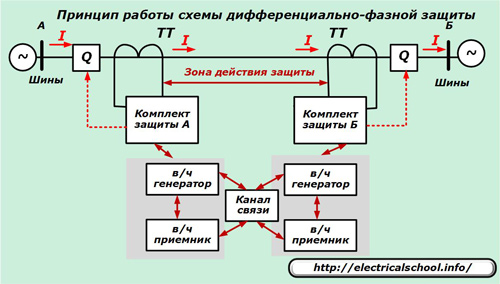
A feature of differential protection is their ability to react to:
1. voltage fluctuation in the system. This is the name of the phenomena associated with periodic voltage drops and current increases, caused by violations of the synchronous operation of multiple generators that generate electricity in the system;
2. faults that may occur in voltage circuits.
In order to exclude cases of false operation of distance protections, blocking devices are introduced into their composition, which perform:
-
prohibits tripping of the circuit breaker in case of oscillations in the system:
-
monitoring the state of the voltage source.
Relay protection of frequency, power, phase
The whole assortment of these devices works on the general principle when creating a measuring device that, based on a relay, monitors the state of frequency, power or phase of an electrical signal. In the event of a violation of the set value assigned to it, the relay is activated and the logic circuit connected to its contact processes the information and according to the prescribed algorithm turns off the power equipment.
Protection of gas and jet relays
These types of devices are used to equip transformers, reactors and other similar structures operating in oil tanks. When malfunctions occur in them, a high temperature is created, accompanied by the release of dissolved gases from the oil, decomposition of its chemical composition and a decrease in dielectric properties.
The mechanical structures of the relay react to such malfunctions, taking into account the appearance of gases and products of oil decomposition in the middle of the tank. After closing the contact, they are given a command to activate the logic circuit and open the switches.
This type of protection refers to relay protection, but is based on the measurement of mechanical rather than electrical parameters of the operating equipment.
The surge protection relay works on the same principle:
-
temperature;
-
mean pressure and other mechanical factors.
