The effect of electric current on a person
What is the danger of electric current? How electric current affects a person
 The fact of electric current action on a person was established in the last quarter of the 18th century. The danger of this action was first identified by the inventor of the high voltage electrochemical voltage source V. V. Petrov. The description of the first industrial electrical injuries appeared much later: in 1863 — from direct current and in 1882 — from alternating current.
The fact of electric current action on a person was established in the last quarter of the 18th century. The danger of this action was first identified by the inventor of the high voltage electrochemical voltage source V. V. Petrov. The description of the first industrial electrical injuries appeared much later: in 1863 — from direct current and in 1882 — from alternating current.
Electricity — directed movement of free electric charges. The magnitude of the electric current is the sum of electric charges (electrons, ions) passing through a unit of cross-sectional area per second. In semiconductors, along with electrons, there are also "holes". The "holes" are carriers of a positive electric charge.
The unit for measuring electric current is the ampere, denoted by the letter A. In an electric lamp of medium brightness, when connected to the network, a current of 0.3 to 0.5 A appears. In lightning, it can reach 200,000 A.
Electric current, electrical injuries and electrical injuries
Electric shock means trauma caused by the action of an electric current or an electric arc.
Electric injury characterize the following features: a protective reaction of the body occurs only after a person comes under voltage, that is, when an electric current is already flowing through his body; the electric current acts not only in the places of contact with the human body and on the way of passage through the body, but also causes a reflex action, manifested in the disruption of the normal activity of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, breathing, etc. with live parts, and in case of shock by touch or step voltage, through an electric arc.
 Electrical injuries compared to other types of industrial injuries are a small percentage, but in terms of the number of injuries with severe and especially fatal, it occupies one of the first places. The largest number of electrical injuries (60-70%) occur when working with electrical installations with a voltage of up to 1000 V. This is due to the widespread use of such electrical installations and the relatively low level of electrical training of persons who operate them. Electrical installations with a voltage above 1000 V work much less and serve specially trained personnel, which causes less electrical injury.
Electrical injuries compared to other types of industrial injuries are a small percentage, but in terms of the number of injuries with severe and especially fatal, it occupies one of the first places. The largest number of electrical injuries (60-70%) occur when working with electrical installations with a voltage of up to 1000 V. This is due to the widespread use of such electrical installations and the relatively low level of electrical training of persons who operate them. Electrical installations with a voltage above 1000 V work much less and serve specially trained personnel, which causes less electrical injury.
Causes of electric shock to a person
 The causes of electric shock to a person are as follows: touching non-insulated live parts; to metal parts of the equipment that are under voltage due to insulation damage; to non-metallic objects that are under voltage; surge voltage step and across the arc.
The causes of electric shock to a person are as follows: touching non-insulated live parts; to metal parts of the equipment that are under voltage due to insulation damage; to non-metallic objects that are under voltage; surge voltage step and across the arc.
Types of electric shock to a person
The flow of electricity through the human body affects it thermally, electrolytically and biologically. The thermal action is characterized by heating of the tissues, to burns; electrolytic — by breaking down organic fluids, including blood; the biological effect of electric current manifests itself in the disruption of bioelectrical processes and is accompanied by irritation and excitation of living tissues and muscle contraction.
There are two types of electrical shock to the body: electrical injury and electrocution.
Electrical injury — these are local lesions of tissues and organs: electrical burns, electrical signs and electrometalization of the skin.
Electrical burns occur as a result of heating of human tissues by an electric current flowing through them with a force of more than 1 A. Burns can be superficial, when the skin is affected, and internal — when deep-seated tissues of the body are damaged. According to the conditions of occurrence, contact, arc and mixed burns are distinguished.
Electric signs are spots of gray or pale yellow in the form of calluses on the surface of the skin at the point of contact with live parts. Electrical signs are usually painless and subside over time.
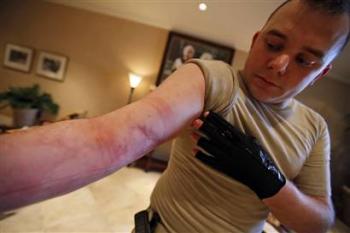
Electrometallization of the skin — this is the impregnation of the surface of the skin with metal particles when it is sprayed or vaporized under the influence of an electric current. The affected area of the skin has a rough surface, the color of which is determined by the color of the metal compounds on the skin. Electroplating of the skin is not dangerous and disappears with time, as do the electrical signs. Metallization of the eyes is a great danger.
