Wires and cables with rubber insulation: types, advantages and disadvantages, materials, production technology
Rubber-insulated wires and cables are used to connect pantographs and distribute electricity in secondary electric current networks, and are also widely used in industry, agriculture, transportation, construction and daily life.
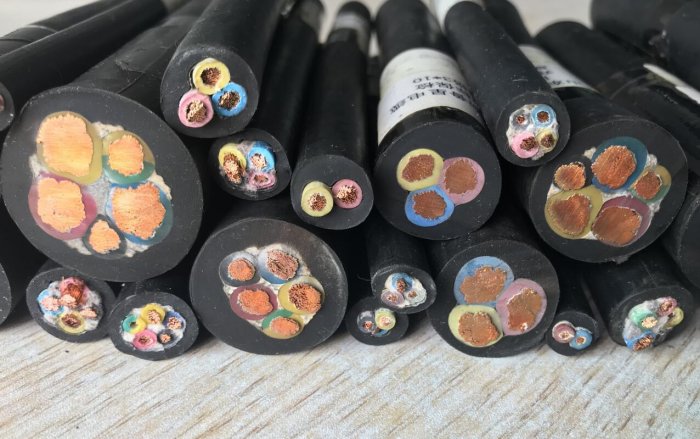
Types of cables and wires with rubber insulation
Cables, wires and cables with rubber insulation can be divided into the following groups:
- installation cables, wires and cables;
- power cables;
- control cables;
- flexible cables and wires for hoses;
- marine cables and wires;
- body cables;
- wires for electric rolling stock;
- aircraft, automobile and tractor wires.
The use of rubber or plastic insulation is caused not so much by the desire to obtain a flexible cable, as it is done to facilitate and simplify the cable terminals.
The use of a lead sheath does not make it possible to use the increased flexibility of the insulation layer of the cable, and therefore in cases where a cable with increased flexibility is needed, not lead, but hose jackets made of vulcanized rubber or plastic are used.
The high average dielectric strength of rubber insulation in most cases cannot be used due to the presence of weak places in the insulation layer, which necessitates an increase in the thickness of the insulation layer compared to, for example, impregnated paper insulation and leads to an excessive consumption of protective materials coatings.to increase the diameter of the cable.
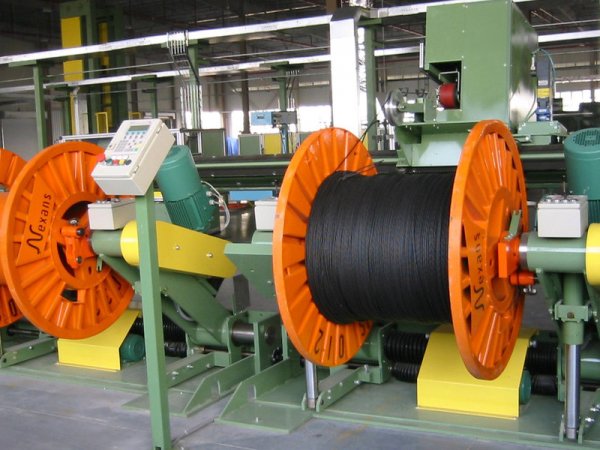
The initial stage of production is the stretching of multi-core wires for wires, cables and cords from tinned and untinned copper wires.
Technology for the production of wires and cables with rubber insulation
The main process operations include the production of rubber and plastic and their application to a core or wire. The production of rubber includes plasticizing rubber and the introduction of fillers (chalk, talc), softeners, improvers and vulcanizing agents.
The rubber compound is applied to the core by hot pressing on worm presses or cold pressing on special profiled rollers. The thickness of the rubber insulation depends on the size of the cross-section of the wire and the rated voltage of the wire or cable, while the thickness of the hose jacket is determined by the diameter of the cable.
The sheath thickness can vary from 1 to 8 mm for rubber hoses and from 2 to 4 mm for vinyl PVC jackets.
The rubber insulation, after applying it to the core by a cold or hot method, is vulcanized to give the insulation layer the necessary physical properties: mechanical strength and elasticity. Plastic wraps do not require vulcanization.
On top of the layer of rubber insulation of the wires, a braid of cotton yarn is applied, which can be impregnated with bitumen or another composition or covered with a layer of nitro-lacquer (aircraft and automobile wires).
The rest of the technological operations, such as twisting into a cable and placing protective covers, are carried out in the same way as for the others. cable products.
Advantages and disadvantages of rubber insulation
The high electrical and mechanical characteristics of rubber insulation made it possible to realize a number of wire and cable structures operating under extremely difficult working conditions (cutting, logging, excavators, etc.).
A wide range of resistivity values (from 1013 to 1017 omcm) and considerable variation dielectric constant depending on the composition of the rubber and the technology of its production, provide the possibility of production insulation of wires and cables of various types.
Along with the positive qualities of rubber insulation, there are also negative ones, the most characteristic of which are the following:
- the presence of air bubbles and films in the insulation layer;
- instability of vulcanized rubber against ozone;
- the influence of mechanical forces and stresses on the dielectric strength of the insulation;
- reduction of the mechanical and electrical characteristics of rubber when heated;
- heterogeneity of the macrostructure (presence of grains of fillers, impurities, etc.);
- noticeable moisture permeability and moisture absorption;
- low resistance to the effects of petroleum products and mineral oils;
- loss of mechanical properties depending on the duration of heating in the presence of atmospheric oxygen (thermal aging).
Rubber insulating materials and technological characteristics
Vulcanized rubber over natural and synthetic rubber is used to manufacture various types of cable products and thus plays a significant role in cable manufacturing.
The greatest difficulties are encountered when using rubber insulation for the production of high-voltage AC wires and cables, for example, for 6 and 10 kV power cables that supply electricity to moving excavators, dredges, peat machines, electric tractors, etc.
The insufficient ozone resistance of the rubber leads to rapid destruction and a sharp reduction in the service life of such a cable. In these cases, a special ozone-resistant rubber is used, which is less susceptible to the action of ozone, and the shell is varnished as a protective coating.
Oil- and gasoline-resistant rubber recipes have been developed that enable the production of rubber insulation for cable bodies operating in oil wells at high temperatures under particularly severe conditions. High-voltage ignition wires operate at high electric field strength and in a wide temperature range from -50 to + 150 ° C.
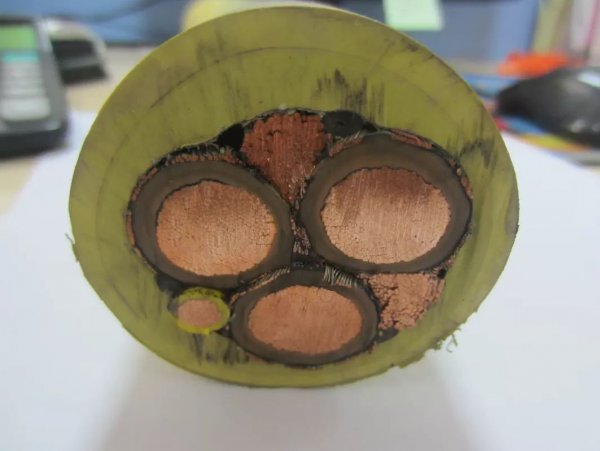
The composition of the rubber insulation includes the following basic materials:
- Rubber — natural (NK) or synthetic (SK);
- Fillers — chalk, kaolin, talc, etc.
- Emollients - stearic acid, paraffin, petroleum jelly, bitumen, etc.
- Reinforcements improve the mechanical properties of rubber compounds (carbon black).

The amount of rubber in rubber compounds used in the production of wires and cables varies (by weight) in the range from 25 to 60%, and the total amount of all fillers - from 70 to 35% / About 2% fall on softeners and about 1 .5% for vulcanizers (sulfur).
Currently, rubber is widely used to insulate wires and cables, the vulcanization of which is carried out due to the sulfur released during vulcanization during the decomposition of certain sulfur compounds, for example, tetramethylthiuram disulfide (thiuram). Such "sulphur-free" tires have increased heat resistance and therefore a long service life. The mechanical properties of this rubber are slightly lower than those of sulfur vulcanized rubber.
It should be especially noted that sulfur-free or, as they are called, heat-resistant rubbers do not have a destructive effect on the copper conductors of a wire or cable, and therefore there is no need for tinning of the wire and conductors that go into the production of rubber-insulated wires and cables.
Along with rubbers, as mentioned earlier, synthetic thermoplastic materials, also called elastomers, are widely used.
Among them, first of all, it should be included a very common plastic mixture made of PVC resin, which is widely used in the cable industry, mainly for the production of low-voltage wires and cable protective coatings (hoses).
PVC resin is obtained by polymerization of vinyl chloride. The elastic is obtained by mixing finely divided resin with plasticizers, stabilizer and filler.
White carbon black, kaolin are most often used as fillers, and trichrysyl phosphate, dibutide phthalate, etc. are used as plasticizers.In addition to PVC, copolymers of vinyl chloride, for example with vinyl acetate, are also used.
The main disadvantages of PVC insulation:
- insufficient electrical properties (insufficient insulation resistance and a large value of the tangent of the dielectric loss angle), which is explained by the presence of plasticizers, as well as the ease of elimination of the Cl ion in PVC resin;
- insufficient frost resistance.
With an appropriate choice of plasticizers, satisfactory electrical characteristics can be achieved.
The positive properties of PVC include:
- high resistance to heat aging;
- resistance against the effects of oils and any lubricants;
- high wear resistance;
- water resistance;
- resistance to a number of solvents, acids and bases, except 93% sulfuric acid and glacial acetic acid; benzene is adversely affected by solvents, which reduces the tensile strength of the plastic compound exposed to the action of benzene for 12 days by more than 7 times, and the specific volume resistance by 2-2.5 times;
- non-flammability.
Polyethylene is widely used for the production of high-quality insulation of wires and cables... It is a relatively soft material (when heated to 70 ° C, its density uniformly decreases), which has good frost resistance and ozone resistance, and is widely used for insulation as energy (XLPE insulated cables) and high frequency wires and cables.
The quality of the plastic compound is determined not only by the properties of the basic polymer, but to a large extent by the correct selection and quality of fillers and plasticizers.The choice of fillers and plasticizers is a major challenge for manufacturers who want to obtain the required properties.
All the most difficult tasks in technical and economic terms, for example, obtaining ozone-resistant rubber, etc., are solved by choosing the basic plastic or synthetic material with the necessary properties.
With the current state of chemistry, the appearance of a number of synthetic materials can be expected in the near future, the use of which will make it possible to completely solve the still unsolved problems with the insulation of wires and cables.