Relay protection of synchronous machines
Synchronous electrical machines are alternating current machines, usually three-phase. Like most electromechanical converters, they can operate in both generator and motor modes. A special mode of operation of a synchronous machine is the reactive power compensation mode. Special machines designed for this purpose are called synchronous compensators.

Despite the fundamental reversibility of synchronous motors and generators, they usually have design features that rarely make it possible to use motors as generators and vice versa.
Damaged generators
Damage to the stator winding:
-
Multiphase short circuits;
-
Single-phase earth faults (if applicable);
-
Twin Earth Faults;
-
Short circuit between turns of one phase (for synchronous generators with output parallel branches).
Fault in the rotor winding (in the field winding):
-
Grounding (rotor body) at one point;
-
Grounding at two points of the excitation circuit.
Abnormal operating modes of the generators
-
Stator overloading of a synchronous generator (symmetrical and asymmetric).
-
Overloads in case of external short circuits.
-
Increase in voltage across the stator winding terminals.
-
Asynchronous mode.
Requirements for relay protection of generators
Selectivity — the protection must switch off the generator only in those faults and modes that represent a real danger to the generator.
productivity — to reduce the degree of machine failure and to prevent unstable parallel operation of generators and systems.
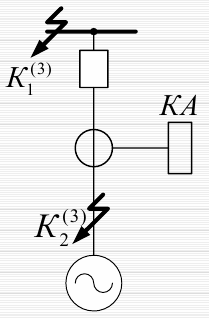
Sensitivity — on all types of failures in a synchronous generator, as well as on short circuits of adjacent elements to back up the protections and switches of these elements in the event of their failure. The defense must work not only on Q but also on an AGP device to stop the short circuit current sent by the generator itself.
Current shutdown without time delay
It is used as the main protection for generators with a power of less than 1 MW against multi-phase short circuits in the stator winding. Installed on the side of the busbar terminals.
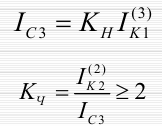
Longitudinal differential protection
It is used as the main protection for generators above 1 MW against polyphase short circuits in the stator winding.
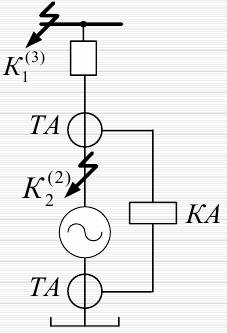
The TA is installed on the busbar side and on the neutral side.
Calculation of the parameters of the longitudinal differential protection
Protection current:
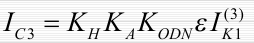
Usually, depending on the power of the generator, the tripping current of the protection is in the range:
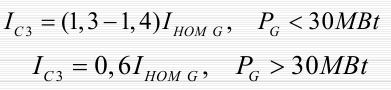
Protection sensitivity test:
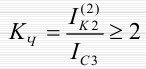
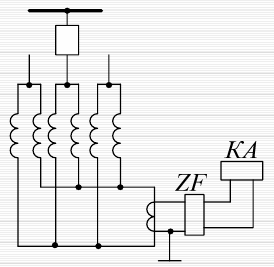
Transverse differential protection
It is used as the main protection for generators with a power of more than 1 MW against a short circuit per turn. Maintains longitudinal differential protection in the event of a multiphase short circuit in the stator winding.
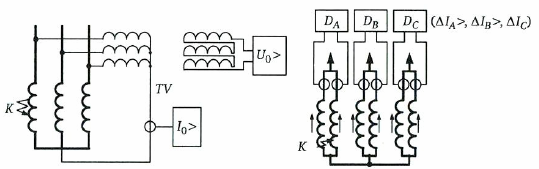
Single-relay transverse differential protection circuit
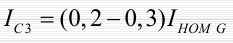
The current transformer is installed in a circuit between two zero points of parallel branches of the stator winding connected in a star.
ZF-filter for tuning from higher harmonics flowing in the neutral circuit, multiples of three.
Protection against earth faults in the stator winding of generators or its terminals
1. Current directional protection for generators operating in a unit with a transformer in a network with isolated neutral.
2. Earth fault protection using low-frequency components of consumer goods generated by an intermittent arc fault for generators networked with compensated neutral.
3. Earth fault protection for generators operating in network with resistively grounded neutral.
4. Signaling in case of single-phase grounding of zero-sequence voltage.
Earth fault protection for generators operating in networks with an isolated or resonantly grounded neutral
Ground protection has a "dead zone" of about 5% of the stator winding resistance for a short circuit near zero (point K2). The values 3U0, 3I0 are proportional to the number of phase turns between the neutral and the location of the fault.
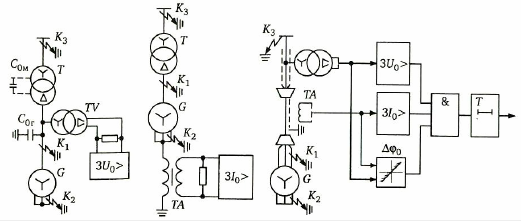
Single-phase ground fault alarm at zero-sequence voltage
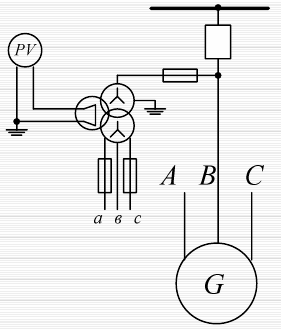
Earth fault protection for generators operating on a resistive earthed neutral network
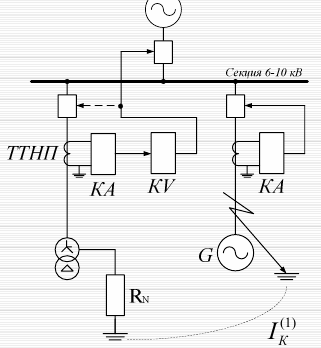
Protection against secondary grounding in the rotor winding
Voltage distribution on the rotor winding in case of earth faults.
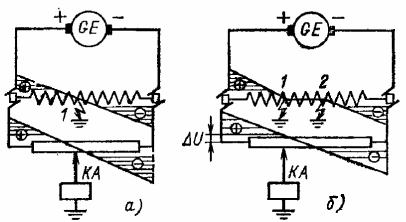
Protection circuit of the generator against a short circuit at two points of the excitation circuit
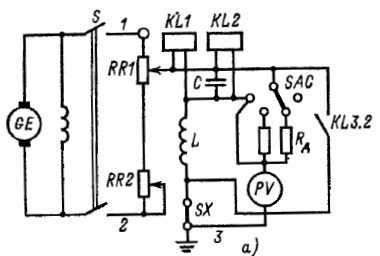
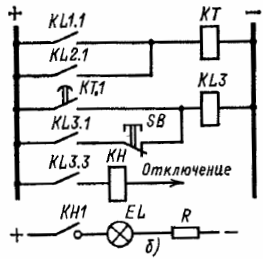
(a) excitation scheme; b) operating current circuits
Overvoltage blocking against overvoltage
-
Designed to protect generators from overcurrent during external short circuits.
-
Suitable for generators with a power of less than 30 MW.
-
It is performed in two stages.
Surge blocking circuit