Electrical injuries also include mechanical damage as a result of involuntary convulsive muscle contractions during current (lacerations of the skin, blood vessels and nerves, joint dislocations, bone fractures) and electroophthalmia — inflammation of the eyes as a result of the action of the ultraviolet rays of the electric arc.
 An electric shock is the excitation of living tissues with an electric current, accompanied by an involuntary convulsive muscle contraction. According to the result, electric shocks are conditionally divided into five groups: without loss of consciousness; with loss of consciousness, but without disturbance of heart activity and breathing; with loss of consciousness and impaired heart activity or breathing; clinical death and electrocution.
An electric shock is the excitation of living tissues with an electric current, accompanied by an involuntary convulsive muscle contraction. According to the result, electric shocks are conditionally divided into five groups: without loss of consciousness; with loss of consciousness, but without disturbance of heart activity and breathing; with loss of consciousness and impaired heart activity or breathing; clinical death and electrocution.
Clinical or "imagined" death This is a transitional state from life to death. In a state of clinical death, the heart stops and breathing stops. The duration of clinical death is 6 ... 8 minutes. Then the cells of the cerebral cortex die, life fades, and irreversible biological death occurs. Signs of clinical death: cardiac arrest or fibrillation (and as a result lack of pulse), lack of breathing, bluish skin, the pupils of the eyes are sharply dilated due to oxygen starvation of the cerebral cortex and do not respond to light.
Electric shock — This is a severe neuroreflex reaction of the body to irritation with electric current. In shock, deep disturbances of breathing, circulation, nervous system and other body systems occur. Immediately after the action of the current, the excitement phase of the body begins: a pain reaction occurs, blood pressure rises, etc.Then comes the inhibition phase: the nervous system is exhausted, blood pressure decreases, breathing weakens, the heart rate drops and increases, a state of depression occurs. The state of shock can last from several tens of minutes to a day, after which recovery or biological death can occur.
Thresholds for electric current
Electric currents of different strengths have different effects on a person. Threshold values of electric current are underlined: receptive current threshold — 0.6 ... 1.5 mA at alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz and 5 ... 7 mA at direct current; Threshold of release current (current that causes, when passing through a person, irresistible convulsive contractions of the muscles of the arm in which the wire is caught) — 10 ... 15 mA at 50 Hz and 50 ... 80 mA at direct current; threshold of fibrillation current (current causing cardiac fibrillation when passing through the body) — 100 mA at 50 Hz and 300 mA at direct electric current.
What determines the degree of action of electric current on the human body
The outcome of the lesion also depends on the duration of the current flowing through the face. As the duration of a person's stay under tension increases, this danger increases.
Individual characteristics of the human body significantly affect the outcome of an electrical injury. For example, the non-diluting current for some people may be a receptive threshold for others. The nature of the action of the current of the same strength depends on the mass of a person and his physical development. It was found that for women the current threshold values were approximately 1.5 times lower than for men.
The degree of action of the current depends on the state of the nervous system and the whole organism.So, in a state of excitement of the nervous system, depression, diseases (especially diseases of the skin, cardiovascular system, nervous system, etc.) and intoxication, people are more sensitive to the current flowing through them.
The "attention factor" also plays a significant role. If a person is prepared for an electric shock, then the degree of danger decreases sharply, while an unexpected shock leads to more serious consequences.
The path of the current through the human body significantly affects the output of the lesion. The danger of injury is especially great if the current passing through the vital organs — heart, lungs, brain — acts directly on those organs. If the current does not pass through these organs, then its effect on them is only reflexive and the probability of injury is less. The most common current paths through a person, the so-called «current loops», have been established. In most cases, a circuit of current through a person occurs along the path of the right hand - the legs. The loss of working capacity for more than three working days is caused by the flow of current along the path hand - hand - 40%, right path - leg current path - 20%, left hand - leg - 17%, other paths are less common.
What is more dangerous — alternating current or direct current?
The danger of alternating current depends on the frequency of that current. Studies have found that currents in the 10 to 500 Hz range are almost equally dangerous. With a further increase in frequency, the values of the threshold currents increase. A noticeable reduction in the risk of electric shock to a person is observed at frequencies above 1000 Hz.
Direct current is less dangerous and its threshold values are 3-4 times higher than alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz.However, when the direct current circuit is interrupted below the receptive threshold, acute painful sensations caused by the transient current occur. The statement about the lower danger of direct current compared to alternating current is valid for voltages up to 400 V. In the range of 400 … 600 V, the risks of direct and alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz are practically the same and with further increases in voltage the relative danger of direct current increases. This is due to the physiological processes of action on a living cell.
Therefore, the effect of electric current on the human body is diverse and depends on many factors.
