Metal halide lamps — types, characteristics, applications, advantages
Metal Halide Lamp (MGL) refers to high pressure gas discharge sources. During the operation of the lamp, the arc discharge appears in mercury vapor in an inert argon atmosphere, while the spectrum is determined by special emitting additives — halides of some metals.

Halides such as scandium and sodium iodides help the discharge exist and do not react with the quartz glass of the bulb. While the lamp is cold, the halides condense in the form of a thin film on the walls of the discharge tube (burner), but as the temperature rises, the halides evaporate, mix with the mercury vapor in the discharge area and decompose into ions. As a result, excited ionized atoms emits visible light.
The burner is made of quartz glass or ceramic, and the outer protective bulb is made of borosilicate glass (except for the protective mechanical function, the bulb cuts the ultraviolet light from the spectrum).
In a number of industrial MGL types, the outer flask is absent; in this case, zoneless quartz glass is used to manufacture the base. It prevents increased ozone formation and reduces the risk of mercury resonance (185 nm) in the lamp.
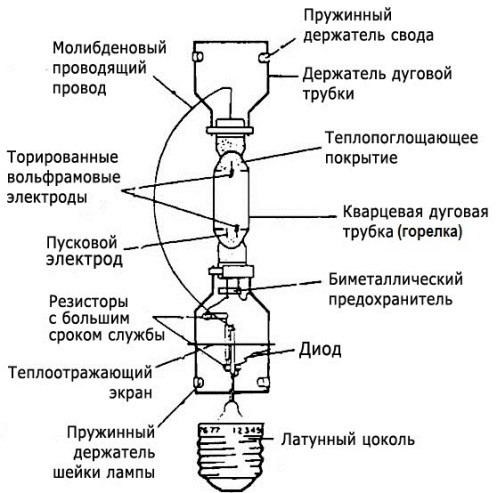
The principle of operation of a metal halide lamp in 1911 was described and proposed by the American electrical engineer Charles Steinmetz. The lamp starts up using high voltage pulses from ballast, which initially provides the ignition of the arc and then keeps the lamp running.
The starting device can be the choke itself or a high voltage auxiliary transformer. Then, when the discharge is ignited, the nominal voltage is maintained across the electrodes and the lamp emits visible light.
Types of metal halide lamps
Today, MGL lamps are produced in a wide range of wattages. For outdoor lighting, lamps with a power of 70, 150, 250, 400, 1000, 2000 watts, with one or two caps, with pins or soffit caps are used. They are designated as SE or DE-single and double.
Since the force of gravity acts on the plasma of the arc, the working position of the lamp must be strictly defined. So, metal halide lamps are horizontal, vertical and universal. Markings respectively: BH, BUD, U — base horizontal, base up / down and universal. If the lamp is not used in the correct working position, the life of the lamp will be shorter and the performance will be worse.
According to the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), metal halide lamps are labeled starting with the letter "M" followed by a numerical code indicating the electrical characteristics of the lamp and the type of ballast.The numbers are followed by two letters indicating the size and shape of the flask and its coating. In addition, each manufacturer in its own way indicates the power of the lamp and the color of its glow. European markings differ slightly from ANSI.

The bulb of a metal halide lamp is identified by letters indicating its shape and numbers indicating the maximum diameter of the bulb. Letters BT (Bulbous Tubular), E or ED (Ellipsoidal) — ellipsoidal, ET (Ellipsoidal Tubular) — ellipsoidal tubular, PAR (Parabolic) — parabolic, R (Reflector) — reflex, T (Tubular) — tubular .. .
For example, the lamp «Lisma DRI 250-7» is marked with respect to the bulb E90 — ellipsoidal shape, diameter about 90 mm. Socket type E40, power 250 watts. As you can see, the notation here is different. In general, the range of metal halide lamps is very wide.
Characteristics of metal halide lamps
The light color of the metal halide lamp and the color temperature are mainly related to the type of halogen used. Sodium compounds give a yellow tint, thallium - green, indium - blue. Initially, metal halide lamps were used wherever close to natural light, white, without blue impurities, was required.
It is possible to obtain pure daylight from metal halide lamps with a color rendering index above 90. In principle, any color temperature in the range of 2500 to 20,000 K is achievable.
Special types of MGL are used in greenhouses and greenhouses for plants, in aquariums for animals, where a special spectrum is required.At the same time, when choosing a lamp, it is important to remember that the color characteristics in reality will initially differ from those indicated in the specification, since the indicated characteristics refer to a lamp that has already worked for 100 hours, i.e. in the beginning they will be a little different.
The biggest discrepancy in characteristics is observed for metal halide lamps with preheating, in them the difference in color temperature reaches 300 K. For lamps with pulse start, the discrepancy is less - from 100 to 200 K.
A long-term deviation of the supply voltage from the nominal can lead to a change in the color of the light and the luminous flux. Sharp fluctuations in the mains voltage of more than +/- 10% can cause the lamps to turn off.
If the mains supply jumps, the color temperature will also be scared — if the voltage is less than the nominal, then the light will be colder, because the additives responsible for the color are not ionized in sufficient quantities.
If the voltage turns out to be higher than the nominal, the color will be warmer, but a prolonged excess of the voltage threatens to explode the bulb due to the increased pressure in it. It is best to provide stabilization of the supply voltage.
Advantages of metal halide lamps
The spectral and electrical characteristics of metal halide lamps can vary widely, and the scope of the market is vast. The light quality and high luminous efficiency explain the wide use of MGL today in various lighting installations and light signaling devices.
The lamps are compact, powerful, efficient as a light source and today are a promising replacement for traditional arc fluorescent mercury lamps (DRL) and high pressure sodium lamps (HPL) due to the softer and safer spectrum for people.
The luminous flux of MGL lamps is up to 4 times higher than that of incandescent lamps, and the luminous efficiency is on average 80-100 lm / W. Color temperatures: 6400 K (cold light), 4200 K (natural light) or 2700 K (warm light) - easily achievable with a color rendering of around 90-95% - this is very good color rendering for a lamp that is 8 times more efficient than incandescent lamps.
The power can vary from 20 W to 3500 W with a single source and continuous operation does not depend on the ambient temperature and its differences if the lamp is already lit. The service life of the MGL lamp is calculated on an average of 10,000 hours of continuous operation.
Applications of metal halide lamps

MGL lamps are very widely used today. Lighting for filming, outdoor lighting in architecture, decorative lighting, stage and studio lighting, etc. Metal halide lamps are extremely popular in industrial lighting in workshops, in floodlights in open spaces at stations, in quarries, on construction sites, on sports facilities, etc. etc.
Lighting of public and industrial buildings, special lighting for plants and animals, as a source of near ultraviolet radiation. Finally, street lighting, landscape lighting and showcases, to create lighting effects in design and advertising, in shopping malls... — metal halide lamps have taken their rightful place everywhere.
