Solenoids — device, operation, application
This article will focus on solenoids. First we will consider the theoretical side of this topic, then the practical, where we will note the areas of application of solenoids in different modes of their work.
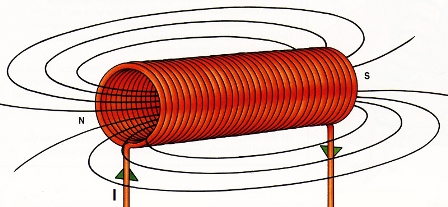
A solenoid is a cylindrical coil whose length is much greater than its diameter. The word solenoid itself is formed from a combination of two words — solen and eidos, the first of which translates as tube, the second — similar. That is, a solenoid is a coil shaped like a tube.
Solenoids in a broad sense are inductors wound by a wire on a cylindrical frame, which can be single-layer or multi-layer... Since the length of the coil of a solenoid greatly exceeds its diameter, then when a direct current is applied through such a coil, inside it, in the internal cavity, an almost uniform magnetic field is formed.
Solenoids are often referred to some actuators on an electromechanical principle of operation, such as an automatic transmission solenoid valve in a car or a starter retraction relay.As a rule, the ferromagnetic core acts as a retracted part and the solenoid itself fitted with a magnetic core on the outside, the so-called ferromagnetic yoke.
If there is no magnetic material in the design of the solenoid, then when a direct current flows through the wire, a magnetic field is formed along the axis of the coil, the induction of which is numerically equal to:
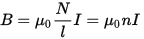
Where, N is the number of turns in the solenoid, l is the length of the solenoid coil, I is the current in the solenoid, μ0 is the magnetic permeability of the vacuum.
At the ends of the solenoid, the magnetic induction is half that inside it, because both halves of the solenoid at their junction make an equal contribution to the magnetic field created by the solenoid current. This can be said for a semi-infinite solenoid or for a coil that is long enough for the diameter of the frame. The magnetic induction at the edges will be equal to:
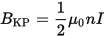
Since the solenoid is primarily an inductive coil, like any coil with an inductance, the solenoid is able to store energy in a magnetic field numerically equal to the work the source does to create a current in the coil that generates the solenoid's magnetic field:
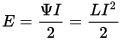
A change in the current in the coil will lead to the appearance of an EMF of self-induction, and the voltage at the ends of the wire of the solenoid coil will be equal to:
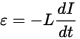
The inductance of the solenoid will be equal to:
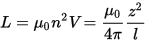
Where V is the volume of the solenoid, z is the length of the wire in the solenoid coil, n is the number of turns per unit length of the solenoid, l is the length of the solenoid, μ0 is the vacuum magnetic permeability.
When an alternating current flows through the solenoid wire, the magnetic field of the solenoid will also be alternating. The AC resistance of a solenoid is complex in nature and includes both active and reactive components determined by the inductance and active resistance of the coil.
Practical use of solenoids
Solenoids are used in many industrial and civil applications. Often linear drives are just an example of DC solenoid operation. Check the shears in the cash registers, engine valves, starter pull relay, hydraulic valves, etc. In alternating current, solenoids act as inductors crucible furnaces.
Solenoid coils, as a rule, are made of copper, less often of aluminum wire. In high-tech industries, superconducting coils are used. The cores may be iron, cast iron, ferrite or other alloys, often in the form of a bundle of sheets, or they may not be present at all.
Depending on the purpose of the electric machine, the core is made of one or another material. Devices such as lifting electromagnets, sorting seeds, cleaning coal, etc. Next we will look at some examples of using solenoids.
Line Solenoid Valve
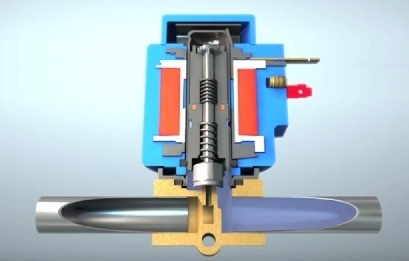
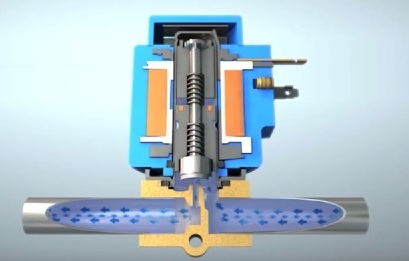
By applying voltage to the solenoid coil, the valve disc is pressed firmly against the pilot port by a spring and the line is closed. When current is applied to the valve coil, the armature and associated valve disc rise, pulled by the coil, opposing the spring and opening the pilot hole.
The difference in pressure on different sides of the valve causes the fluid to move in the pipeline, and as long as voltage is applied to the valve coil, the pipeline is not blocked.
When the solenoid is turned off, the spring no longer holds anything back and the valve rushes down, blocking the pilot hole. The pipeline is closed again.
Car electromagnetic starter relay
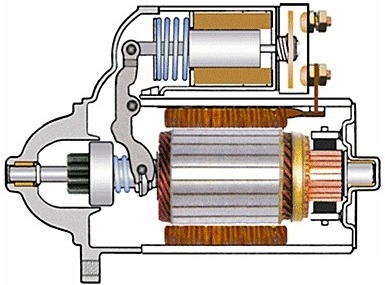
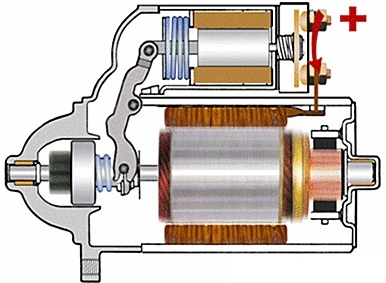
A starter motor is essentially a powerful DC motor powered by the car's battery. At the time of starting the engine, the starter gear (bendix) must be quickly engaged for a while with the crankshaft flywheel, and at the same time the starter motor is turned on. The solenoid here is the starter solenoid coil.
The retractor relay is mounted on the starter housing and when power is applied to the relay coil, an iron core connected to a mechanism that moves the gear forward is drawn. After the engine is started, the power supply is cut off by the relay coil and the gear is returned back thanks to the spring.
Solenoid lock

