Floating solar power plants
Since 2013, the French company Ciel & Terre, which specializes in the supply of solar energy equipment for large-scale solar power plants, has completely switched to work on an innovative project for floating solar power plants.
After 2011, interest in this topic began to actively heat up by the Japanese, who were faced with an accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant. They decided to actively deal with the introduction of safer and cleaner alternative sources of energy than nuclear in their country.
To date, more than 85 floating solar power plants with a total capacity of 80 MW have already been built in 20 countries around the world. And this is not surprising, because the merits of such an unusual solution can hardly be overestimated: although the huge surfaces of the tanks were essentially not used in any way, now they can generate electricity! And it is not at all necessary to occupy the entire tank, it is enough to equip a small part of it.
Photovoltaic panels are installed on large bodies of water, such as drinking water tanks, quarries, lakes, irrigation canals, treatment tanks, etc. This is especially useful for enterprises whose work is somehow related to both the consumption of electricity and water bodies: wineries, dairy and fish farms, water treatment plants, reservoirs, greenhouses - they simply cannot afford to spend extra space on the ground, but are fully capable of distributing part of the area on the surface of the water.
Floating system with solar panels, cooling system and reflective mirrors to concentrate incident solar radiation (Colignola, Italy)
The floating power plant system is easily scalable, configurable for any grid configuration, does not require special maintenance, and the presence of water from the bottom helps to maintain an acceptable operating temperature of the panels and allows them to have higher efficiency. In addition, the floating power plant is distinguished by the environmental friendliness of the materials used, reduces evaporation from the water surface, does not spoil the water quality and with its presence slows down the growth of algae.
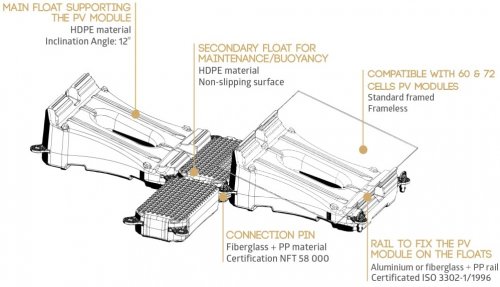
In fact, it is a plastic island that generates energy, assembled from separate parts. Its individual parts, containing aluminum and high-density polyethylene, are modules that are connected to each other using special anchors. Between the blocks and along the edges there are float inserts, which are blocks without panels, needed only to protect against vibration and possible shocks in high winds.
The platform, complete with solar panels, is assembled piece by piece on the shore and then gradually lowered into the water.The assembled platform with panels is towed to the destination and fixed in a static position using anchors. The cables are taken ashore. The minimum length of such a station is 5 meters, and the minimum width is one polyethylene module.
A vivid example of a fairly powerful floating solar power plant was built in 2015 in Japan near Tokyo. The solar power plant with a then-record design capacity of 2.9 MW consists of two parts: 1.2 and 1.7 MW. In total, more than 11,256 modular units equipped with the company's solar panels with a power of 225 W each have been assembled here.
The floating station allows electricity to be supplied to 920 households located in the area of the reservoir. This is approximately 3300 MWh of electricity per year without damaging land areas. Perhaps the only drawback of such a system is, as some ecologists believe, a significant increase in the temperature of the water in the reservoir.
Another large floating solar power plant with a design capacity of 13.4 MW was launched in Japan's Yamakura Reservoir. On an area of 180,000 square meters, there are 50,904 Kyocera solar panels with 270 watts each. The energy generated here is enough to power approximately 4,970 households.
Some environmental associations have expressed concerns that valuable land could be used to install floating solar systems, and therefore it is important to ensure that the sites used are only degraded or already existing man-made reservoirs. Another controversial point is the position that aquatic flora and fauna can be disturbed by such attitudes.