Automation of ventilation systems
In order to provide the necessary conditions for the proper movement of air in the premises, to create reliable ventilation and air conditioning systems, to reduce the need for service personnel, as well as to save energy and preserve cold and heat, they resort to the use of automated air conditioning and ventilation systems, which include, among other things, the automatic shutdown and activation of equipment in emergency situations.
In order for the automated system to work correctly and most economically, control devices are placed on the boards to monitor the main parameters. On individual nodes, in order to be able to track the work of individual elements, local control devices for monitoring intermediate indicators are installed.
The automation of recording devices allows for record keeping and analysis of the current operation of the ventilation equipment, and signaling devices designed to prevent disruption of the technological process and, as a result, product defects, are used for the timely elimination of dangerous deviations.
The indicators of the ventilation and air conditioning system are installed both in the supply ventilation system and in combined systems with air heating, as well as in air conditioning systems. It is important to control the air temperature along with the control of the coolant parameters.
Regarding air conditioning specifically, it is important to monitor both air humidity, hot and cold water temperature, and pressure in order to properly regulate the operation of the pumps that supply water to the irrigation chamber.
Depending on how accurate the regulation of the supported parameters should be, on the purpose of the system, on economic and technical feasibility, a positional, proportional or proportionally integrated method of controlling the automated system is chosen. And depending on the type of energy that is used to ensure the operation of the system, the control system can be electric or pneumatic.
If the company does not have a compressed air network or its installation is economically unacceptable, then an electric control system is used. If the company has a network of compressed air (with a pressure of 0.3 to 0.6 MPa), or for fire safety purposes, a pneumatic control system is used.
The principle of automatic air temperature regulation consists in mixing recirculating air and outside air, as well as changing the operating modes of the air heaters. These methods can be used together or separately. At the same time, thanks to the regulation in the climate system, the required temperature, pressure and relative humidity are achieved.
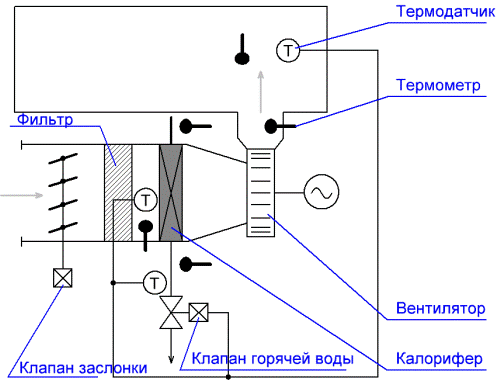
An automated ventilation system for power supply is characterized by measuring the temperature of the air in the room (after the fan) and the temperature of the hot water before and after the heater. At the same time, thanks to the thermostat, which automatically acts on the regulating valve for hot water, the room temperature changes in the desired direction.
The system has two temperature sensors whose function is to protect the air heater from freezing. The first sensor monitors the temperature of the coolant after the heater (in the return pipe), the second — the temperature of the air between the heater and the filter.
If, during operation of the ventilation unit, the first sensor detects a decrease in the temperature of the coolant to +20 — + 25 ° C, then the fan will automatically turn off and the control valve will be fully open to supply the coolant to the heater for warming.
If the inlet air temperature is more than 0 ° C, then the freezing of the air heater is, of course, impossible, and there is no need to turn off the fan, there is no need to open the hot water valve, — the second sensor will turn off the frost protection module of the air heater.

Leave the fan turned off at night and the heater must be protected from freezing, then the second sensor (in front of the heater), fixing the temperature below + 3 ° C, will open the valve for supplying hot water. When the heater heats up, the valve will close.
Thus, the automatic two-position regulation of the air temperature in front of the heater is realized when the fan is turned off. When the system is started, the heater is preheated before the fan turns on. When the fan is turned on, the damper opens.
One of the two schemes can be used to heat the air. In the first scheme, installed in the flow of heated air, the thermostat, when the air temperature deviates from the set level, turns on the engine valve, which regulates the supply of coolant to the heater (it is recommended to use it if the coolant is water). Water enters the heater in proportion to the position of the valve above the seat in height.
When steam is used as the heat carrier, its supply will not be proportional and then the second method of control is suitable. In a steam-friendly circuit, the thermostat controls a servo motor connected to throttle valves that adjust the ratio of bypass air to air flowing directly through the heater.
Humidification of the air in the nozzle chamber is controlled by one of two methods based on adiabatic saturation. The ratio? R is directly related to the irrigation coefficient p and by changing p we change the ? P.The humidity controller controls a motor valve mounted on the discharge side of the pump that supplies water to the nozzles from the chamber opening. But there is a second way.
The second way is that by changing the temperature of the air passing through the heater, you can change the humidity while leaving it intact? and p. Simply, the humidity regulator in this case regulates the supply of the heat carrier to the heater.
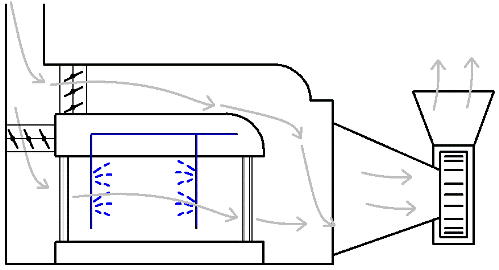
The following process is used to cool the air. The air transported through the channel enters the nozzle chamber, where it must be cooled by spraying cold water. The position of the throttle valves is changed so that part of the air flow is bypassed and part is in the nozzle chamber. The temperature in the bypass channel does not change.
After part of the flow passes through the nozzle chamber, the separated flows are combined again, mixed, and as a result, the air temperature becomes the correct one according to the conditions in the room. The proportion of air passing through the nozzle chamber or bypass is adjustable and can reach 100% — all flow through the chamber or all flow through the bypass.
Which system to choose - proportional or two-position? Depending on the ratio of the production of the regulating agent to the volume of its consumption. If the agent's production is much greater than the consumption capacity, then the proportional system is better, otherwise, the two-position system.
When a decision is made to build a humidity control system in the room, the amount of water vapor that the air in the room will be able to accept is determined.
The temperature in the room is affected by the internal surfaces in it, and for simplicity we will assume that the things located in the room do not affect the air temperature.
It is common knowledge that surfaces differ in temperature from air, and since they are large, the thermal effect is always such that the temperature of the air becomes consistent with the temperature of the surface, and a change in the temperature of the air indicates a changed temperature of the surface.
