Rules for the use of electrical safety equipment when performing work in electrical installations
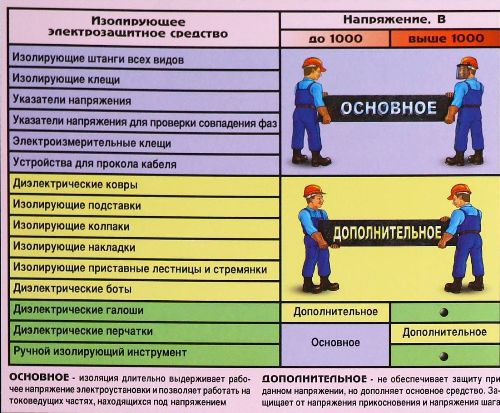
Electrical protective insulating means are designed to ensure the safety of service personnel when performing work in existing electrical installations. Depending on the purpose and type, an electrical protective device can provide both complete protection of a person from voltage and act as additional protection.
Electrical installations present a hazard in terms of the possibility of electric shock and the thermal effects of an electric arc. Every year, a number of accidents occur in electrical installations, most of which occur due to non-compliance by workers with labor protection requirements, in particular, incorrect use of protective equipment during work. Therefore, it is very important to know and be able to correctly use electrical safety equipment when working on electrical equipment.
Consider the basic rules for the use of various protective devices that are used in electrical installations.
General recommendations for all electrical safety equipment
Here are the basic rules for using electrical protective equipment that apply to all protective equipment.
If it is necessary to work with one or another means of protection, it is necessary first of all to check its suitability for use. First, attention is paid to the appearance of the insulating agent. It must be free of dirt, damage to the housing, including varnishing.
Every protective insulating device must be periodically tested — checking for suitability for use in electrical installations. Therefore, before applying a protective agent, it is necessary to check its expiration date — the date of the next test on the stamp of the established sample.
If the electrical protective equipment is dirty, damaged on the casing or if the period of periodic tests has expired, then such protective equipment should not be used, as it may result in electric shock to a person. Such a protective device must be taken out of service for troubleshooting, testing.
The electrical protective equipment that is planned to be used provides its insulating properties only if it is dry. This characteristic must be taken into account if it is necessary to work in open switchgear, avoiding the use of protective means that have become wet (rain, rain, frost, snow).If it is necessary to carry out work in conditions of penetration of moisture, electrical protective equipment specially designed for this purpose must be used.
In addition, protective seals must be kept clean. This is especially true for dielectric gloves, shoes and other protective equipment, which quickly become unusable if various aggressive liquids and lubricants get on their rubber surface.
Electrical protective devices above 1000 V with grip handles are structurally equipped with limiting rings. When carrying out work, it is necessary to take protective measures for the handles no further than this limiting ring. This is due to the fact that there is a permissible safe distance to live parts and the protective device is designed in such a way that its insulating part (the part that separates the working part from the handle) is long enough to provide protection against electric shock.
It should also be noted that each electrical protective device is designed to operate at a certain voltage. The voltage class is indicated on the body of the protective device, but this value may differ from the voltage value from which the protective device is really able to protect a person. Therefore, when testing a protective device, specify the voltage value up to which this device can be used.
Dielectric gloves
Dielectric gloves serve as the main means of protection against electric shock in electrical installations up to 1000 V and as additional protection in electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V.
Only absolutely dry dielectric gloves are allowed to be used. If the room where they are stored has a high level of humidity, then before working with gloves, they should be dried indoors at room temperature.
Before using gloves, in addition to an external examination, checking the date of the next test, it is necessary to check them for punctures. To do this, you need to start twisting them from the edge to the fingers. In this case, the glove inflates a little, and by pressing it is possible to find possible breakthroughs through which the air will escape.

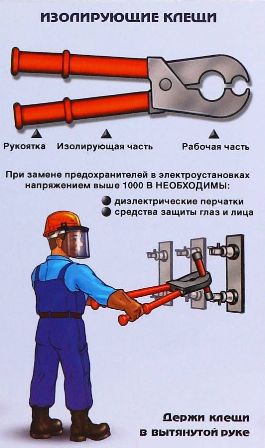
Insulation pliers
Insulation pliers are used to replace fuses. When replacing fuses with a voltage class higher than 1000 V, in addition to the insulating clamp, dielectric gloves and protective glasses or masks must be used as additional protection. In electrical installations up to 1000 V, you can only use pliers or dielectric gloves together with goggles or masks to replace fuses.
Replacing the fuses must be done with the load disconnected in advance. The exception is the fuses of those sections of the electrical network in which there are no switching devices through which the load can be removed.
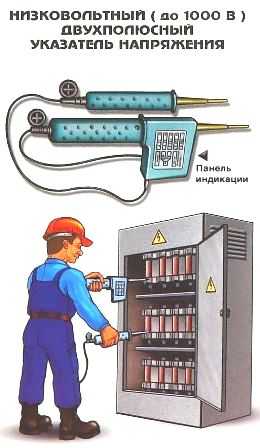
Voltage indicators
Voltage indicators are used in electrical installations to check the presence or absence of voltage on live parts.
If the voltage indicator is equipped with a voltage class switch, before using it, make sure that the selected mode is correct.
If it is necessary to check the absence of voltage on live parts, it is necessary to first check the operability of the voltage indicator used. The indicator is tested for operability on those live parts that are under operating voltage. Also, to test the operation of indicators for voltages above 1000 V, special indicator testing devices can be used.
Checking the presence of voltage or checking the operation of the indicator must be done carefully to avoid overlapping between phases or one of the phases of the equipment frame or other earthed metal structures of the switchgear.
When checking the absence of voltage, the peculiarities of the operation of individual types of voltage indicators should be taken into account. If the voltage indicator is of the pulse type, it works with a certain delay. Before using one or another type of voltage indicator, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the instructions for its operation, which indicate the characteristic features in relation to this or that voltage indicator.
When working on electrical installations above 1000 V, voltage alarms can be used as an additional safety measure.
Voltage alarms are attached to an employee's hard hat or on the wrist and are triggered when a person approaches live parts that are live. Voltage alarms should not be used as the primary means of verifying the absence of voltage. Only voltage indicators should be used for this purpose.
If the voltage signaling device does not have a built-in health check, then before starting work it must be checked in the prescribed manner in accordance with safety measures.
Insulating rods
Insulating rods, depending on the design, can be designed for: installing portable protective grounding, performing operations with switching devices, installing insulating pads, replacing fuses, performing measurements.
Before using this or that tape, you need to make sure that it can actually perform this or that operation. It is forbidden to perform the work with the barbell for which it is not intended.
Individual types of insulating rods must be properly earthed before use. Such rods cannot be used without grounding.
Insulating rods and voltage indicators for voltages above 1000 V may consist of several parts connected by a threaded connection. Before using such electrical protective equipment, it is necessary to check the reliability of their threaded connections to avoid accidents during work.

Dielectric shoes - boots, galoshes
Dielectric boots and galoshes are designed to protect a person from an electric shock to a person in the area of propagation of earth fault currents — from the so-called. Step voltage. Dielectric shoes also serve as a protective device when it is necessary to provide isolation of a person from the ground (the surface of the floor in the room), in this case the shoes act as an alternative to a rubber dielectric carpet and an insulating stand.
Before use, dielectric shoes must be carefully inspected for punctures, visible damage. When using dielectric shoes, you should move carefully, avoiding punctures, which is especially important if you have to move in open places. Damage to the surface of the dielectric shoes can lead to an electric shock, for example in the area of the step voltage.
Before using bot or galoshes, it is mandatory to check the stamp with the date of the next test, which should also indicate the voltage at which these protective means can isolate a person from the effects of current.
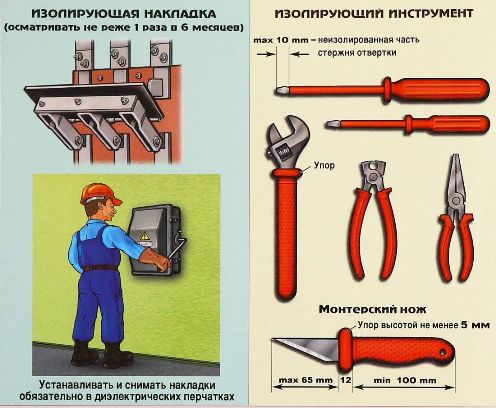
Isolation tool
Hand tools with insulating handles (screwdrivers, pliers, side cutters, pliers, wrenches, etc.) serve as the main electrical protective equipment when working in electrical installations up to 1000 V without removing the voltage.
In electrical installations above 1000 V, hand tools with insulating handles do not ensure safety when performing work, therefore, if it is necessary to perform work on high voltage equipment, it must be disconnected from all sides from which voltage can be applied, earthed, fuses installed and other measures taken to avoid a person coming within an unacceptable distance of the powered equipment.
When working in electrical installations up to 1000 V without voltage removal, except for tools with insulating handles, it is necessary to ensure isolation of a person from the ground (floor surface) using dielectric carpets, insulating supports or dielectric shoes.Depending on the nature of the work to be carried out, it is necessary to use additional protective maxi or glasses.
Before using a hand tool, it is necessary to inspect it for damage to the insulating part - bends, cracks, unevenness. Hand tools with insulating handles, like other protective equipment, are periodically tested in an electrical laboratory, therefore, before using them, it is also you need to check the time of the next test.
Portable protective earthing
To protect a person from accidentally applied voltage, as well as from the effect of induced voltage on some power lines, the equipment is grounded - the electrical connection of live parts to grounded elements of the equipment, directly to the grounding loop. Earthing is done using stationary earthing knives and portable protective earthing.
Stationary grounding knives are a structural element of disconnectors, separate types of cells, chambers with equipment. Portable grounding is a protective device that should be given special attention. This protective device is installed manually or uses built-in or removable rods to install grounding.
Grounding installation is carried out directly on live parts, which must first be disconnected and make sure that there is no voltage on them.
Many accidents happen because before installing the ground, the absence of voltage is not checked in all three phases.The fact is that the switching devices, through which a part of the equipment is turned off (creating a visible gap), can be turned off incompletely, that is, one of the phases can remain under voltage, which subsequently, when installing grounding, leads to an electric shock to a person .
As mentioned above, before checking the absence of voltage, it is necessary to check the operability of the voltage indicator.
If we are talking about the installation of portable grounding of equipment above 1000 V, then it is mandatory to use special rods, while also using dielectric gloves. To ensure safety, the installation of portable earths must be carried out by two people; removal can be done independently.
If this or that section of the electrical network is grounded at the same time with stationary grounding and portable, then it is necessary to turn on the stationary grounding first so that the installation of portable grounding is safe.
Before using portable grounding devices, it is necessary to check them for the integrity of the wires, clamps, fasteners of the wires to them. Minor, no more than 5%, core damage is allowed.
In order for portable grounding to fully perform protective functions, it is necessary to correctly select its type, cross-section in accordance with the voltage class and operating currents of the electrical installation in which the grounding is planned to be installed.
In addition to the protective equipment listed above, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment - coveralls, shoes, protective helmet.Depending on the local conditions and the nature of the work performed, it is necessary to use protective means against the impact of various negative factors.
For example, in an area with an increased level of electromagnetic field influence, it is necessary to use special sets of protective clothing. When performing operational switching, use a special protective suit and shield that provides protection against possible effects of electric arc.
In conclusion, it should be noted that, in addition to the knowledge and skills for the correct application of protective equipment when performing work, it is very important to perform the work correctly, deliberately, carefully, in order to avoid mistakes and create dangerous situations. Protective equipment cannot provide absolute protection to a person from possible dangerous situations.
Incorrectly selected switching device, incorrect operation and other errors can lead to accidents. Therefore, the issue of safety during work in electrical installations must be approached comprehensively, taking into account all possible nuances.

