Voltage indicators for phase-in installations above 1000 V
Stepwise installations above 1000 V can be carried out voltage indicatorsspecially designed for this purpose. The indicator set, as a rule, includes the actual voltage indicator, a tube with an additional resistor and a wire connecting them.
The figure shows the appearance and the wiring diagram of the indicator type UVNF for stepwise installation up to 10 kV.
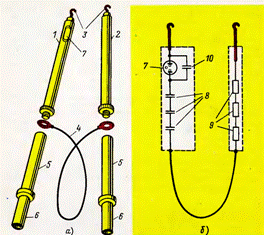
Phasing voltage indicating device
In the housing (tube of insulating material) of the voltage indicator 1, a signal lamp 7 of the TNUV type is installed, maneuverable capacitor 10 and three additional polystyrene capacitors 8 of the POV-15 type for an operating voltage of 1 kV each. Up to ten heat-resistant resistors 9 of the MLT-2 type are built into the tube 2, the total resistance of which is 8-10 MΩ. Both pipes are connected in series by wire 4, type PVL-1, withstanding the test voltage up to 20. kV. Metal probes 3 are screwed to the upper parts of the pipes connected to the electric circuit, to the lower ones — insulating rods 5 with grip handle 6.
Step-by-step procedure in installations above 1000 V
For step-by-step phase voltage is applied to the tripped device (switch, disconnector) from each of its sides. The probes of the indicator are brought to the clamps belonging to one pole of the disconnected apparatus and observe the light of the signal lamp. In this case, two cases of turning on the indicator are possible: the reverse turn-on includes out-of-phase voltage, the indicator in this case should burn brightly, signaling a phase mismatch, a coherent turn-on includes the voltage of the same phase. In this case, the indicator should not light up. The absence of luminescence of the lamp indicates the same name of the phase voltages applied to the pole terminals and the possibility of connecting these phases to each other by turning on the switching device.
Let's note some of the requirements for voltage indicators designed for phasing. The rules for the use and testing of protective equipment used in electrical installations normalize the so-called Threshold for lighting the indicator warning lamp when it is on and consents.
By ignition threshold they understand the minimum voltage applied to the indicator probes, at which a visible constant glow of the signal lamp appears.
Depending on the switching circuit of the indicator, the ignition threshold is taken as follows:
-
phase voltage 6 kV — ignition voltage with opposite switching not higher than 1500 V, ignition voltage with matched switching not lower than 7000 V
-
phase voltage 10 kV — ignition voltage with opposite switching not higher than 2750 V, ignition voltage with matched switching not lower than 12700 V
Note that the seemingly paradoxical glow of the lamp when both probes of the pointer are connected to the same phase is actually explained by the influence of the electrical capacitances of different elements of the pointer on grounded structures. Passing current through these containers causes the lamp to glow.
In order to avoid an error during phasing, it is assumed that the ignition voltage of the indicator when turned on coherently is higher than the working voltage at which phasing takes place. This leads to the fact that when connected to the working voltage of the electrical installation, the indicator lamp will not light up. And vice versa, with the opposite connection, when it is out-of-phase voltage, the indicator lamp should light up when the voltage is significantly less than the nominal one.
The reverse ignition threshold characterizes the sensitivity of the indicator. The lower the lamp ignition voltage, the more sensitive the pointer. Indicators with increased sensitivity are not suitable for phases, however, because the voltage difference between the same phases of two phase parts of the installation can reach 8 — 10% of the operating voltage. Therefore, the reverse ignition voltage should be slightly more than the specified value. In practice, it is assumed equal to 1000-1500 V.
In obtaining the required ignition voltages of the indicator lamp with matched and opposite switching, a well-known role is played by the shunting of the capacitance lamp.The introduction of a 200 pF shunt capacitor into the circuit made it possible to exclude the effect of the partial capacitances of the individual elements of the indicator and to ensure the required value and stability of the lamp ignition thresholds.
When developing a UVNF pointer structure, the UVN-80 type voltage indicator series, after having assembled a total length of 715 mm and a length of the working part of 350 mm. Experience shows that the size of the working part of such a pointer when used for phasing overhead lines 6 — 10 kV directly on external disconnectors does not provide safe working conditions.
The length of the working part of the UVN -80 voltage indicator is comparable to the height of the conductive parts above the ground frame - the base of the disconnector, which can lead to phase-to-ground overlap when the pipes approach the steel structure. Therefore, for the phased use of pole-mounted disconnectors, a pointer has been developed with the length of the working part and the tube with an additional resistor up to 700 mm with a total pointer length of 1400 mm.

Phasing at 35 and 110 kV
It is used for phasing at voltages 35 and 110 kV voltage indicator type UVNF-35-110... Its design is similar to that of the UVNF indicator.
A distinctive feature of the circuit is POV-15 polystyrene capacitors, which have replaced resistors. The circuit parameters were chosen so that the pointer becomes insensitive to the phase voltage to ground when connected. This upset by the action of the operating voltage provided a clear selectivity of the indicator to the voltage of the same and opposite phases.
The indicator phasing kit includes one common working tube and two working tubes (each working tube is used in phasing at its own voltage — 35 or 110 kV). The insulation of the connecting wire is reinforced. The insulating rods are intended for operation under voltage in installations up to 110 kV.
Also, for the phasing of 35-110 kV lines, an indicator is used, which uses the principle of comparing the voltage drop in two identical voltage dividers collected by resistors. Compensation is applied to the capacitance of the measuring circuit to the mass.
It consists of two fiberglass tubes, inside which are placed resistors of the KEV-100 type. Two sets of resistors are used: one for phasing in 110 kV installations, the other for 35 kV installations. The resistance of the resistors of each tube from the first set is 400 MΩ and an additional resistor of 150 kΩ, from the second - 200 MΩ and an additional 150 kΩ. The voltage sampling points of the resistors are interconnected by a shielded wire, in the section of which a diode rectifier and a microammeter are included. The measuring part of the circuit is shielded. The screen and ends of the additional resistors are grounded during phases.
