The use of radioactive isotopes in automatic control devices, radiometric measuring devices
Radioactive isotopes are used in various automatic control devices (radiometric measuring devices). In industrial processes, radiometric technology has been used for complex measurements since the 1950s.
The main advantages of radioisotope devices:
- non-contact measurement (without direct contact of the measuring elements with the controlled environment);
- high metrological qualities provided by the stability of the radiation sources;
- ease of use in typical automation schemes (electrical output, unified blocks).
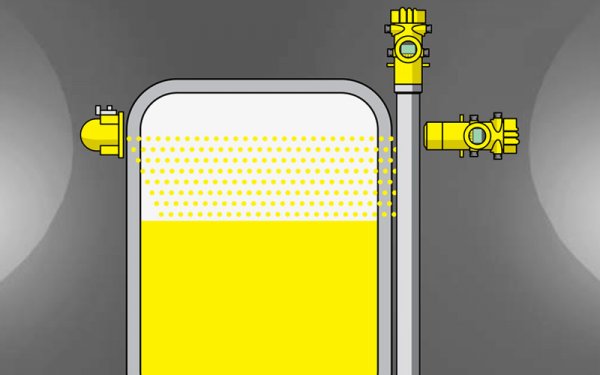
The principles of operation of radioisotope devices are based on the phenomena of interaction of nuclear radiation with a controlled environment. The scheme of the device, as a rule, contains a source of radiation, a receiver of radiation (detector), an intermediate converter of the received signal and an output device.
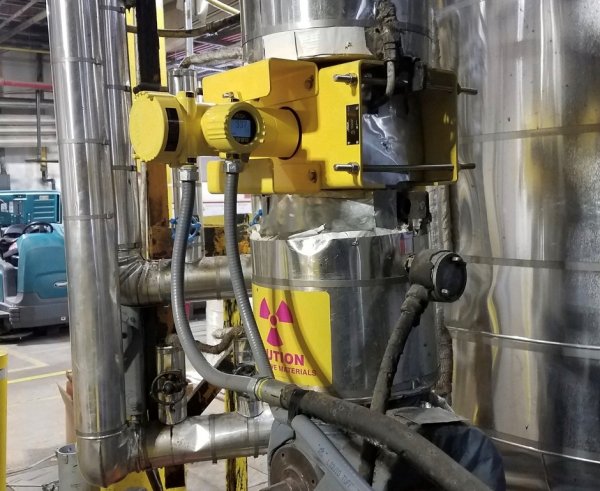
Radiometric systems consist of two parts: a low-level radioactive isotope in the source emits radioactive energy through technological equipment, for example, a vessel, and a detector installed on the other side measures the radiation coming to it. As the mass between the source and detector changes (level height, slurry density, or weight of solid particles on a conveyor), the radiation field strength of the detector changes.
Main properties and areas of application of some types of radiation:
1) alpha radiation — a stream of helium nuclei. It is strongly absorbed from the environment. The range of alpha particles in air is several centimeters, and in liquids - several tens of microns. It is used for gas pressure measurement and gas analysis. The measurement methods are based on the ionization of the gas medium;
2) beta radiation — a stream of electrons or positrons. The range of beta particles in air reaches several meters, in solids — several mm. The absorption of beta particles by the medium is used to measure the thickness, density and weight of materials (fabric, paper, tobacco pulp, foil, etc.) and to control the composition of liquids. The reflection (backscatter) of beta radiation from the environment allows you to measure the thickness of coatings and the concentration of individual components in a given substance, beta radiation is also used in the analysis of ionizing gases and for ionization to remove charges from static electricity;
3) gamma radiation — a flow of quanta of electromagnetic energy accompanying nuclear transformations. Works in solid bodies - up to tens of cm.Gamma radiation is used in cases where high penetrating power is required (defect detection, density control, level control) or the features of the interaction of gamma radiation with liquid and solid media (composition control) are used;
4) n-neutron radiation This is the flow of uncharged particles. Po — Be sources (in which Po alpha particles bombard Be, emitting neutrons are often used). It is used to measure the humidity and composition of the medium.
