Heating cable systems
Heating systems based on cables, which generate heat through the heating effect of electric current, have gained great popularity in many industrial areas in recent years. These are the so-called cable heating systems.
The heat generated by the current in the heating element will safely warm the floor, retain heat in industrial pipes, warm the roof, help prevent icing on the pavement and drains, will be useful in heating concrete, soil in greenhouses, playgrounds , steps, etc. At the same time, one of the advantages of the cable heating system is that it is not bulky, its installation will hardly change the size of the object on which it will be installed.
In this article we will talk about cable systems used in the pipe and roof heating industry.
Installing a cable heating system is much easier than installing a water heating system. The heat carrier here is essentially electricity, no additional piping is needed, just cables.The efficiency of the system is high due to the low energy losses, since the power is supplied through low resistance wires.
The system itself is an assembly of a special cable and thermostat. The principle of operation is simple: current passes through a special cable and causes it to heat up. The cable sheath is specially made heat-resistant, withstands a constant operating temperature, while at the same time it is characterized by high thermal conductivity, due to which the heating of the space and objects in the area of the cable is effective.
The heating cables are:
-
unmarried
-
two-wire,
-
self-regulating.
But whatever the cable, thermal calculations are always performed first, so that nothing overheats, does not remain heated, so that the system emits heat in the most optimal mode. In general, there are three types of heating cables:
-
resistive,
-
self-regulating,
-
zonal.
Types of cables for heating systems

The resistive cable has a constant output power that is practically independent of the temperature of the surrounding space or the temperature of the heated objects. Such a cable can be used, among other things, to create electric underfloor heating.
Among other features, resistance heating cables are significantly less expensive than other types of heating cables. But resistive cable has one drawback — it, like a thermostat for an electric heated floor, needs a temperature sensor to keep it from overheating.
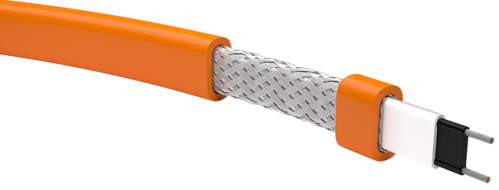
Self-regulating cable has a unique characteristic — it can increase or decrease its resistance when the temperature of adjacent objects rises or falls.
In this way, the power supplied by the cable is automatically adjusted as it warms up. Thus, the heating as a whole is optimally uniform, different areas with different temperatures are heated with different intensity, as a result of which good efficiency is achieved. Overheating of the cable is basically excluded due to its design features. The disadvantage of the self-adjusting cable is the high cost.
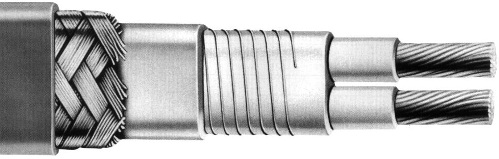
The zone cable has a heating coil located around the frame, which is the cable itself. Connecting to the wire, the coil receives power — at regular intervals, all parts of the heating element are powered in parallel.
The zone cable is cheaper than the self-regulating cable, it is unpretentious in the installation, like others, and, like the self-regulating cable, it can be cut into pieces of exactly the required length, which cannot be said about the resistive cable. Disadvantages are similar to resistive cable (thermostat required, power independent of temperature).
Roof heating using a cable system
In winter, a lot of snow always accumulates on the roofs or roofs for various purposes, everything freezes on the edges and near the gutters, there are reasons for fears, for example: whether the snow and ice will not fall where they should not ...
The heating element is mounted on the roof (inside the roof) and the control panel is located in the room. In this case, the cable can be installed both self-regulating and resistive.

Resistive cable will give constant temperature at constant power consumption when included as an independent heating circuit. The self-regulating one is more technological — its temperature will decrease when the roof warms up.The choice is the owner's. Resistive is cheaper, but its efficiency leaves much to be desired — the power itself is not regulated, the same is consumed all the time.
A self-regulating cable — on the contrary, will work more economically when the temperature of the surrounding objects rises — the power consumed by the cable decreases. You'll have to fork out for the cable purchase, though it will pay off in time.
Heating of drainage pipes, sewage and water pipes with a cable system
If the roof is covered with snow in winter and freezes, then the situation is even worse with the sewer, drainage and water pipes - they freeze with the onset of frost.
How to solve this problem? You can bury the pipes or resort to thermal insulation, but this approach is not always effective, and besides, it is far from always possible to bury a pipe beyond the depth of freezing.
But what about the pipe outlet that somehow stays cold? The same thermal insulation will not save the liquid passing through the pipe, at best it will prevent the rapid freezing of only part of the pipe, but not the pipe completely, and over time, in the cold, the pipe will still freeze and that's fraught with an accident for the sewer or water supply.
For gutters, deepening is not even worth discussing. In the end, there is only one way out — to use a pipe heating system based on a heating cable.
For climate zones where winter air often has temperatures well below 30°C, the only solution is to resort to heating for sewers, water pipes and drainage pipes.
It is best to choose an antifreeze system based on a self-regulating cable that can be installed inside or outside the pipe. The installation option is selected on site, based on the design characteristics of a specific object, taking into account external conditions, as well as technical and financial capabilities.

A pipe heating system with a self-regulating cable will be very economical and efficient, since the temperature in each local section of the pipe will be automatically regulated individually. Electricity consumption will be appropriate, as the energy consumption will be regulated by itself, and in the warm season the system will turn off completely.
The self-adjusting cable allows cutting parts of the required length, only the maximum length is limited — 150 m. The cable can be installed either inside the pipe or outside.
Internal and external pipe heating
For water pipes with a maximum diameter of 50 mm, an internal installation of a self-adjusting cable is suitable, but one important point must be taken into account. The cable is inserted with a seal and during wear is fixed so that it does not slip.
External installation is suitable for sewer pipes; it is carried out in one of two ways - spiral or linear. Linear arrangement is more economical, since the cable is laid along the pipe, material is saved, and for better heating, you can install a pair of cables on opposite sides of the pipe, fixing them with aluminum tape. Laying in a spiral will give more uniform heating of the pipes, but the cable will need 4 times more. In both the first and second cases, the cable is fixed with reinforced heat-resistant tape.
As noted above, an important advantage of self-regulating cable is its ability to change its temperature in accordance with external temperature conditions, resulting in significant efficiency in energy consumption.
Thanks to this advantage, self-regulating cables have become widely used in the gas, chemical, oil and construction industries - wherever the fight against freezing of water and icing of pipes is an urgent task. By the way, a self-regulating cable is not afraid of overvoltages.

