How powerful industrial wind turbines work
The natural reaction of the atmosphere to the uneven heating of its different layers is wind. The resulting drops in atmospheric pressure cause wind to blow from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, and the greater the pressure difference, the stronger the wind—the higher its speed. Theoretically, it is estimated that up to 2% of solar radiation is converted into mechanical wind energy due to the natural movement of air in the atmosphere.

It is known that the topography of a certain area can either amplify the wind or restrict the air flow. So, in areas of mountain ranges, passes, near river canyons, the conditions for installing wind turbines are really ideal. And if we remember that the power that can be obtained from the wind is proportional to the mass of air passing through the turbine and the cube of its speed, then it is easy to understand the prospects that are quickly opening in this direction.

Wind is undoubtedly one of the most promising renewable sources of natural energy.It is not for nothing that in many countries, year after year, more and more wind farms are being built, wind farms, in particular, on the coastal parts of the seas, oceans and in the plains.
The gusty nature of the wind does not contribute to the stable supply of electrical networks, therefore the accumulation of energy for the purpose of its further use becomes an important task. But this task is being solved — industrial and private battery storage systems are being built, measures are being taken to ensure uninterrupted power supply.
And now we can confidently say that a powerful industrial wind generator (such as Enercon E-126) with a capacity of 6-8 MW, integrated into the power supply system of a small city, will be able to satisfy the needs of its residents and the needs of the electrified infrastructure.
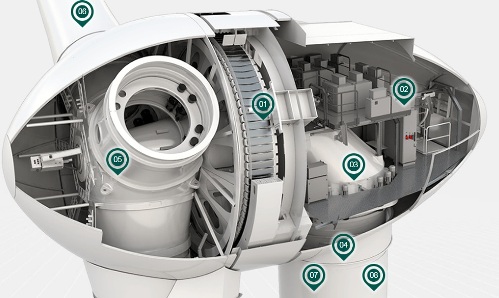
However, let's get to the point and look at the device of an industrial wind generator. After all, each wind generator is a product of meticulous engineering thought, the result of precise calculations and long design to obtain an efficient and reliable converter of wind energy into electrical energy, which is why every detail of a huge structure is by no means accidental. For example, we will refer to the design of the Enercon E-126 wind generator and look at its main parts.
Tower

The tower (7), tens of meters high, is the support of an industrial wind generator. It is made entirely of reinforced concrete by sequential casting in the formwork or assembled from short reinforced concrete rings that are mounted sequentially on top of each other and connected by pulling frame cables through them.The reinforced concrete is strong enough to hold a heavy turbine and nacelle aloft, as well as withstand the load resulting from the operation of the wind turbine, preventing the structure from overturning.
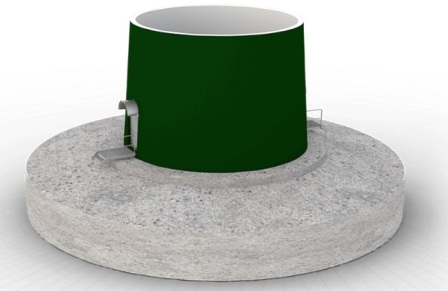
The base of the tower rests on a reinforced concrete base (8), the weight of which is proportional to the weight of the tower itself. For example, the Enercon E-126 wind turbine has a total weight of about 6,000 tons. The support is not cylindrical in shape, having a shape closer to a truncated cone than to a cylinder. Expanded at the base, the tower securely holds the entire structure in the correct position.
Blades and rotor

The blades (6) and the rotor (5) of an industrial wind turbine are made of a special composite fiber based on steel. The blades are assembled from separate segments or made as a monolith, depending on their scope. As a rule, bolts and a hub are used to attach the blades to the rotor. The blades themselves are attached to the hub, and the hub is attached directly to the generator rotor.
Rotation of the turbine around the tower

To rotate the turbine around the tower, a asynchronous engine (3) connected by a gear to the ring at the base of the nacelle. Depending on the size of the wind generator and its power, there can be from one to three such engines.
Power generator
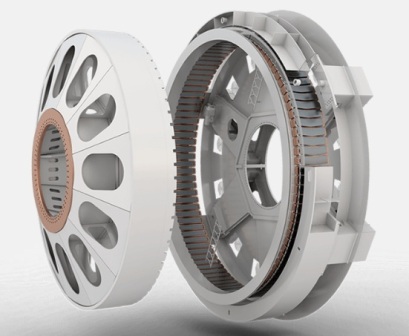
If earlier units similar in design to standard synchronous generators were used as generators for wind turbines, then at the beginning of the 2000s such an innovation as a ring generator (1) appeared. Here the turbine rotor connected to the hub is also the generator rotor.
Independent excitation windings are located on the ring rotor, forming magnetic poles, and respectively on the stator of the stator winding. The stator winding is divided into parts (in the case of the Enercon E -126 — into four parts), each of which is connected to a separate rectifier. The generator controller is located in the engine room (2) of the nacelle.
Inverter

After rectification, a direct voltage of 400 volts is supplied to the inverter (4) installed at the base of the tower, where the energy is converted into alternating current and after transformation is supplied to the power line.

We looked at the key components of a modern industrial wind turbine using the example of the Enercon E-126 model, first installed near the German city of Emden in 2007. The generator's capacity is currently 7.58 MW, which is enough to power 4,500 villas with electricity all year round.
To date, Enercon has built more than 13,000 such wind turbines worldwide, with their total installed capacity already in 2010 exceeding 2,846 MW.
