Point method for lighting calculation
 The point method makes it possible to determine the illuminance at any point of the room both in the horizontal and vertical or inclined plane.
The point method makes it possible to determine the illuminance at any point of the room both in the horizontal and vertical or inclined plane.
In general, a point method for calculating lighting is used when calculating localized and outdoor lighting in cases where some of the lighting fixtures are covered by equipment located in the room, when illuminating inclined or vertical surfaces, as well as for calculating the lighting of industrial premises with dark walls and ceilings (foundries, blacksmiths, most shops of metallurgical plants, etc.).
The point method is based on the equation relating illuminance and light intensity:
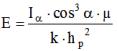
where: azα — light intensity in the direction from the source to a given point on the working surface (determined by the light intensity curves or the tables of the selected type of lighting fixtures), α — the angle between the normal to the working surface and the direction of the light intensity to the calculated point, μ is a coefficient that takes into account the effect of lighting fixtures distant from the design point and the reflected light flux from walls, ceiling, floor, equipment falling on the working surface at the design point (taken within μ = 1.05 ... 1 ,2), k is the safety factor, hp is the height of the luminaire suspension above the working surface.
Before starting the point lighting calculation, it is necessary to draw a scale of the placement of the lighting fixtures to determine the geometric relationships and angles.
The calculation by the point method is more complicated than the calculation by the specific power and utilization rate method... The calculation is carried out according to special formulas, nomograms, graphs and auxiliary tables.
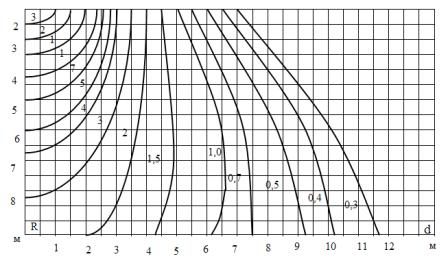
The simplest is to determine the illuminance in the horizontal plane from lighting fixtures using LN spatial isolux graphs... Such graphs are built for each type of lighting fixtures and are available in electrical lighting design reference books. «Isolux» is a line connecting points with the same lighting.
In fig. 1 the vertical axis shows the height of the luminaire above the calculated surface h in meters and the horizontal axis shows the distance d in meters 30, 20, 15, 10, 7 … — each curve has the illumination in lux of the luminaire having a light flux lamp, equal to 1000 lm.
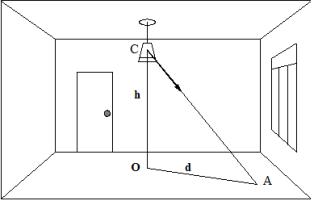
To understand the purpose of the spatial isolux and the essence of the calculation based on them, let's make a simple drawing (Fig. 2). Let the light fixture C be installed in the room at a height h above the calculated surface, for example above the floor. Let's take point A on the floor, where it is necessary to determine the illuminance. Let us denote the distance from the projection of the lighting fixture on the calculated plane O to point A by d.
To determine the illuminance at point A, you need to know the values of h and d. Suppose that h = 4 m, d = 6 m. In fig. 2 draw a horizontal line from the number 4 on the vertical axis and a vertical line from the number 6 on the horizontal axis. The lines intersect at the point through which the curve passes, marked with the number 1. This means that at point A, the luminaire C creates a conditional illumination e = 1 lux.
Rice. 1. Spatial isoluxes of conditional horizontal lighting from a lighting fixture with frosted glass.
Rice. 2. To the calculation of lighting by the point method. C — lighting fixture, O — projection of the lighting fixture on the calculated plane, A — control point.
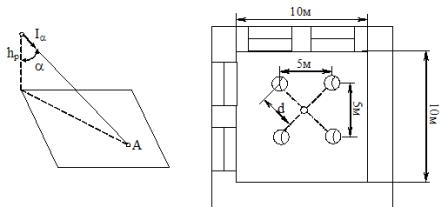
Rice. 3. To the calculation of illumination by the point method
The calculation of illuminance by the point method from lighting fixtures with symmetrical light distribution (Fig. 3) is recommended to be carried out in the following sequence:
1. According to the ratio d / hp, tga is determined and therefore the angle α and cos3α, where d is the distance from the design point to the projection of the axis of symmetry of the lighting fixture on a plane perpendicular to it and passing through the design point.
 2. Ia is selected according to the light intensity curve (or table data) for the selected type of lighting fixtures and angle a.
2. Ia is selected according to the light intensity curve (or table data) for the selected type of lighting fixtures and angle a.
3.The basic formula is used to calculate the horizontal illumination from each light fixture at the calculated point.
4. Determine the total illumination at the control point created by all the fixtures.
5. Calculate the estimated luminous flux (in lumens) that must be created by each lamp to obtain the required (normalized) illuminance at the calculated point.
6. Based on the calculated light flux, select a lamp with the required power.
An example of calculating lighting by the point method
A room with an area of 100 m2 and a height of 5 m is illuminated by four lamps of the type RSP113-400 with 400 W DRL lamps. The lighting fixtures are located in the corners of a square with a side of 5 m (Fig. 2). The height of the suspension of the lighting unit above the work surface is k.s. = 4.5 m. Normalized illumination at control point A is 250 lux. Determine if the lighting at the control point is within the required norm.
1. Determine tgα (Fig. 3), α and cos3α , α= 37 °, cos3α=0.49.
2. Determine Ia. According to the light intensity curve of RSP13 luminaires (DRL) with a conventional lamp with a luminous flux ФL = 1000 lm, we find the light intensity Ia at α = 37 ° (interpolation between the light intensity values for the angle α = 35 ° and 45 °), Ia1000 = 214 cd.
The luminous flux of a 400 W DRL lamp installed in the luminaire is 19,000 lm. Therefore Ia = 214 × (19000/1000) = 214 × 19 = 4066 cd.
3. We calculate the illumination from one light fixture in the horizontal plane at control point A. Taking the safety factor k = 1.5 for one light fixture and μ = 1.05 we get
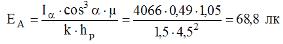
Since at the design point each of the four lamps produces the same illumination, the total horizontal illumination at point A will be ∑EA = 4 × 68.8 = 275.2 lux
The actual illumination increases the normalized (250 lux) by about 10%, which is within the acceptable limits.
To rationalize the technique for calculating the illuminance by the point method, spatial isolux reference curves constructed for each type of lighting fixtures are used.