Lighting of repair workshops of industrial enterprises
 The repair includes:
The repair includes:
- repair and mechanical, repair and installation, as well as workshops for metal structures of repair blocks and building bases;
- woodworking workshops for repair blocks and construction bases;
- foundries for repair blocks and construction bases;
- electrical repair (electrical repair) workshops;
- paint shops for repair blocks and construction bases.
The recommended illuminance values for repair workshops, repair blocks and construction bases are adopted in accordance with the industrial standards for artificial lighting of the main workshops of the machine building and tool industry.
Emergency lighting should be provided in foundries (places where metal is extracted from a furnace or cupola, melting and pouring department), thermal workshops (areas for working with acids, molten salts and in gas installations), in metal coating workshops (baths) . In the remaining sections, evacuation lighting is located, provided along the main paths of the premises where more than 50 people work.
Portable lighting for repair, adjustment and inspection of equipment is installed in all premises of the repair shops. It is allowed, in the presence of metalworking machines that have local lighting in the set, to use the low voltage terminals of the machines to power portable lighting devices (OP).
The voltage of the portable lighting is taken depending on the voltage of the local lighting of the machines or the portable lighting for the site as a whole 40 and 24 V. works inside domes, bunkers and other containers of foundries.
It is recommended to install emergency lighting for cleaning and security of the premises in all main rooms of the repair shops. As emergency lighting, it is recommended to use evacuation lighting (EO) and emergency lighting (AO).
 For general lighting of service workshops, discharge lamps (LL, DRL, MGL) and in some cases NLVD should be used. Fluorescent lamps should be used, as a rule, in rooms with a low height (up to 6-8 m). For crane sections over 6-8 m high, RLVD should be used.
For general lighting of service workshops, discharge lamps (LL, DRL, MGL) and in some cases NLVD should be used. Fluorescent lamps should be used, as a rule, in rooms with a low height (up to 6-8 m). For crane sections over 6-8 m high, RLVD should be used.
Incandescent lamps are used in the appropriate possible and economically justified cases, mainly as backup, portable and local lighting, in small explosion-hazardous rooms, for AO and EO, when used as RLVD work lighting.
If, in the presence of bridge cranes, the maintenance of the lighting fixtures in the sections of the repair workshops does not usually cause difficulties, then in the presence of bridge cranes, the project must provide for the possibility of servicing the overhead general lighting.To do this, it is necessary to issue an assignment to the organization — the general designer for registration in the project of floor mobile devices, assignments of the organization designing the construction part, for the device of bridge lighting, the device of operational forces of suspended cranes on mobile swings, installation of special trailer cranes with platforms for maintenance lamps, etc.
In rooms with a small width (up to 9 m), it is allowed to install OP on the walls (as a rule, lamps with LL) under the crane tracks, with the support of the OP from stairs and ladders.
In the conditions of repair workshops (mechanical, electrical, etc.), a combined lighting system is mainly used, in which the local lighting of work surfaces, assembly tables can significantly increase the illumination, create the necessary direction of light, provide illumination of the inner surface of products shielded from general lighting create a favorable distribution of brightness in the work area.
The use of local lighting allows you to increase labor productivity and often reduce product waste. At the same time, as a rule, a sharp reduction in energy consumption and capital costs for installing lighting is observed.
In a combined lighting system, the illumination of the working surface created by the common lighting fixtures must be at least 10% of the standardized for combined lighting with those light sources that are used for local lighting.In this case, the illumination from the general lighting in the combined lighting system should be at least 150 and not more than 500 Lx when used for general illumination of the radar and, respectively, not less than 50 and not more than 100 Lx — with LN .
In rooms without natural light, the lighting produced by lighting fixtures for general lighting in a combined lighting system may have greater values than those listed above.
The lighting to be provided at the workplace with local lighting fixtures is defined as the difference between the standardized lighting and the lighting provided by the common lighting fixtures in the combined system.
In order to limit the direct glare of local lighting fixtures, the minimum necessary protective angle is regulated, which for lighting fixtures moving along the height should be at least 30 ° (with reflectors made of opaque materials) and at least 10 ° in other cases. Since glare can arise not only from direct but also from reflected glare, measures must be taken to limit the latter.
