Static electricity in pictures
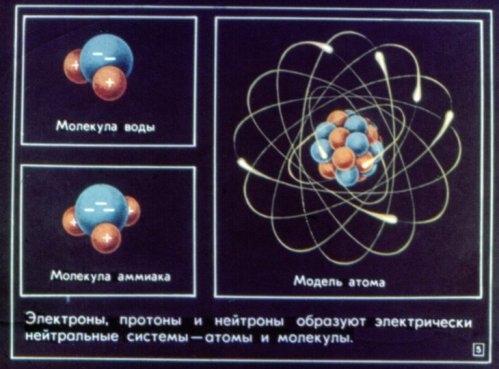
 Electric charge is a quantitative measure of a body's ability to electromagnetically influence. The amount of charge on the electron is the smallest in nature. Electrons, protons, and neurons form electrically neutral systems—atoms and molecules. Most bodies in their normal state are electrically neutral: they have the same number of electrons and protons.
Electric charge is a quantitative measure of a body's ability to electromagnetically influence. The amount of charge on the electron is the smallest in nature. Electrons, protons, and neurons form electrically neutral systems—atoms and molecules. Most bodies in their normal state are electrically neutral: they have the same number of electrons and protons.
The process of transfer of charge from one body to another or displacement of charges inside a body is its electrification. In this case, the algebraic sum of charges in an isolated system remains constant (the law of conservation of charge).
The interaction of electric charges takes place through a special type of matter — an electric field. Fields of stationary charges are called electrostatic.
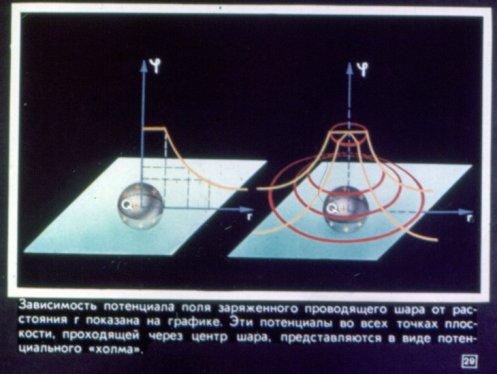
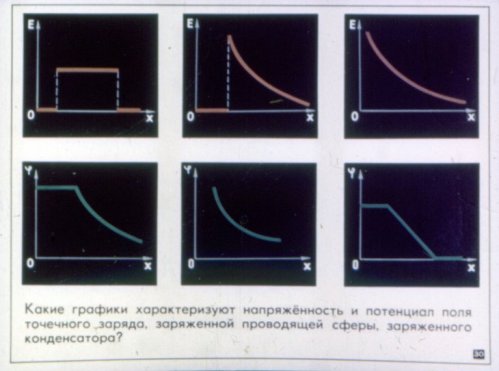
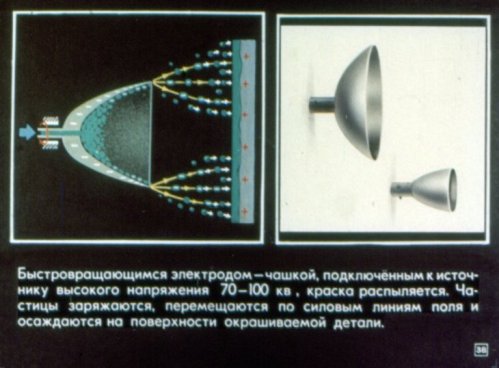
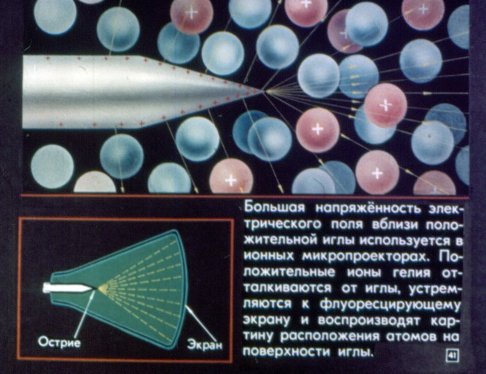
The pictures shown below are taken from the Static Electricity in Physics lesson. The filmstrip consists of four sections: electric charges in the field, conductors and dielectrics in the electrostatic field, the potential difference of the electrostatic field, and how static electricity serves people. 