In electromagnetic locks, the bolt is driven by the force of an electromagnet. Such locks are used in access control systems and sluice gate systems. A door equipped with such a lock can only be opened during the period of validity of the control signal. After removing this signal, the closed door will remain locked, regardless of whether it was opened.
The advantages of solenoid locks include their design — it is much simpler than that of engine locks, more wear-resistant. As you can see, here the solenoid is again paired with a return spring.
Inductor with solenoid by heating

Solenoid multiturn inductors are usually used for heating. The inductor coil is made of water-cooled copper tube or copper busbar.
In medium frequency installations, single-layer windings are used, and in industrial frequency windings, the winding can be single-layer or multi-layer. This is due to a possible reduction of electrical losses in the inductor and with the conditions of compliance of the load parameters and with the voltage parameters and the power factor of the power supply. To ensure the rigidity of the inductive coil, its putty is most often used between the final asbestos-cement plates.
In modern installations induction hardening and heating Solenoids operate in high-frequency AC mode, so they usually do not need a ferromagnetic core.
Solenoid motor
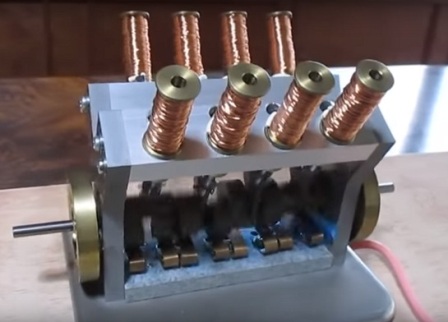
In single-coil solenoid motors, switching on and off the operating coil results in a mechanical movement of the crank mechanism, and return is done by a spring, similar to what happens in a solenoid valve and solenoid lock.
In multi-winding solenoid motors, the alternating activation of the coils is carried out with the help of valves. To each coil, the current from the power source is supplied in one of the half cycles of the sinusoidal voltage. The core is successively attracted by one or the other coil, making a reciprocating movement, driving the crankshaft or wheel to rotate.
Solenoids in experimental facilities

Experimental installations such as the ATLAS detector operating at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN use powerful electromagnets that also include solenoids. Particle physics experiments are conducted to discover the building blocks of matter and to investigate the fundamental forces of nature that sustain our universe.
Tesla coils

Finally, connoisseurs of the legacy of Nikola Tesla always use solenoids to build coils. The secondary winding of a Tesla transformer is nothing more than a solenoid. And the length of the wire in the coil turns out to be very important, because the builders of the coils here use solenoids not as electromagnets, but as waveguides, as resonators, in which, as in any oscillating circuit, there is not only the inductance of the wire, but also the capacitance formed in this case from closely spaced to friend on turns. By the way, the toroid at the top of the secondary winding is designed to compensate for this distributed capacitance.
We hope that our article was useful to you and now you know what a solenoid is and how many areas of its application there are in the modern world, because we did not list them all.
