Fuses PR-2 and PN-2-device, technical characteristics
Fuses are electrical devices that, at high setpoint currents, open the circuit when a fuse blows, which is heated directly by the current until it melts. The fuses are subdivided according to their purpose for protecting installations with a voltage of up to 1000 V and fuses for protection at a voltage greater than or equal to 1000 V.
Fuses are devices that protect installations from overload and short circuit currents.
The main elements of the fuse are a fuse, which is included in the section of the protected circuit, and an arc extinguishing device, which extinguishes the arc that occurs after the insert melts.
The selection of fuses is done according to the rated voltage, the rated fuse and fuse currents and the maximum breaking current.
Basic requirements. for fuses
The following requirements apply to fuses:
1. The current-time characteristic of the fuse must be lower, but as close as possible to the current-time characteristic of the protected object.
2.In the event of a short circuit, the fuses must operate selectively.
3. The tripping time of the fuse in the event of a short circuit should be as short as possible, especially when protecting semiconductor devices. Fuses must be current limited.
4. The characteristics of the fuse must be stable. Dispersion of parameters due to manufacturing deviations must not impair the protective properties of the fuse.
5. Due to the increased capacity of the installations, the fuses must have a high breaking capacity.
6. Replacing a blown fuse or fuse should not take much time.
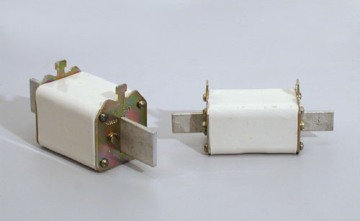
In industry, the most widely used fuses are of the PR-2 and PN-2 types.
Arc extinguishing fuses in a closed volume PR-2
Fuse PR-2
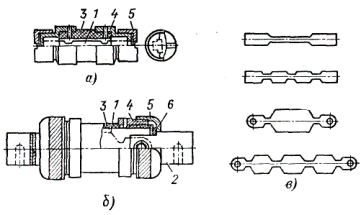
 PR-2 fuses for currents from 15 to 60 A have a simple design. The fusible insert 1 is pressed against the brass holder 4 by the cap 5, which is the output contact. The fusible insert 1 is stamped from zinc, which is a low-melting and corrosion-resistant material. The specified shape of the insert allows you to get a favorable current characteristic over time (protective). For fuses for currents over 60 A, the safety link 1 is connected to the contact blades 2 with bolts.
PR-2 fuses for currents from 15 to 60 A have a simple design. The fusible insert 1 is pressed against the brass holder 4 by the cap 5, which is the output contact. The fusible insert 1 is stamped from zinc, which is a low-melting and corrosion-resistant material. The specified shape of the insert allows you to get a favorable current characteristic over time (protective). For fuses for currents over 60 A, the safety link 1 is connected to the contact blades 2 with bolts.
The fuse insert PR-2 is located in a sealed tubular cartridge, which consists of a fiber cylinder 3, a brass holder 4 and a brass cap 5.
Principle of operation of fuses PR-2
The process of extinguishing the arc in the PR-2 fuse is as follows. When turned off, the narrowed spines of the fuse burn, after which an arc occurs.Under the action of the high temperature of the arc, the fiber walls of the cartridge emit gas, as a result of which the pressure in the cartridge increases to 4-8 MPa for part of the half-cycle. By increasing the pressure, the current-voltage characteristic of the arc increases, which contributes to its rapid extinction.
The fusible link of the PR-2 fuse can have from one to four tapers, depending on the voltage rating. The narrowed parts of the insert facilitate its rapid melting in the event of a short circuit and create a current-limiting effect.
Fuse type PR-2
Since arc extinguishing in the PR-2 fuse is very fast (0.002 s), it can be assumed that the extended parts of the insert remain stationary during the extinguishing process.
The pressure inside the fuse holder is proportional to the square of the current at the moment the fuse melts and can reach high values. Therefore, the fiber cylinder must have high mechanical strength, for which brass clamps 4 are installed at its ends. Disks 6, firmly connected with contact knives 2, are attached to the clamp 4 of the cartridge with the help of caps 5.