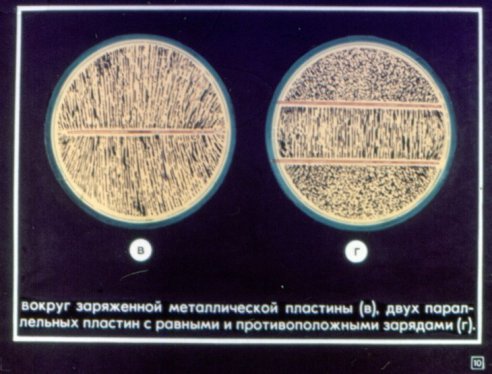


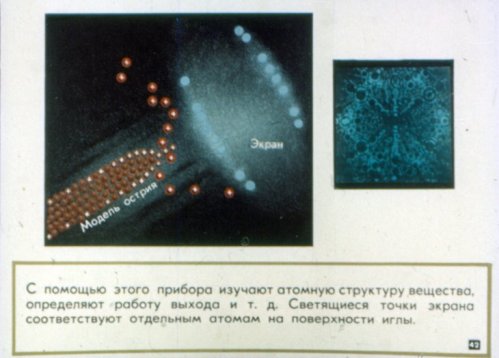
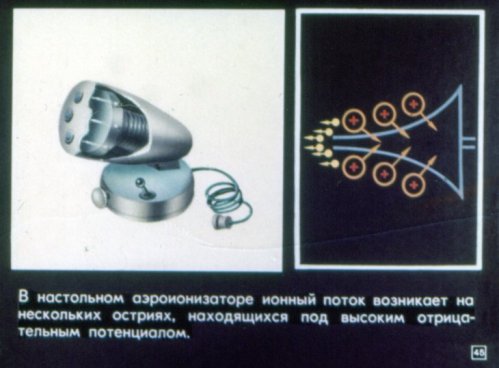
The electrostatic field does not penetrate the conductor. The charge has the highest density at the ends of the wire and the lowest in the recesses.
The dipoles of polar dielectrics under the action of an electrostatic field are located parallel to the field lines. But complete orientation is hindered by their thermal motion. The orientation effect increases with increasing field strength and decreasing dielectric temperature. If you introduce a non-polar dielectric into an electric field, the centers of negative charges of the electron shells of the atoms shift relative to the nuclei (electron polarization). It increases with increasing field strength and does not depend on the temperature of the dielectric.
In ionic crystals placed in an electric field, the positive and negative ions shift in opposite directions (ionic polarization).
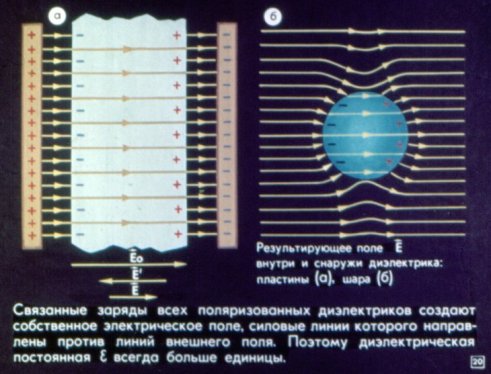
The associated charges of all polarized dielectrics create their own electric field, the lines of force of which are directed against the lines of the external field.







Between the polluted gas clouds and the surface of the Earth, a powerful electrostatic field is formed, which electrifies especially tall buildings, pipes, trees. As a result, damage to the air dielectric can occur - lightning.