a) current circuits; b) voltage circuits; c) operating current circuits
Negative sequence overcurrent protection
-
It is used for generators with a power of 30-60 MW.
-
Designed to protect generators from external asymmetric short circuits.
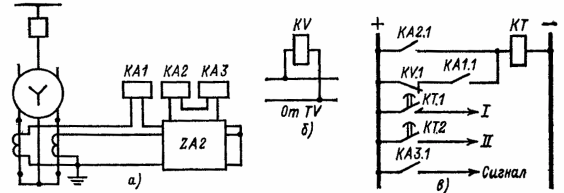
a) current circuits; b) voltage circuits; c) operating current circuits
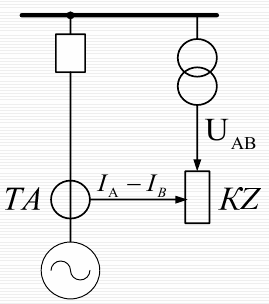
Generator distance protection
-
It is used for generators with a power of more than 60 MW.
-
Designed to protect generators from external asymmetric short circuits.
The resistance of the protective operation is selected according to the setting condition from the maximum load at the minimum operating voltage:
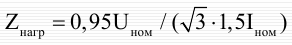
Generator distance protection circuit
Trigger protection:
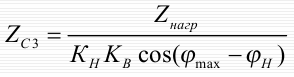
Surge protection
Installed on hydro generators:
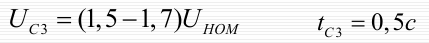
Installed on turbine generators with a capacity of 160 MW and above:

Generator protection against asynchronous modes
Types of AR generators
1. With full or partial excitement.
2. No excitement.
The principle of protection of generators from asynchronous modes — remotely, the resistance of the generator is monitored.
Engine protection
Damage to electric motors:
-
single-phase earth faults;
-
Closures between turns of one phase;
-
phase phase short circuits.
Abnormal modes of operation of the ED:
-
Overloading with currents higher than nominal;
-
Actuator overload.
Multiphase short circuit protection
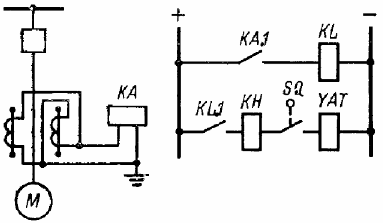
Instantaneous overcurrent protection circuit
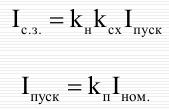
Low voltage protection
Self-starting of the engines may not occur if the tire pressure is lower:
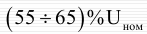
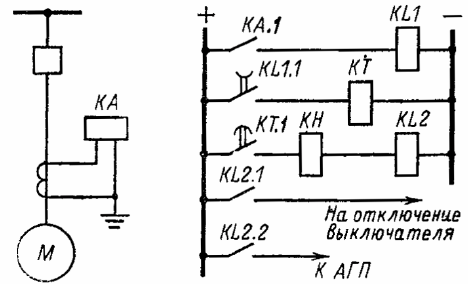
Undervoltage protection circuit with direct relay:
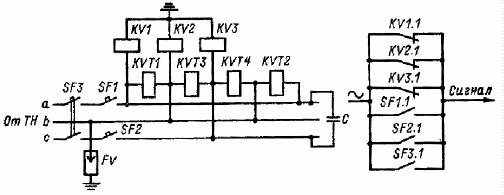
Protection of synchronous electric motors against falling from a synchronous network: