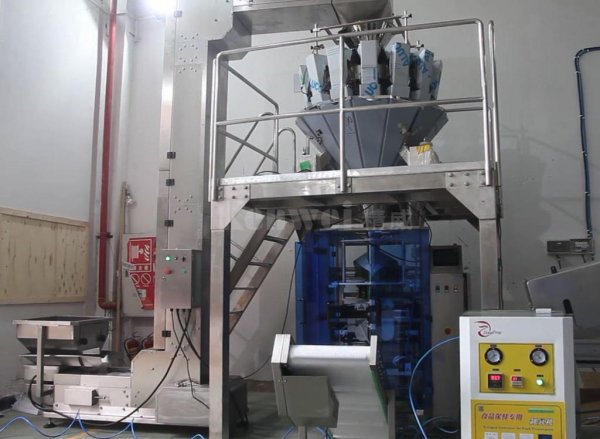
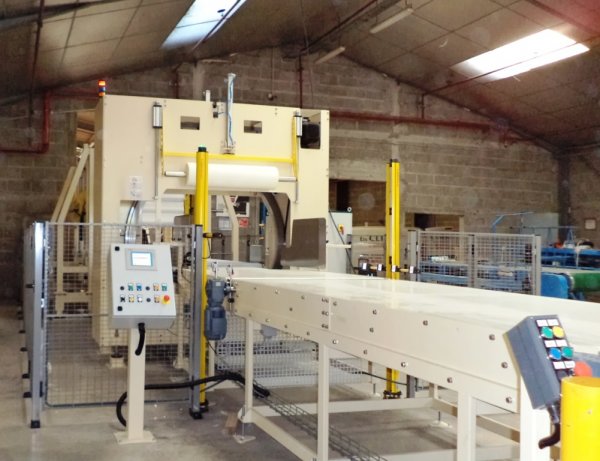
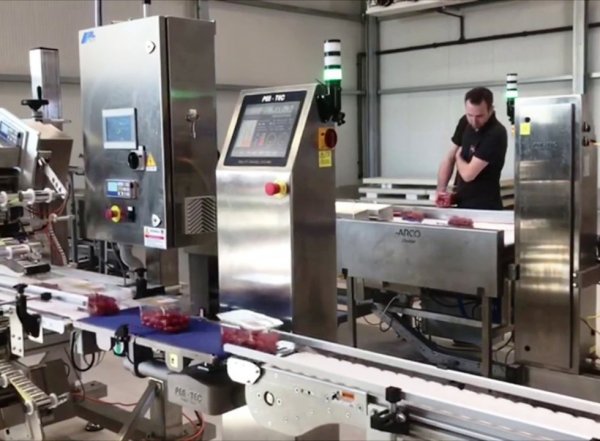
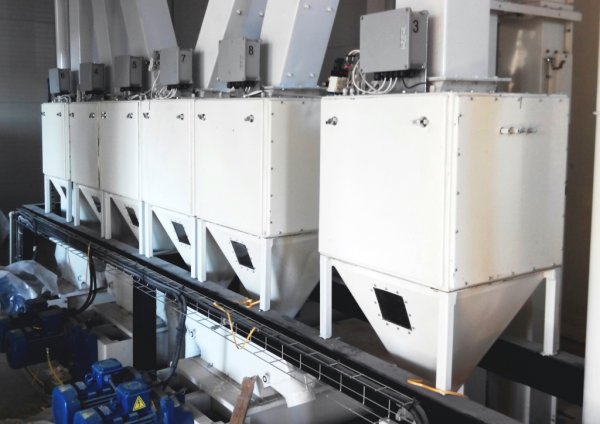
How automatic weighing is done in factories
Automatic weighing is a general term that covers the operations of determining:
- values of mass (weight) of bodies; changes in mass over time;
- deviations of mass values from a given value;
- the total value of the mass of the transported goods, as well as the weighing of the indicated portions (doses).
Automatic weighing is carried out using automatic weighing devices, which, according to the degree of automation, are divided into:
- scales with automatic balancing;
- scales with remote transmission and recording of readings;
- automatic portion scales;
- automatic portion dispensers;
- continuous automatic scales;
- continuous automatic weighing machines and automatic sorting scales.
When choosing industrial scales, standing or table, it is necessary to take into account several important aspects: their type, purpose (function of the scale), construction material, volume, size, weighing range, accuracy (measurement error), conditions of use.
For scales with automatic balancing, only the process of determining (balancing) the load is automated. This is achieved by deflecting pendulum counterweights or deforming elastic measuring elements.
The auto-balancing scale has a maximum load range of 100 g — 1000 t (depending on the coupling system). Laboratory balances with automatic balancing have higher accuracy classes.
Scales with remote transmission and recording of readings are scales with automatic balancing, in which the movement of the measuring elements is converted into a signal (most often electrical).
In order to convert the readings of dial and spring scales with a large (about millimeters) deformation of the elastic body of the scale, selsins are used (the disadvantage is an increase in error due to the reverse effect on the measuring system and transmission errors), potentiometers (the disadvantage is an increase in the error due to friction), pulse reading devices (photoelectric, magnetic heads, etc.), encoders, as well as tracking systems.
To convert spring balance readings with small (tenths of a mm or less) deformation of an elastic body, wire gauges (electric strain gauges) and is used direct and inverse effect of magnetostriction.
Most often, strain gauges are used to measure weight in the automation of technological processes — converters of the measured deformation of solid bodies into an electrical signal. Resistive strain gauges (wire and foil) are widely used, converting strain into a change in electrical resistance.
The operation of a resistance meter is based on the property of a metal wire (or foil) under the influence of deformation (tension or compression) to change its electrical resistance.
As scales with remote transmission and recording of the readings, automatic (electromagnetic) force-compensating devices are also used, consisting of sensors and a feedback system that compensates for changes in the load on the sensor. The current (pressure) in the feedback loop is analogous to the weight acting on the load cell.
Automatic portions are used for weighing in equal portions of bulk and liquid materials, mainly for general accounting or packaging. In such scales, the processes of feeding, weighing and unloading materials are automated.
Typically, these scales are a beam to which a counterweight with weights and a bucket for receiving the load are suspended. The material is fed into the bucket by gravity or by a feeder. When the specified weight of material in the bucket is reached, the swing arm is deflected, the material feed stops and the bucket is unloaded.
Less commonly, scales with automatic balancing or with remote transmission and recording of readings, equipped with sensors that are activated when a predetermined weight is reached and shut off further feeding of material, are used as automatic portion scales.
Automatic batch dispensers are used to make up mixtures of a given composition and are conventional scales with automatic balancing or with remote transmission and recording of readings, equipped with an automation system that controls the supply of materials.The final load of batch dispensers is from a few g to several tons. Accuracy class 1b and lower.
Automatic continuous scales are used to determine the total amount of bulk materials transported by belt conveyors (conveyor scales) or by gravity (dynamic scales).
For weighing goods on belt conveyors, the belt part rests on roller supports mounted on a weighing platform or on sensors (electric voltage, pneumatic, etc.).
The total value of the mass of the load passed through the scale is determined by integrating the product of a signal proportional to the instantaneous load value by a signal proportional to the belt speed (for example, tachogenerator voltage).
For the complete determination of the mass of goods transported vertically by gravity, the principle of measuring the reaction of a flow of material to an inclined plate or the reaction of an electric motor rotating in a horizontal plane on an impeller (but a type of centrifugal fan) installed in the flow of material is used . Force compensation is used to measure the response.
Continuous-acting automatic weighers are used to automatically adjust the flow of material to achieve a specified throughput (or a given throughput ratio when multiple feeders are operating simultaneously). They are automatic scales with continuous operation, equipped with a system of automatic control of feeders that regulate the consumption of material.
Most often, continuous dispensers are used in the form of a short belt conveyor supported on a weight lever system or on sensors (electrical strain gauge, pneumatic) and controlling a vibrating feeder. Dosers in the form of a tank (bucket) are also used, supported by a weighing device that regulates the consumption of material so that the speed of reduction in the weight of the bucket corresponds to the specified one.
Automatic sorting scales are used to sort products (packages) by weight. To improve accuracy and performance, deviations of the weight of the controlled product from the standard are usually measured. The amount of deflection is measured by a force-compensated electrodynamic system. An artificial (centrifugal) accelerating field (centrifugal sorting scales) is created for sorting light (of the order of several g) products.
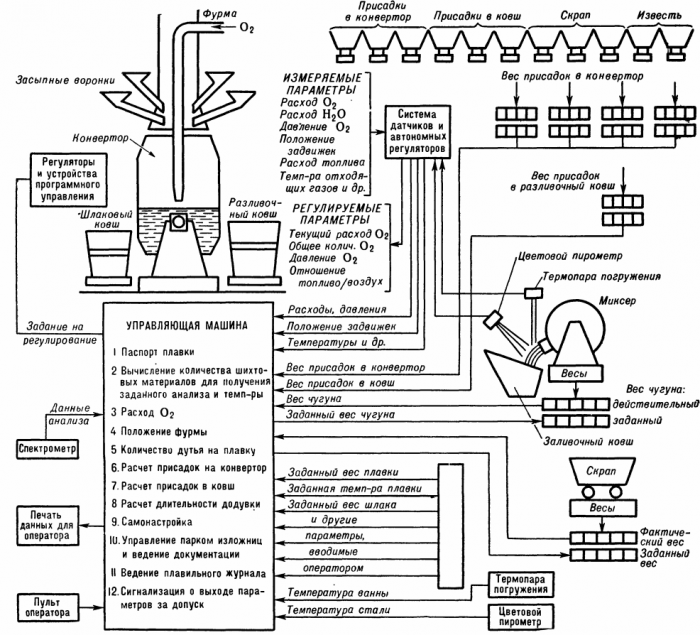
An example of the use of automatic weighing devices in the automation scheme of a converter workshop:
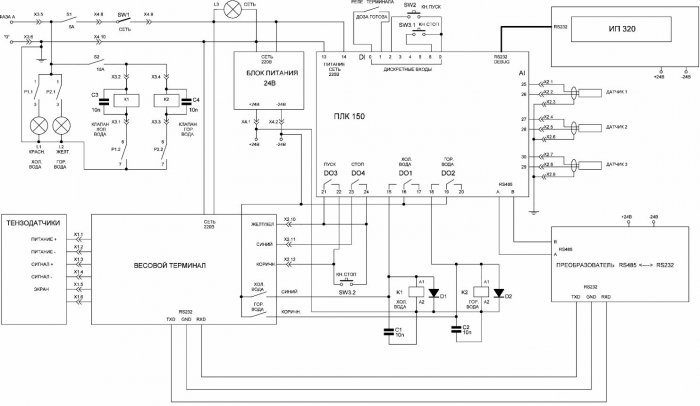
Schematic diagram of a modern PLC automatic water dispensing cabinet: