Underground cable
 Laying a cable in the ground is used for the purpose of powering buildings, structures, providing street lighting, powering cottages, shift houses and in many other cases.
Laying a cable in the ground is used for the purpose of powering buildings, structures, providing street lighting, powering cottages, shift houses and in many other cases.
This power supply method is very reliable because the cable laid in the ground is protected from negative climatic factors such as wind, rain or snow, frost, etc. The cable is hidden underground and does not disturb the aesthetics of the familiar landscape.
Special power cables of several major brands are used for this purpose. Depending on the corrosiveness of the soil, its type and the operating conditions of the cable, one or another brand of power cable is generally chosen.
For example, wet and acidic soil is highly corrosive and in some cases the cable may be subjected to tensile stress and then require additional strength. Armored cables meet these requirements and do not need additional protection during installation.
Usually, an armored copper cable of the VBbShv brand (according to the updated GOST R 53769-2010 — VBShv) or its aluminum analogue AVBbShv is used for laying in the ground... Thanks to the armor of steel strips, the laying of this cable is carried out without additional protective pipes, since precisely the armor provides the cable with protection, both from mechanical influences and from rodents. It is also permissible to run this cable through the air if we are talking about special cable structures or for damp places. The steel armor of the cable must be grounded.

VBbShv and AVBbShv means the following:
-
A — aluminum wires;
-
B — insulation of wires from polyvinyl chloride plastic;
-
B — armor of two steel belts;
-
b — without a protective cushion imposed under the armor, which protects the layers under the armor from corrosion and mechanical damage;
-
Seam — PVC plastic hose;
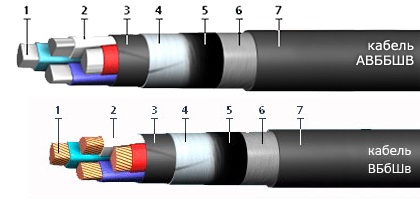
The cable includes the following elements:
1. Conductive wires (copper or A - aluminum), which can be from 1 to 5, and there is also a 3 + 1 option, when the fourth wire intended for grounding has a smaller cross-section.
The conductors, in turn, can be of 1 or 2 classes: single-core (cross-section from 2.5 to 625 sq. Mm) or multi-core (cross-section from 2.5 to 240 sq. Mm).
2. PVC insulation, providing color and digital (for cables with a cross-section of 70 sq. Mm and more) marking of the core: white or yellow, red or purple, blue or green, brown or black or yellow-green, numbers 0 , 1, 2, 3, 4.
3. Insulation of the belt from PVC strips.
4. Two steel or steel galvanized strips forming armor.
5. In cables with a cross-section of more than 6 square meters. mm bitumen is used.
6.A polyethylene terephthalate film is additionally used in cables with a cross-section of more than 6 square mm.
7. Protective PVC plastic hose.
The laying of the VBbShv cable is permissible even in soil chemically active in relation to metal; it can be installed near railway and tram tracks, which can be sources of stray currents.
The VBbShv cable can be laid in places with an increased risk of explosion, it is resistant to temperature extremes, and the range of permissible temperatures is from minus 50 to plus 50 degrees Celsius, which makes it possible to use the cable in any climatic zone. The cable is installed in an inclined and horizontal position to eliminate tension loads and thus save steel reinforcing bars. When passing the cable from the reel, sharp bends are not allowed.

Another popular brand of underground cable is paper insulated cable… These are the following types: SB, SBL, SKL, which can also be either aluminum conductors or copper. In addition to the armor, these cables have a metal sheath to protect the paper insulation from the damaging effects of moisture. Sector wires save space and reduce cable weight.
The main purpose of this type of cables is the transmission of electrical energy at a voltage of up to 35,000 volts, with the possibility of laying not only in the ground, but also in the air and even in the water environment, if the condition of stationarity is met. SB, SBl and SKl have the following decoding:
C — lead sheath;
-
B — the armor is made of two steel belts;
-
K — the armor is made of galvanized steel round wires;
-
l — under the bumper there is a cushion containing a layer of plastic strips.
Consider the structural elements of these cables (SB, SBL):
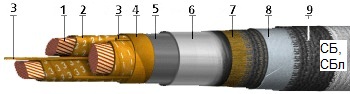
1. Single-core (25-50 sq. Mm) or multi-core (25-800 sq. Mm) copper conductor.
2. Paper insulation impregnated with a non-flowing or viscous impregnating mixture; There are colored and digital markings on the wires.
3. Filling paper harnesses.
4. Belt-impregnated paper insulation.
5. For cables with a voltage of 6000 volts and more, a screen made of electrically conductive paper is provided.
6. Lead sheath.
7. Pillow made of crepe paper and bitumen.
8. Steel strip armor.
9. Fibrous materials (glass yarns) form the outer cover.
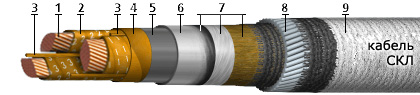
The SKl cable features an armor made of round galvanized steel wires.
SB cables can also be used in direct current networks where the voltage value is 2.5 times higher than the nominal value of the alternating current voltage. They can be buried in low corrosive soil.
SBL cables, on the other hand, with the same voltage characteristics, allow a medium level of soil corrosivity in the presence of stray currents or a high level of soil corrosion in the absence of stray currents. The SKl cable is mainly intended for underwater installation, but it is also applicable where the cable can be tensioned.
You can not lay such a cable with a difference in levels of more than 15 meters, because the impregnation of paper insulation can drain, it is better in such cases to use a cable with polyethylene insulation or containing a special impregnation based on ceresin, these are the following brands: CSP, CSB, CSKL, etc...