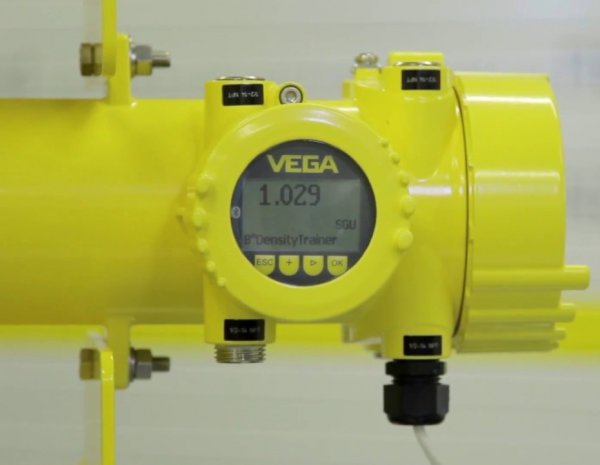
Radiometric density measurement. For pipeline and vessel sensing processes, density knowledge helps operators make informed decisions.
The most common radiation receivers in automatic control devices are ionization chambers, gas discharge and scintillation counters.
The intermediate converter of the received radiation signal may contain an amplifying (shaping) circuit and a pulse counting rate meter (integrator). In addition, special spectrometric schemes are used in some cases. Sometimes automatic control devices are incorporated directly into the control system.
A distinctive feature of radioisotope devices is the presence, in addition to the usual instrumental errors, of additional probabilistic errors. They are due to the statistical nature of radioactive decay, and therefore, with a constant average value of the radiation flux at any given moment in time, different values of this flux can be recorded.
A reduction in measurement errors can be achieved by increasing the intensity of the radiation flux or the measurement time.However, the former is limited by safety requirements, and the latter degrades the performance of the device. Therefore, it is recommended in all cases to use radiation detectors with the highest detection efficiency.
Although accurate measurement of radiation flux intensity is mandatory for most devices of the considered type, this is not the ultimate goal, since in reality it is important to precisely control not the intensity, but the technological parameter.
Radioisotope thickness and density meters
The most widely used devices for measuring thickness or density by absorption of radiation. The simplest scheme for measuring the thickness or density of a material by absorbing radiation contains a radiation source, a test material, a radiation receiver, an intermediate transducer, and an output device.
Various industries use radiometric technology to measure density. Mines, paper mills, coal-fired power plants, building materials manufacturers, and oil and gas utilities all use this density measurement technology somewhere in their processes.
Density measurements allow operators to better understand their processes, helping them optimize slurry performance, identify blockages and even improve control in complex applications.
Radiometric density sensors are non-contact, which means they do not interfere with the process, do not wear out and do not require maintenance, allowing them to last longer. External mounting simplifies sensor mounting.
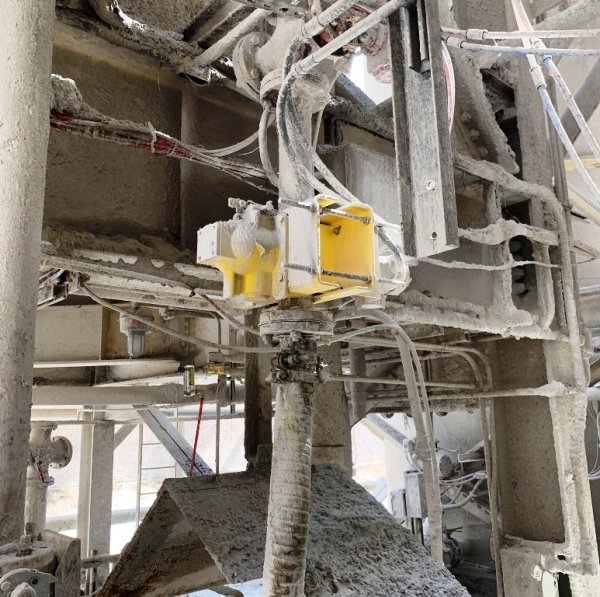
Radiometric technology is used to measure density because these sensors perform measurements without coming into contact with the material being processed. Non-contact measurement ensures wear-free and maintenance-free operation. Abrasive, corrosive or corrosive products often result in frequent and expensive maintenance or replacement of other sensors, but radiometric density detectors can last 20 to 30 years.
The sensor is immune to dusty conditions in a cement factory and continues to accurately measure density in a vertical pipe
Radiometric instruments are mounted outside of a pipe or tank so the system is immune to build-up, thermal shock, pressure surges or other extreme process conditions. And thanks to their robust design, these devices are able to withstand vibrations from the pipe or tank they are installed on.
