Electric Current Energy and Power — Screen Training Tape Factory and Visual Aids
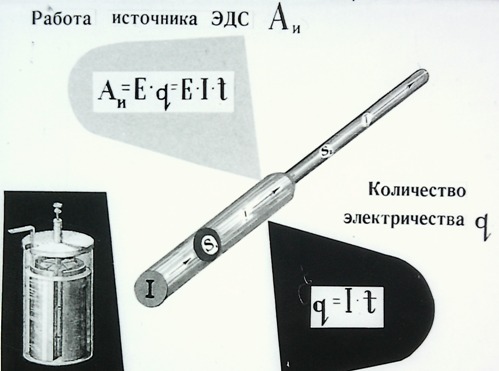
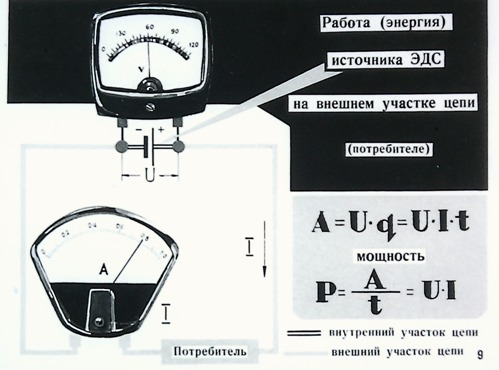
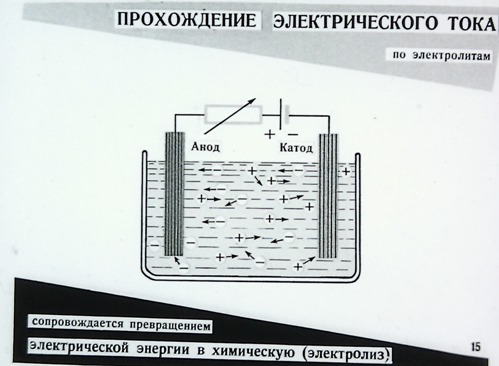
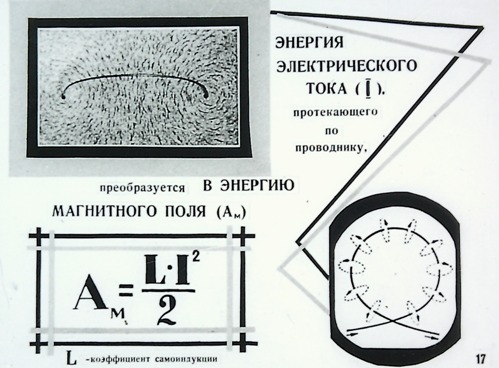
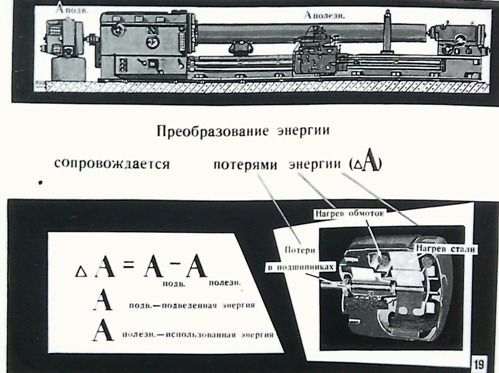
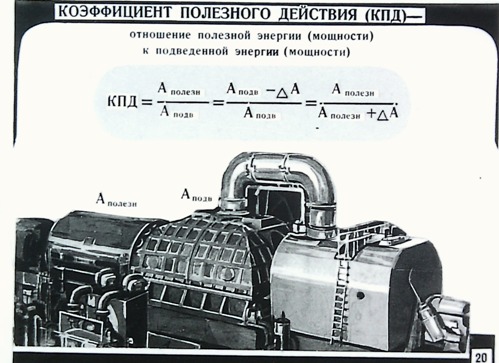
The work done by the electric field when a positive charge Q moves along an unbranched section of an electric circuit that does not contain sources of electrical energy is equal to the product of this charge by the voltage U between the ends of the section: A = QU. With uniform movement of the charge during time t, i.e. at direct current, charge Q = It and work A = UIt. In order to evaluate the energy conditions, it is important to know how fast the work is done, that is, to determine the power P = UI.
The main SI unit of work is the joule (J), power is the watt (W). The practical unit for measuring electrical energy is the kilowatt-hour (kWh), i.e. work done at a constant power of 1 kW for 1 hour. Since 1 W • s = 1 J, then 1 kW • h = 3,600,000 J.
Filmstrip in good quality in large format:

The Energy and Power of Electric Current Screen Tutorial Factory Filmstrip: