How to calculate the cross section of a portable ground
To ensure safety during work on electrical equipment and power lines, it is necessary to disconnect (create a visible gap) and ground the section of the electrical installation where the work is planned to be carried out from all sides where it can be fed tension.
Grounding protects against accidental voltage supply at the place of the electrical installation where work is carried out, and also carries out the removal of dangerous potential — residual (capacitive) line charge, magnetizing current of the transformer, as well as induced voltage.
The earthing of live parts can be done by including the structurally provided fixed pinch knives or by installing portable protective earthing. Reliable grounding of the section of the electrical network is ensured only if the cross-section of the grounding wires is correctly selected. Let's look at how to calculate the cross-section of a portable protective earth.
Requirements for grounding conductors
Ground wires are usually made of flexible copper wires without an insulating layer. The conductors must be firmly connected to the clamps and clamp, ensuring that the good live earth parts are in good contact with the equipment earth circuit.
Portable protective grounding conductors must be resistant to mechanical loads, therefore the minimum cross-section of the conductors of the conductors must be at least 16 sq. mm for equipment with a voltage class of up to 1000 V and not less than 25 sq. mm in electrical installations with a voltage above 1 kV.
But the cross-section of the grounding wires must also meet the requirements for thermal resistance in the event of a three-phase short circuit at the place of the electrical installation, where the installation of grounding is planned. And in the event that the neutral of the electrical network has a solid earth, then single-phase short-circuit currents must also be taken into account. Therefore, the minimum permissible cross-section of the protective earthing conductors for use in a particular electrical installation must be calculated.
Calculation of the cross-section of portable grounding conductors
To calculate the minimum permissible cross-section of portable protective grounding conductors (PZZ), it is necessary to take into account the stationary short-circuit current for the section of the electrical network and the value of the delay time for the operation of the relay protection.In this case, the longest time is taken into account — that is, the time during which the back-up protection is triggered in the event of failure of the main short-circuit protection in a certain section of the electrical network.
The section is calculated using the following formula:
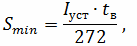
where Smin is the minimum permissible cross-section of PZZ conductors, Iset is the value of the largest stationary short-circuit current in the section of the electrical network, tc is the maximum response time of the relay protective device.
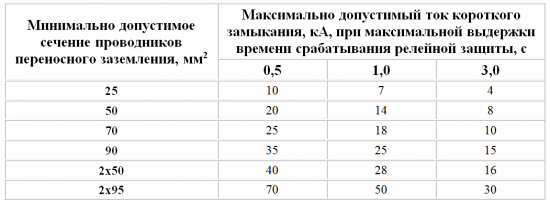
The cross-section of portable earthing devices can also be selected from the table using the above initial data:
In electrical installations with high short-circuit currents (as a rule, in electrical networks with a voltage class of 6-10 kV), the cross-section of the portable grounding may be too large, and the portable grounding itself will be heavy. Therefore, for the convenience of its installation and removal, it is allowed to install two portable earthings with a smaller cross-section, provided that the total cross-section of the earthings is not less than the minimum permissible based on thermal stability in the case of short circuit in the electrical network.
The exception is portable grounding used during electrical laboratory tests, grounding of the lightning protection cable of the overhead line and grounding of mobile installations (workshops, laboratories).
Protective portable grounding with a wire cross-section of at least 4 sq. mm
For grounding the lightning protection cable of the power line (isolated from the supports of the overhead line), as well as mobile installations, portable protective grounding with a conductor cross-section of at least 10 sq. mm