These radiometric sensors are much easier to install than other technologies. Appliances of this type can be installed without interrupting an expensive process. Other technologies require the removal of sections of piping or other significant changes to the process itself.
The initial cost of radioactive isotopes is higher than other density measurement solutions. However, a radiometric solution can last 20 or 30 years with little or no maintenance.
Unlike other solutions, radiometric density sensors are a long-term investment in the entire process, ensuring safe and efficient operation for decades to come. A single radiometric density sensor provides significant savings in operating costs over the lifetime of the instrument.
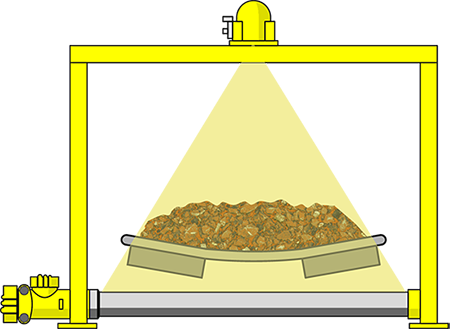
Radiometric mass flow measurement provides accurate charging in lime plants. Numerous conveyor belts varying in length from a few meters to one kilometer ensure that the rock under a wide variety of processing conditions is transported to the right place for further processing.
Along with devices, the accuracy of which is determined by the accuracy of measuring the intensity of the radiation flux, are important devices in which the task of accurately measuring the intensity of the radiation flux is not set at all. These are systems operating in relay mode, in which only the very fact of the presence or absence of radiation flow is important, as well as systems operating according to the phase or frequency principle.
In these cases, neither the presence of radiation nor its intensity, for example, the frequency or phase of alternation of states, which are characterized by different intensity of the radiation flux or different degree of interaction of this flux with a controlled environment, is registered. One of the most widespread applications of relay systems is position level control.
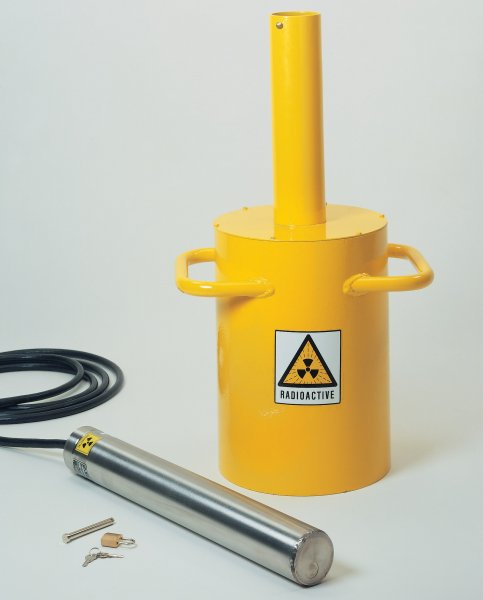
Radioactive manometer
Relay systems are also used for counting products on a conveyor, for monitoring the position of moving objects, non-contact measurement of rotational speed and in many other cases.
Ionization methods
If a source of alpha or beta radiation is placed in the ionization chamber, the chamber current will depend on the pressure of the gas at constant composition or on the composition at constant pressure. This phenomenon is used in the design of radioisotope manometers and gas analyzers for binary mixtures.
Using neutron fluxes
When passing through a controlled substance, interacting with its nuclei, neutrons lose some of their energy and slow down. By virtue of the law of conservation of momentum, neutrons transfer to the nucleus the more energy the closer the mass of the nucleus is to the mass of the neutron. Therefore, fast neutrons experience the strongest moderation when they collide with hydrogen nuclei. This is used, for example, to control the humidity of various media or the level of hydrogen-containing media.
The LB 350 humidity measuring system uses neutron measurement technology. The measurement is done either from the outside, through the walls of the silo, or through a strong immersion tube that is installed inside the silo. In this way, the measuring device itself is not subject to wear.
Measuring the extent of neutron absorption by various substances is used to determine the content of elements with a large neutron absorption cross section. A method is also used to control the composition of substances by spectral analysis of gamma radiation resulting from the capture of neutrons by substances. This technique is used, for example, for casing oil wells.
Some industries that use radiometric process measurement technology also use non-destructive X-ray inspection or radiographic inspection to verify the integrity of welds and vessels. These devices also radiate gamma energy from the source in a manner similar to radiometric meters.
See also:
Sensors and measuring devices for determining the composition and properties of substances