For more severe conditions, such as: laying at low temperatures without the need for heating, use without restrictions on routes, laying outdoors - suitable XLPE insulated cables… They are more expensive than other brands, but they are reliable, efficient and economical, as they require minimal maintenance, installation and reconstruction costs. These are brands: PvBbShp, PvP, PvPg.
Abbreviations have the following meanings:
-
Pv — cross-linked polyethylene as core insulation;
-
B — the armor is made of two steel belts;
-
b — no pillow;
-
Shp — polyethylene hose as a protective cover;
-
P — polyethylene sheath
-
d — sealing with waterproof strips.
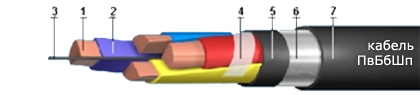
PvBbShp cable consists of the following parts:
1. Copper wire with a cross-section from 4 to 50 sq. mm for solid wires and from 16 to 240 sq. mm for stranded wires. The number of cores can be: 3 + 1, 4 or 5.
2. XLPE for insulation, color coded.
3. Core.
4. For cables with a cross-section of 50 sq. mm, a fixing coil is used.
5. Belt insulation.
6. Two galvanized steel strips form the armor.
7. Protective polyethylene hose.
The PvBbShp cable can even be used in water bodies. Both inclined and vertical position of the cable route is permissible. It is possible to heat up to 130 degrees Celsius for 6 hours. The only important requirement during operation is to avoid strong stretching. We will apply this cable in corrosive soil conditions of any level, including the presence of stray currents and high humidity.
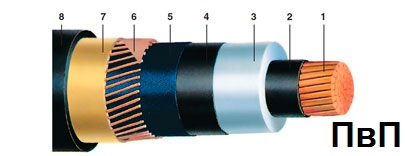
The PvP cable is arranged as follows:
1. In the center there is a round stranded copper wire with a cross section of 35 to 800 sq. mm
2.The core is enclosed in a screen made of extruded semiconducting cross-linked polyethylene.
3. Additional insulation is cross-linked polyethylene.
4. A screen made of extruded semi-conductive cross-linked polyethylene is laid along the insulation.
5. Separating layer.
6. Copper wires fastened with copper tape form a screen, and its cross-section is different: not less than 16 sq. Mm, if the wires have a cross-section of 35 to 120 sq. Mm. mm; not less than 25 sq. mm if the wires have a cross section of 150 to 300 sq. mm; not less than 35 sq. mm if the wires have a cross-section of 400 sq. mm and more;
7. Separating layer.
8. Polyethylene wrap.
PvP cable is carried out in trenches under any conditions of soil corrosion activity; laying in the open atmosphere and in collectors is permissible. Compliance with fire safety measures is required. There are no limits on the difference in levels.
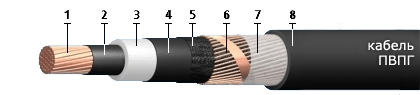
A PvPg cable has the following components:
1. In the center there is a sealed round copper wire with a cross section of 50 to 800 sq. mm
2. The core is enclosed in a screen made of extruded semiconducting cross-linked polyethylene.
3. Additional insulation is cross-linked polyethylene.
4. A screen made of extruded semi-conductive cross-linked polyethylene is laid along the insulation.
5. The separation layer is made of electrically conductive tape, which has the function of blocking water.
6. Copper wires fastened with copper tape form a screen, and its cross-section is different: at least 16 square meters. mm, if the wires have a cross section of 35 to 120 sq. mm; not less than 25 sq. mm if the wires have a cross-section of 150 to 300 sq. mm; not less than 35 sq.mm, if the wires have a cross-section of 400 sq. mm and more;
7. Separating layer.
8. Polyethylene wrap.
The high level of sealing allows the laying of PvPg cable in soils characterized by high humidity, as well as in periodically flooded structures. If the possibility of mechanical damage is excluded, the laying of cables is allowed even in navigable waters. Especially the PvPg cable laid in trenches, on routes of different levels, regardless of soil corrosivity. When laying in air, fire prevention measures are mandatory.
Also read on this topic: How power cords work
