Wind power plants
 A wind power plant (HPP) is a complex of interconnected facilities and structures designed to convert wind energy into other types of energy (electrical, mechanical, thermal, etc.).
A wind power plant (HPP) is a complex of interconnected facilities and structures designed to convert wind energy into other types of energy (electrical, mechanical, thermal, etc.).
Wind turbine as the main part of the wind turbine, it consists of a wind turbine, a system for transmitting wind energy to a load (user) and the user of wind energy itself (each device: electric machine generator, water pump, heater, etc.) .
A wind turbine is a device for converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy of the working motion of the wind turbine. The working movements that a wind turbine makes can be different. On existing wind turbines today, circular rotary motion is used as the working motion. At the same time, numerous proposals are known (sometimes even implemented) for the use of other types of labor movement, for example, oscillating.
A wind turbine blade system (wind wheel) can have a different design.In modern wind turbines, the blade system is made in the form of solid blades with a wing profile in cross section (sometimes the terms «blade» or propeller wind turbines are used in this case).

Known successfully operating blade systems in which rotating cylinders are used instead of blades (using the Magnus effect). There are proposals to create a blade system based on different types of blades with flexible surfaces (sails).
Therefore, blade — This is a component of the propeller that generates torque. The blade system of a wind turbine with an operating circular rotary motion can have a horizontal or vertical axis of rotation.
When calculating and designing a specific wind turbine, in addition to the wind conditions of its operation, it is necessary to take into account both the characteristics of the wind turbine, teak wood, and the entire wind turbine. In this regard, wind turbines are classified according to the following criteria:
-
type of energy generated,
-
power level,
-
appointment
-
Areas of application,
-
the sign for constant or variable speed operation of the wind turbine,
-
management methods,
-
type of transmission system.

Depending on the type of energy generated, all wind power plants are divided into wind energy and wind energy. Electric wind turbines, in turn, are divided into embedded installations that generate direct or alternating current electricity. Mechanical wind turbines are used to drive running machines.
Depending on the purpose, DC electric wind turbines are divided into wind-guaranteed, user-guaranteed power supply, non-guaranteed power supply.Electric wind turbines with alternating current are divided into autonomous, hybrid, operating in parallel with an electric power system of comparable power (for example, with a diesel plant), grid, operating in parallel with a powerful electric power system.
The classification of wind turbines by areas of application is determined by their purpose.
When calculating and designing a wind turbine and choosing its nominal parameters, it is necessary to take into account the type of load (electric generator, water pump, etc.), the type of wind power transmission system to the user, the type of electricity generation and storage system.
A wind energy transmission system is a defined set of different devices for transmitting power from the shaft of the wind wheel to the shaft of the corresponding wind turbine machine (user) with or without increasing the rotational speed of the machine. In modern wind energy, the mechanical method of energy transmission is most often used.
The power generation system is a generator of electric machines and a set of devices (control devices, power electronics, battery, etc.) to connect to a user with standard electricity parameters.

Wind turbines with power from a few watts to thousands of kilowatts are manufactured and operated. There are four groups: very low power — less than 5 kW, low power — from 5 to 99 kW, medium power — from 100 to 1000 kW, high power — over 1 MW. Wind turbines of each group differ from each other primarily in design, foundation type, wind turbine installation method, control system, wind energy transmission system, installation method and maintenance method.
The predominant distribution of horizontal axis wind turbines has been achieved.
In fig. 1 shows the construction of a wind farm and a general view of the wind farm.
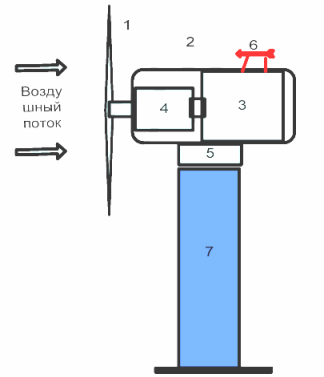
Rice. 1. The design of the wind power plant: 1 — wind turbine (wind wheel), 2 — wind turbine, 3 — generator, 4 — gearbox, 5 — turntable, 6 — measuring device, 7 — wind turbine mast contains a wind turbine and an electric generator connected to the wind turbine shaft directly or through a gearbox.
A wind turbine contains a wind turbine and an electric generator connected to the shaft of the wind turbine directly or through a gearbox.
A wind farm (WPP) consists of several wind turbines operating in parallel and supplying generated electricity to the power system.
The measuring device gives a signal to turn the head of the wind when the direction or strength of the wind changes, and also adjusts the angle of rotation of the blades depending on the strength of the wind.
There are wind turbines for 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 4000 kW. The wind turbine for 500 kW has: a mast with a height of 40-110 m, a wind head with a mass of 15-30 tons, a rotation frequency n = 20-200 rpm, the speed of the generator rotor is 750-1500 rpm (drive with gear) or 20-200 rpm (direct drive).
As generators in wind turbines, asynchronous squirrel generators are often used, which differ from synchronous ones in greater reliability, simplicity of design and less weight, which is necessary to increase the reliability of the wind power plant.
Wind turbines can operate autonomously or in parallel with the power system.During autonomous operation, the rotation speed of the HP wind turbine is not regulated or maintained within ± 50%, therefore the frequency and voltage of the generator terminals are not constant, that is, the generated electric power is of poor quality, and the users of such wind turbines often do not have high quality requirements (mainly heating devices). To obtain high-quality energy, stabilizers consisting of a rectifier, inverter and battery are used.
Powerful wind turbines operate in parallel with the power system (Fig. 2). This parallel connection ensures that the frequency, voltage and speed of the wind turbine are constant. The power that the generator gives to the grid depends on the torque of the engine and is determined by the force of the wind.
Possible co-operation of the wind turbine with the grid with a connection via an intermediate frequency converter at a variable frequency of rotation of the wind turbine.
When an asynchronous generator is used, the wind turbine can also operate at variable speed, and the generator supplies high-quality electricity to the network. For excitation, the asynchronous generator consumes reactive power from the network or from a special capacitor bank, and the synchronous generator itself creates it.

Rice. 2… Parallel operation of a wind power plant with a powerful power supply system: VD — wind machine, R — gearbox, G — generator, V — rectifier, I — inverter, U — control unit, ES — power system
Characteristics of system wind power plants (WPP):
1. They are located in places with high wind potential.
2.They have the capacity of power units: 1500-2000 kW and more for a continental base and 4000-5000 kW for a sea and shore base.
3. Asynchronous generators with squirrel rotor and synchronous (often with permanent magnet excitation) with low generator voltage (0.50-0.69 kV) are used.
4. Low efficiency of the station — 30-40%.
5. Lack of heat load.
6. High maneuverability, but full dependence on weather conditions.
7. Range of operating wind speeds from 3.0-3.5 to 20-25 m / s. When the wind speed is less than 3.0-3.5 m / s and more than 20-25 m / s, the wind turbines are disconnected from the grid and installed in a non-working position, and when the wind speed is restored, wind turbines are connected to the grid and accelerated using a generator operating in engine mode.
8. Lack of choice of electrical power at generator voltage (except for own needs).
9. Transmission of electricity to consumers at voltages of 10, 35, 110, kV.
Modern wind energy in many countries of the world is part of the energy systems, and in some countries it is one of the main components of alternative energy based on renewable energy sources. Read more about it here: Development of wind energy in the world

