How automatic reclosers (AR) work in electrical networks
The main power requirements of consumers are reliability and uninterrupted power supply. Transport energy flows from electrical networks cover hundreds and thousands of kilometers. At such distances, power lines can be affected by various natural and physical processes that damage equipment, create leakage currents or short circuits.

To prevent the spread of accidents, all power lines are equipped with protections that constantly monitor all the necessary parameters of electric power in real time and in the event of a malfunction, quickly disconnect the power from the power line by operating a power switch installed on the side of the end of the line of the generator.
For this purpose, all power lines are laid between switching transport nodes, the so-called electrical substations, on which power devices, measuring devices, as well as protection and automation equipment are concentrated.
Power line failure can occur for a variety of reasons with varying durations. Usually they are divided into two groups acting:
1. short-term;
2. for a long time.
An example of the first manifestation of a fault could be a stork flying over the conductors of an overhead power line so that with its spread wings it reduces the electrical resistance of the insulating layer of air between the phase potentials and thus creates a path for a short-circuit current to pass through his body.
The second case is characterized by vandals shooting insulators from a hunting rifle with a firearm, destruction of supports by natural disasters or impacts by vehicles that crash into the poles at high speed in poor visibility.
In either case, the protections will detect the fault and open the breaker. Short-circuit currents will stop passing through the short-circuit location, a no-current break in the supply is formed.
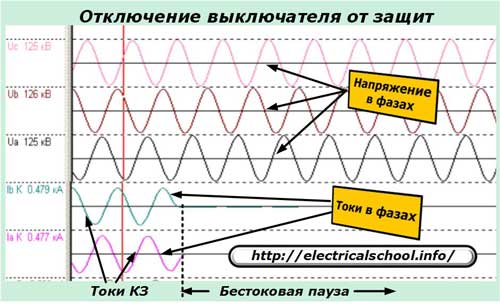
But electricity consumers need electricity supply because they can no longer live without it. Therefore, it is necessary to turn the line live with a switch and as quickly as possible.
This is done automatically in several stages or manually by operating personnel according to a strictly defined algorithm.
How Automatic Reclose (AR) Works
All power substations have power switches that can be controlled by automation systems or by dispatcher actions. This is what they are equipped for solenoids:
-
turn on;
-
shutdown.
Applying voltage to the corresponding solenoid results in commutation of the primary network.Consider the option of automatically controlling circuit breakers through dedicated automatic reclosers.
Once the power line is disconnected from the protections, automatic reclosing starts immediately. But it does not apply voltage to the line immediately after disconnection, but with a time delay necessary for self-destruction of short-term causes, for example, a stork electrocuted on the ground.
For each type of power lines, based on statistical studies, their own times are recommended, ensuring the period of short-term breakdowns. Usually this is about two seconds or a little more (up to four).
After the preset time has elapsed, the automation supplies voltage to the switch-on solenoid: the line is put into operation. In this situation, activation can be done:
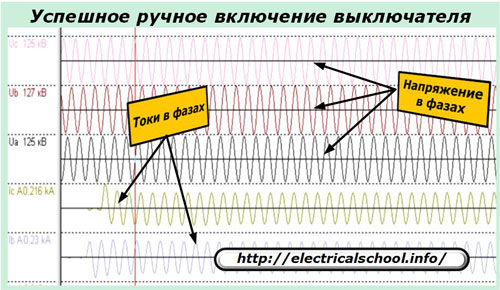
1. successful when the malfunction has self-eliminated (the stork has passed through the wire zone);
2. failed if, for example, a kite got on the wires and the cable of its attachment did not have time to burn to the end.

Upon successful inclusion, everything is clear. A short power outage will not harm users and in most cases they will simply not notice it.
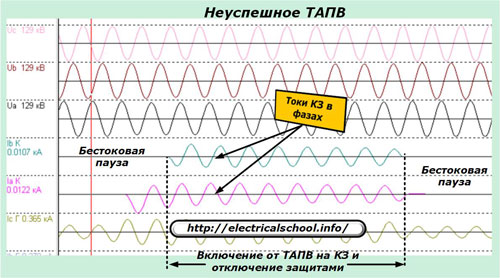
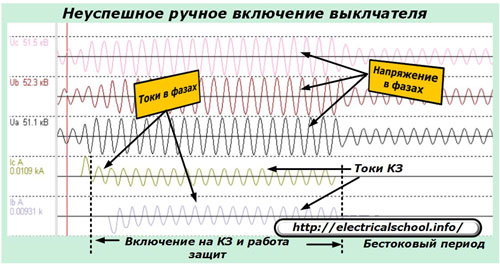
In the event of a failed automatic shutdown, the situation with consumers is complicated: the fault remains, and the line protection has again removed the voltage from it — the consumers are again disconnected. Thus, the first attempt to reclose was unsuccessful.