PR-2 fuses operate silently, with practically no emission of flames and gases, which allows them to be installed at a close distance from each other. PR -2 fuses are manufactured in two axial sizes — short and long. Short PR-2 fuses are designed for operation at an alternating voltage not exceeding 380 V. They have a lower breaking capacity than long ones designed for operation in a network with a voltage of up to 500 V.
Technical characteristics of fuses PR-2
 Six cartridge sizes are produced with different diameters depending on the rated current.Inserts for different rated currents can be installed in the cartridge of any size. So, in a cartridge for a nominal current of 15 A, inserts for a current of 6, 10 and 15 A can be installed.
Six cartridge sizes are produced with different diameters depending on the rated current.Inserts for different rated currents can be installed in the cartridge of any size. So, in a cartridge for a nominal current of 15 A, inserts for a current of 6, 10 and 15 A can be installed.
A distinction is made between the lower and upper test current. The lower test current is the maximum current that does not blow the fuse for 1 hour. The upper value of the test current is the minimum current which, flowing for 1 hour, melts the fuse insert. With sufficient accuracy, it is possible to take the limit current equal to the arithmetic mean value of the test currents.
Fuses with fine grain filler PN-2
Fuse device PN-2
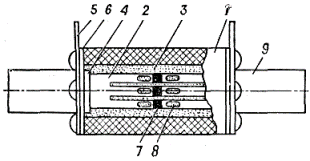
 These fuses are more advanced than the PR-2 fuses. The square-section body of 1 type PN-2 fuse is made of durable porcelain or steatite. Inside the body there are adhesive tape connections 2 and a filler - quartz sand 3. The fusible links are welded to a disk 4, which is attached to plates 5 connected to blade contacts 9. Plates 5 are attached to the body with screws.
These fuses are more advanced than the PR-2 fuses. The square-section body of 1 type PN-2 fuse is made of durable porcelain or steatite. Inside the body there are adhesive tape connections 2 and a filler - quartz sand 3. The fusible links are welded to a disk 4, which is attached to plates 5 connected to blade contacts 9. Plates 5 are attached to the body with screws.
As a filler in PN-2 fuses, quartz sand with a SiO2 content of at least 98%, with grains of size (0.2-0.4) with a size of 10-3 m and a moisture content of no more than 3% is used. Before backfilling, the sand is thoroughly dried at a temperature of 120-180 ° C. Quartz sand grains have high thermal conductivity and a well-developed cooling surface.
The fusible insert of fuses PN-2 is made of copper tape with a thickness of 0.1-0.2 mm. To obtain current limitation, the insert has narrowed sections 8. The fusible insert is divided into three parallel branches for more complete use of the filler.The use of a thin strip, effectively dissipating heat from narrowed areas, allows you to choose a small minimum cross-section of the insert for a given rated current, which provides a high current limiting ability. Therefore, connecting several taper sections helps to slow the rise in current after the fuse melts as the fuse arc voltage increases. To lower the melting temperature, tinned strips 7 (metallurgical effect) are applied to the inserts.
The principle of operation of the fuse PN-2
In the event of a short circuit, the fusible link of the PN-2 fuse burns out and the arc burns out in the channel formed by the grains of the filler. Due to burning in a narrow slot at currents above 100 A, the arc has a rising volt-ampere characteristic. The voltage gradient in the arc is very high and reaches (2-6) 104 V / m. This ensures that the arc is extinguished in a few milliseconds.
After the fuse is burned, the connections of the fuses together with the disk 4 are replaced, after which the cartridge is covered with sand. To seal the cartridge, an asbestos seal 6 is placed under the plates 5, which protects the sand from moisture. At a rated current of 40 A and below, the fuse has a simpler design.
Technical characteristics of fuses PN-2
PN-2 fuses are designed for rated current up to 630 A.effective current metallic short circuit of the network in which the fuse is installed).
Small dimensions, negligible consumption of scarce materials, high current limiting capability are the advantages of the PN-2 fuse.