Placement of lighting fixtures in a room when calculating lighting
 When calculating the electric lighting of the premises, after the selection of lighting fixtures, it is necessary to make the correct placement of the lighting fixtures. The height of the lighting unit is characterized by the design height h (see Fig. 1), i.e. the vertical distance between the level of the work surface and the light source. The design height, as shown in the figure, depends on the height of the overhang hc and the height of the working surface hp.
When calculating the electric lighting of the premises, after the selection of lighting fixtures, it is necessary to make the correct placement of the lighting fixtures. The height of the lighting unit is characterized by the design height h (see Fig. 1), i.e. the vertical distance between the level of the work surface and the light source. The design height, as shown in the figure, depends on the height of the overhang hc and the height of the working surface hp.
In the horizontal plane (on the floor plan), the position of the lighting fixtures is characterized by the size of the side of the «field» (Fig. 2). "Field" is a flat figure on a plan formed by straight lines connecting nearby lamps. As a rule, lamps with incandescent lamps and high-pressure gas discharge lamps (DRL, DRI, DNaT, etc.) are placed in the corners of a square or rectangle, and lamps with fluorescent lamps are placed in rows.
The side of the field or the distance between the rows is L, the distance from the wall to the nearest row of lighting fixtures is l.
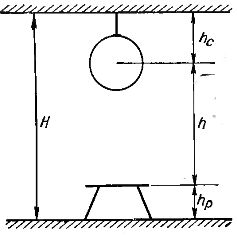
Rice. 1.Values characterizing the position of the lighting fixture in the vertical plane: H — the height of the room; hc — overhang height; hp is the height of the working surface; h — calculated height.
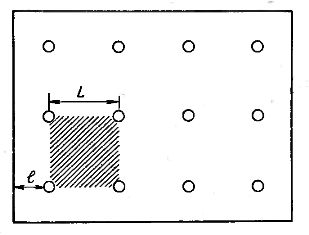
Rice. 2... Values characterizing the position of the lighting fixtures on the plan.
The L and h values determine the calculated power of the light source. It is recommended to take the most advantageous value of L: h = λ... Reference books give meaning to λc (the most advantageous lighting ratio) and λd (the most energetically favorable ratio).
The value λc should be used if the power of the light source is known or indicated (for example, when using fluorescent lamps, together with the choice of the type of light fixture, the power of the lamps is also determined). When the power of the source is unknown and it is possible to choose it close to the calculated one, then the value λe is taken into account.
Thus, having a floor plan with an indication of the height H, a description of the environmental conditions in it and the nature of the work, you can choose the type of light fixture, determine from the reference (for example, GM Knorring. Electrical Lighting Design Reference) the λ value for this luminaire and calculate h.
Then from these data determine L:
L = λc NS h or L = λNSNS h
For fluorescent lamps, this will be the most advantageous inter-row distance, for point light sources (DRL lamps, DRI lamps, incandescent lamps, etc.) — the most advantageous distance between the luminaires.
Then you need to take the distance from the wall to the nearest row of lamps L... There are recommendations that should be taken l = 1/2 L — for corridors and utility rooms, l = 1/3 L — for production and office rooms, l = 0 — for those rooms where there are workplaces next to the wall. Choosing the value l, you can determine the number of rows of lighting fixtures (t) in the room:
n = ((B-2l) / l) +1,
where B is the width of the room.
If point light sources are used for lighting, the number of lamps in the row can also be determined:
m = (((A-2l) / l) +1,
where A is the length of the room.
The total number of lighting fixtures in the room will be equal to N =nm.
Thus, when calculating fluorescent lighting, the number of rows becomes known and it is necessary to determine the number of lamps in each row, and for lighting with incandescent lamps and high-pressure gas discharge lamps, the number of lamps and their location is known and it is necessary to determine the power of the lamp to provide the standardized illumination E.