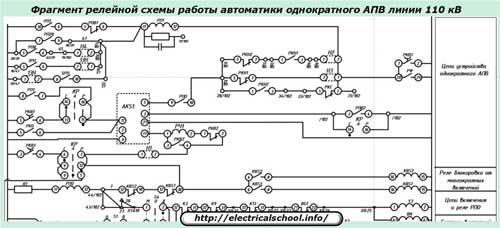
To increase the reliability of the information, after some time, for example 15 ÷ 20 seconds, a second automatic attempt is made to turn on the line under load.
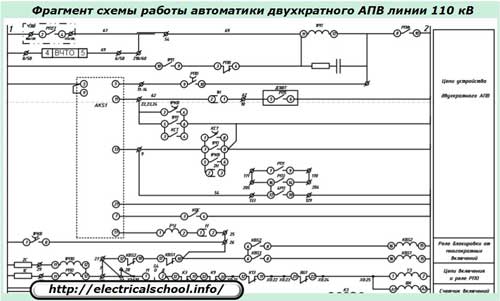
The practice of using double automatic closing of high-voltage power lines has shown its effectiveness in 15 cases of actuation out of a hundred. Considering that up to 50% of emergency shutdowns are eliminated by the first circuit breaker and up to 15% by the second, the overall reliability of switching the line under load by using a double cycle increases significantly, reaching a level of 60 ÷ 65%.
If, after the second reconnection attempt, the fault is not resolved and the protection trips the circuit breaker again, then the fault is permanent and requires visual assessment by service personnel and repair. It is impossible to turn on such a line under load until the fault is eliminated by the field crew. And it takes some time to find that place and do repair work.
The voltage is applied to the repaired area in manual mode after numerous checks have been carried out to rule out the recurrence of the fault.
The principles of operation of automatic reclosers considered for the overhead line are fully suitable for control devices of buses, sections, transformers, electric motors and other low-voltage or high-voltage power equipment.
Automatic Reclose Requirements
Turn-on speed
In order to create system reliability, it is necessary to select the optimal conditions for setting up the automation based on the following factors:
-
provision of interruption to prevent ionization of the medium, excluding re-ignition of the arc in case of hasty switching on;
-
the possibilities of the technical design of the circuit breaker for quickly switching the load to the emergency mode;
-
limiting the interruption of the non-current pause in the operation of the equipment and other characteristics of the technological process.
Launch conditions
Automation must work after any shutdown by protections or spontaneous, erroneous operation of the switch. When switching on manually or using a remote control, automatic reconnection should not work, because in the event of personnel errors, for example, if a portable or stationary earth is left and not removed, the protections will trip the fault, and the voltage cannot be reapplied to it.
Therefore, structurally, the automatic reclosing after a long trip is not ready for operation and recovers its characteristics in a few seconds from the moment the circuit breaker is turned on.
Duration of multiple power-ups
The energy reserve of the automatic closing devices must ensure the automatic execution of cycles by the circuit breaker:
1. Off — On — Off for one-time operation;
2. Off — On — Off — On — Off for dual algorithms.
At the end of the cycle, the automation must be disabled.
Set an hour set point
The length of the delay between the tripping of the circuit breaker and the energization of the automatic equipment must be adjusted by the operating personnel, taking into account the specific local conditions.
Performance recovery
After successful operation of the automatic system, a loss of its energy reserve occurs.It must recover with a short predetermined time to alert the devices for a new operation on startup.
Reliability of the command issued by the automation
The magnitude of the output signal and its duration from the automation must be sufficient to reliably control the circuit breaker.
Capabilities to block operations
In electrical networks, conditions are created when certain protections must exclude the automatic closing operation after their activation. For example, when the frequency in the network decreases due to the connection of a large number of users, some of them must be disconnected. The sequence of such operations is provided in the design of frequency unloading, where less critical connections are already assigned to remove power from them. In this case, the operation of their automatic reclosing must be blocked by a blocking command coming from the corresponding protection.
Types of automatic closing devices
Multiple actions
Depending on the purpose of automatic reclosing, they are designed to operate in one or two cycles. Practical research shows that if you install triple automatic reclosing, then their efficiency does not exceed 3%, and this is very little. Therefore, such automation systems are not used at all.
Methods of influencing the actuation of the circuit breaker
Old spring and load actuators used mechanical closing designs, transferring the force of a preloaded spring or lifted load directly to the disconnect device without a time delay.
Such mechanisms do not require an additional power source, but have a small break without current and a complex device that is not very reliable. Now they are not used and have been completely replaced by electrical systems.
Number of controlled circuit breaker phases
Protective and automatic circuits can act simultaneously on all three phases of the circuit or select the one on which the incident occurred.
Three-phase automatic closing (TAPV) is somewhat simpler in design and principle of operation, and single-phase (OAPV) are built according to a more complex scheme, have a large number of measuring and logic elements. For example, in the relay version of standard panels, the TAPV is placed in a box that is less than half the width of the panel.
Placing logic elements operating according to OAPV algorithms requires space in the area occupied by a separate panel.
