Protective conductors in electrical installations (PE conductors)
The main task that must be solved when creating any electrical installation is to ensure its electrical safety. Normative documents provide for a set of measures to protect people and animals from electric shock, which must be provided for when designing an electrical installation and its installation.
 In normative documentation, a conductor means a conductive part (a part capable of conducting an electric current) designed to conduct an electric current of a certain value. In the electrical installations of buildings, line, neutral, protective and some other wires are used.
In normative documentation, a conductor means a conductive part (a part capable of conducting an electric current) designed to conduct an electric current of a certain value. In the electrical installations of buildings, line, neutral, protective and some other wires are used.
Protective conductors (PE) used in electrical installations to protect people and animals from electric shock. As a rule, the protective conductors are electrically connected to the grounding device and therefore, during normal operation, the electrical installations of the building are at the potential of the local grounding.
Exposed conductive parts are connected to protective conductors Class I electrical equipmentwith which a person has many electrical contacts.
Therefore, when installing the electrical installation of a building, it is very important not to confuse protective conductors with line conductors, in order to exclude a situation where a person who touches the body, for example, of a refrigerator, to which a phase conductor is incorrectly connected, will be struck with current. The unique color identification of the protective wires is designed to drastically reduce such errors.
In the TN-C, TN-S, TN-C-S systems, the protective conductor is connected to the grounded part under voltage, for example, to the grounded neutral of the transformer. It is called the neutral protective conductor.
In the electrical installations of buildings, they are also used combined zero protective and working conductors (PEN conductors), which combine the functions of both protective zero and neutral (zero working) conductors. By design, protective conductors also include grounding conductors and protective equipotential bonding conductors.
TN-S grounding system:
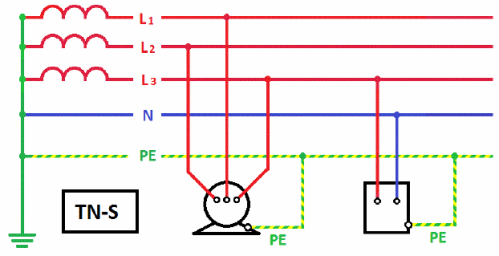 A neutral protective conductor (PE-conductor in the TN-S system) is a conductor that connects the neutralized parts (exposed conductive parts) to a solidly grounded neutral point of a three-phase current supply or to a grounded terminal of a single-phase current supply or to a grounded medium point of supply in direct current networks. The protective neutral wire must be different from the working neutral and PEN wires.
A neutral protective conductor (PE-conductor in the TN-S system) is a conductor that connects the neutralized parts (exposed conductive parts) to a solidly grounded neutral point of a three-phase current supply or to a grounded terminal of a single-phase current supply or to a grounded medium point of supply in direct current networks. The protective neutral wire must be different from the working neutral and PEN wires.
Zero working conductor (N-conductor in the TN-S system) - a conductor in electrical installations with a voltage of up to 1 kV, designed to supply electrical consumers connected to the grounded neutral point of a generator or transformer in three-phase current networks, with a dead output of a single-phase current source, with a dead earth source in the current of direct current networks.
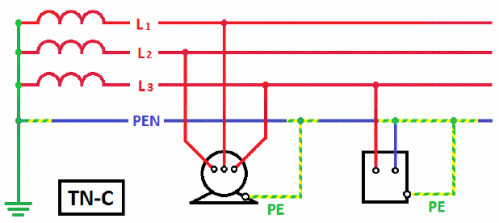
Combined zero protective and neutral working conductor (PEN — conductor in the TN — C system) is a conductor in electrical installations with a voltage of up to 1 kV, combining the functions of a neutral protective and zero working conductor.
Grounding system TN-C:
Grounding conductors are an integral part of the grounding device of the building's electrical installation. They provide the electrical connection of the grounding switch to the main grounding bus, to which, in turn, other protective conductors of the building's electrical installation are connected.
Protective grounding — an intentional electrical connection to earth or its equivalent of non-conductive metal parts that can be energized due to a short-circuit event and for other reasons (inductive influence of adjacent current-carrying parts, removal of potential, lightning discharge, etc.) . The land equivalent can be river or sea water, coal in quarry beds, etc.
The purpose of protective grounding is to eliminate the danger of electric shock in case of contact with the body of the electrical installation and other non-conductive metal parts under voltage due to a short circuit of the housing and for other reasons.
Equipotential bonding conductors are used in electrical installations of buildings and in buildings to perform equipotential bonding (connection between open and conductive parts of third parties to ensure equipotentiality), which is usually intended to protect people and animals from electric current blow. Therefore, in most cases, these conductors are protective equipotential bonding conductors.
In accordance with the requirements of GOST R 50462, yellow and green can be used in combination with yellow-green, which is used exclusively to indicate protective (zero protective) conductors (PE). The use of yellow or green wires for wire identification is not allowed if there is a danger of mixing these colors with a combination of yellow and green colors.
Based on the requirements set forth in GOST R 50462, additions were made to the PUE establishing the following color coding for wires for electrical wiring:
-
a two-color combination of yellow-green color should indicate protective and neutral protective conductors;
-
blue color should be used to identify neutral working conductors;
-
for marking PEN wires, a two-color combination of yellow-green color should be used along the entire length of the wire with blue markings on its ends, which are placed during installation.
In accordance with the requirements of GOST R IEC 245-1, GOST R IEC 60227-1 and GOST R IEC 60173, the combination of yellow and green colors should only be used to indicate the insulated core of the cable, which is intended to be used as protective conductor. The combination of yellow and green should not be used to identify other wires in the cable.
