Advantages and disadvantages of different temperature sensors
In many technological processes, one of the most important physical quantities is temperature. In industry, temperature sensors are used for measurement. These sensors convert temperature information into an electrical signal, which is then processed and interpreted by electronics and automation. As a result, the temperature value is either simply displayed on the display, or serves as the basis for automatically changing the operating mode of one or another piece of equipment.
One way or another, temperature sensors are indispensable today, especially in industry. And it is important to choose the right sensor for your purpose, clearly understanding the distinguishing features of different types of temperature sensors. We'll talk about that later.
Different sensors for different purposes
Technologically, temperature sensors are divided into two large groups: contact and non-contact. Non-contact sensors use the principle of measurement in their work infrared parameterscoming from a distant surface.
Contact sensors, on the other hand, on the market more widely, differ in that their sensor element in the process of measuring temperature is in direct contact with the surface or medium whose temperature is to be measured. Thus, it will be most expedient to examine the contact sensors in detail, to compare their types, characteristics, to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different types of temperature sensors.
When choosing a temperature sensor, the first thing to do is determine how it will be necessary to measure the temperature. The infrared sensor will be able to measure the temperature at a distance from the surface, therefore it is of fundamental importance that between the sensor and the surface to which it will be directed, the atmosphere is as transparent and clean as possible, otherwise the temperature data will be distorted ( look - Non-contact temperature measurement during equipment operation).
The contact sensor will allow you to measure the temperature of the surface directly or of the environment it is in contact with, so the cleanliness of the surrounding atmosphere is generally not important. Here, direct and high-quality contact between the sensor and the test material is crucial.
A contact probe can be manufactured using one of several technologies: thermistor, resistance thermometer, or thermocouple. Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages.
The thermistor is very sensitive, its price is in the middle between thermocouples and resistance thermometers, but it does not differ in accuracy and linearity.
The thermocouple is more expensive, it reacts faster to temperature changes, the measurements will be more linear than the thermistor, but the accuracy and sensitivity are not high.
The resistance thermometer is the most accurate of the three, it is linear but less sensitive, although it is cheaper than the thermocouple in price.
In addition, when choosing a sensor, you should pay attention to the range of measured temperatures, for thermocouples and resistance thermometers it depends on the material of the sensitive element used. So you have to find some compromise.
Thermocouple
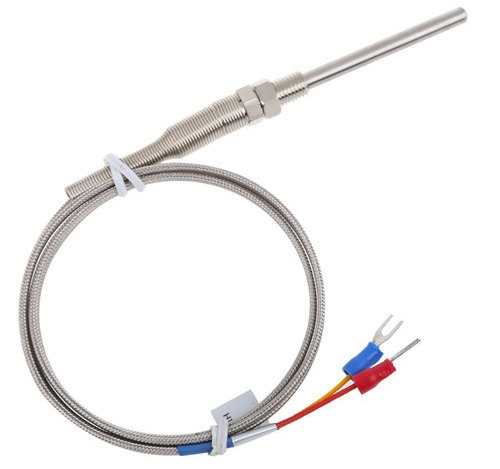

Temperature sensors thermocouple work thanks to Seebekov effect… Two wires of different metals are soldered at one end — this is the so-called hot junction of a thermocouple, which is exposed to the measured temperature. On the opposite side of the wires, the temperature of their ends does not change, a sensitive voltmeter is connected in this place.
The voltage measured by a voltmeter depends on the temperature difference between the hot junction and the wires connected to the voltmeter. Thermocouples differ in the metals that form their hot junctions, which determines the range of measured temperatures for a particular thermocouple sensor.
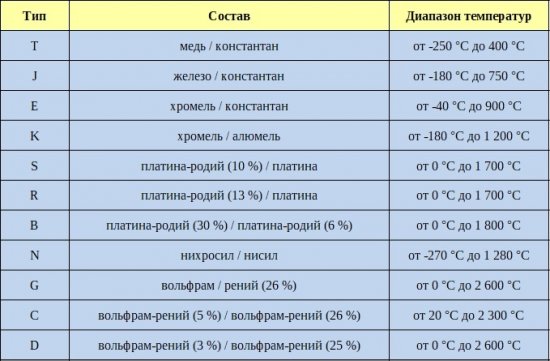
Below is a table of the different types of sensors of this variety. The type of sensor is selected depending on the required temperature range and the nature of the environment.
Type E sensors are suitable for use in oxidizing or inert environments. Type J — for operation in vacuum, inert or reducing environments. Type K — suitable for oxidizing or neutral environments. Type N — has a longer service life compared to type K.
T-type sensors are resistant to corrosion, so they can be used in moist oxidizing, reducing, inert environments, as well as in vacuum. R (industrial) and S (laboratory) — types — are high-temperature sensors that must be protected by special ceramic insulators or non-metallic tubing. Type B is even higher temperature than types R and S.
The advantages of thermocouple sensors are the stability of their operating parameters at high temperatures and the relative speed of response to changes in hot junction temperature. Sensors of this type are presented in a wide range of available diameters. They have a low price.
As for the disadvantages, thermocouples are characterized by low accuracy, have an extremely low measured voltage, and in addition, these sensors always require compensation circuits.
Resistance thermometers
Resistance thermometer or rheostat temperature sensor is abbreviated as RTD. It works on the principle of changing the resistance of the metal depending on the change in its temperature. Metals used: platinum (from -200 ° C to +600 ° C), nickel (from -60 ° C to +180 ° C), copper (from -190 ° C to +150 ° C), tungsten (from -100 ° C to +1400 ° C) — depending on the required measured temperature range.
More often than other metals, platinum is used in resistance thermometers, which gives a fairly wide temperature range and allows you to choose sensors with different sensitivities. So, the Pt100 sensor has a resistance of 100 Ohm at 0 °C, and the Pt1000 sensor has 1kOhm at the same temperature, that is, it is more sensitive and allows you to measure the temperature more accurately.
Compared with the thermocouple, the resistance thermometer has higher accuracy, its parameters are more stable, and the range of measured temperatures is wider. However, the sensitivity is lower and the response time is longer than that of thermocouples.
Thermistors
Another type of contact temperature sensors — thermistors… They use metal oxides that can significantly change their resistance depending on temperature. Thermistors are of two types: PTC — PTC and NTC — NTC.
In the first, the resistance increases with increasing temperature in a certain operating range, in the second, with increasing temperature, the resistance decreases. Thermistors are characterized by a faster response to temperature changes and low cost, but they are quite fragile and have a narrow operating temperature range than the same resistance thermometers and thermocouples.
Infrared sensors
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, infrared sensors interpret the infrared radiation emitted by a distant surface - a target. Their advantage is that the temperature measurement is carried out in a non-contact way, that is, there is no need to press the sensor tightly against the object or immerse it in the environment.
They react very quickly to temperature changes, which is why they are applicable for examining the surfaces of even moving objects, for example on a conveyor. Only with the help of infrared sensors is it possible to measure the temperature of samples located, for example, directly in an oven or in any aggressive zone.
Disadvantages of infrared sensors include their sensitivity to the condition of the heat-emitting surface, as well as to the cleanliness of their own optics and the atmosphere in the path between the sensor and the target. Dust and smoke greatly interfere with accurate measurements.