With the introduction of static relays and microprocessor devices, the size of automation began to decrease significantly.
Control methods for automatic reclosing circuits
When the circuit breaker is energized on command from the automatic recloser, after tripping the protection, the circuit is divided into two sections. At this point, a mismatch of voltage harmonics in time (angle shift, phase) can occur, which creates complex transients and causes the protection to operate.
According to the degree of importance of the equipment, automation can be carried out for work:
1. no synchronization checks;
2. with synchrocheck.
The first constructions can be used:
-
in power systems with guaranteed supply when synchronism and voltage quality checks are not required.Simple TAPV schemes are created for this case;
-
of equipment that allows asynchronous switching on — asynchronous automatic reconnection (NAPV);
-
for circuit-breakers equipped with high-speed protections and drives capable of operating at a time that excludes the division of the power system into asynchronous sections-high-speed automatic reclosing (BAPV).
Synchronization checks are performed when:
-
checking the presence of voltage, for example on the line — KNNL;
-
lack of voltage control — KONL;
-
waiting for sync — KOS;
-
sync capture — KUS.
Compatibility of automatic reclosing with the operation of relay protection and automation devices
Algorithms can be implemented to automatically reclose:
-
defense acceleration;
-
setting the sequence of operation of switches on different interconnected links;
-
interaction with automatic equipment for frequency unloading;
-
the use of non-selective current interruption in combination with automatic reclosing, which makes it possible to reduce short-circuit currents;
-
combinations with the automatic transfer switching operation and some other cases.
Type of operating current
Automation devices operating on the basis of the energy of the storage batteries collected in the power supply system of the working circuits have the best reliability. But they require complex technical equipment and constant maintenance by specialists.
Consequently, other systems have been developed based on power from alternating current circuits taken from auxiliary transformers (TSN), current (CT) or voltage (VT).They are most often used in small, remote substations serviced by mobile electricians.
The principle of operation of the simplest single-shot automatic closing line
The logic used for single cycle automatic reclosers can be explained on the diagram of the old but still working electromagnetic principle of the AR relay (RPV-58).
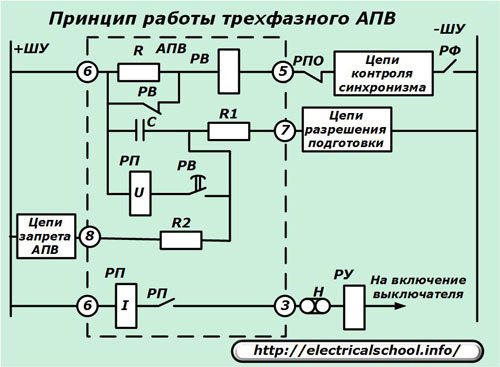
The circuit is supplied with direct operating voltage + ХУ and - ХУ. The AR relay is controlled by the following circuits:
-
synchronism control;
-
the position of the breaker contact in the off state (RPO);
-
permission to prepare;
-
prohibition of automatic reclosing.
The AR kit includes relays:
-
time RT;
-
intermediate RP with two coils:
-
current I;
-
voltage U.
Capacitor C, after the voltage is applied to the control box, is charged through the elements of the logic circuits of the preparation permit. And when automatic non-reclosing circuits are formed, the charge is blocked by selecting resistors R1 and R2.
The ShU voltage is applied to the coil of the time relay RV after the circuit breaker is tripped through the timing control circuits and it performs the specified time delay with its contact.
After closing a normally open contact RV, the capacitor discharges to the voltage coil of the intermediate relay RP, which is triggered and with its closed contact RP, through its own current coil, issues + ShU to the solenoid for closing the power switch.
Thus, the APV relay outputs a current pulse from the pre-charged capacitor C to close the circuit breaker after it is tripped by the RU signal flasher and the N overlay by closing the RP contact.
The purpose of the H plate is to disable automatic reclosing by service personnel when switching operations.
Relay for automatic closing of static elements
The use of semiconductor technology has changed the size and design of electromagnetic relays designed for automatic closing devices. They have become more compact, convenient in settings and setting settings.

And the principle of operation of the relay circuit, embedded in the logic of electromagnetic relays, remained the same.
Features of the support of automatic closing devices
During operation, the protection and automation devices that have been put into operation are only under the supervision of the service personnel who control the correct operation of the equipment. Access to them by other specialists is limited. organizational conditions.
All automatic closing operations are recorded by the automation, recorders and dispatcher records in the operation log. The relay staff analyzes the correctness of each actuation of the relay protection and automation devices and records this in the technical documentation.
To carry out periodic maintenance, automatic reclosing devices, along with other systems, are taken out of service and transferred to the personnel of the MSRZAI service for preventive measures, who, after completing the inspections, draw up a report, make a conclusion about their serviceability and participate in commissioning exploitation relay protection devices to work
See also: How automatic transfer switching devices (ATS) work in electrical networks