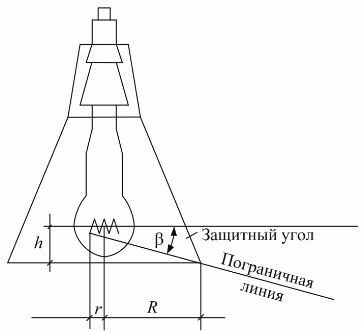
Protective corner of the light fixture
When working with shiny products (for example, metal sheet), it is recommended to use installations that are large luminous surfaces covered with light-diffusing material and arrange them in accordance with the diagram in fig. 1, a. The brightness of the luminous surface of the local lighting fixture should be in the range of 2500-4000 cd / m2.
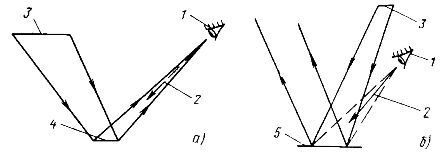
Rice. 1.The location of the lamp, the work surface and the worker's eyes, ensuring a reduction of reflected glare during work: a — with metals or light-colored plastics; b — with dark shiny materials, as well as with diffuse surfaces covered with transparent material, or with surfaces with directional diffuse or mixed reflection; 1 — the worker's eye; 2 — the direction of the line of sight of the worker; 3 — luminous surface; 4 — glossy work surface; 5 — dark glossy work surface or diffuse work surface covered with a layer of transparent material
When working with dark shiny products made of plastic, ceramics, when working that requires the discrimination of diffusely reflective objects on a diffuse background, when working with objects of discrimination and work surfaces with mixed reflection, it is necessary to place local lighting fixtures according to the scheme in fig. . 1, b.
To reduce the ripple of the radar light flux at a frequency of 50-60 Hz, it is necessary to use antistroboscopic circuits (for example, lamps with two lamps, the circuits of which provide a phase shift between the currents supplying different lamps at an angle of 90 ± 40 °). Local lighting fixtures usually have to meet strict requirements for vibration, linearity and shock resistance.
Depending on the location of the same type of workplaces, local lighting can be done individually or in groups. In the first case, each workplace is completed with its own individual lamp, in the second, a group or line of workplaces is supplemented with a single OU for local lighting.
When choosing light sources for local lighting, proceed from the following: incandescent lamps are preferable where an easily movable lamp is required, illumination of the internal cavities of machined parts is required, radio interference is unacceptable, and there is a high risk of electric shock. For lighting most workplaces, it is recommended to use lamps with LL. The use of LL is necessary in a number of cases and for reasons of limiting reflected glare when working with large specular work surfaces.
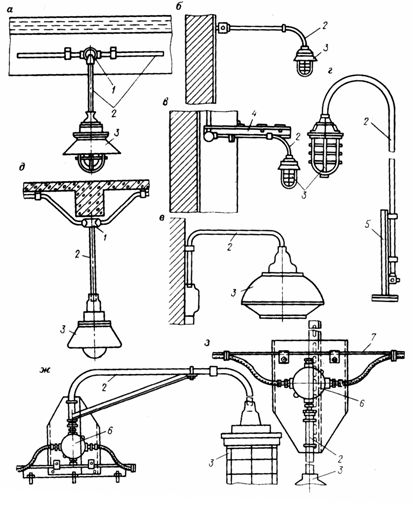 Schemes for mounting and fixing lamps: a — when laying on the beams, b — on the wall, c — on metal structures, d — on the rack, e — on the suspension, f — on the bracket, d — when laying, the cable opens along the lower farm pop, h — for laying cables, 1 — junction box, 2 — tube (suspension or bracket), 3 — lamp, 4 — channel, 5 — metal stand, 6 — junction box U- 409, 7 — cable.
Schemes for mounting and fixing lamps: a — when laying on the beams, b — on the wall, c — on metal structures, d — on the rack, e — on the suspension, f — on the bracket, d — when laying, the cable opens along the lower farm pop, h — for laying cables, 1 — junction box, 2 — tube (suspension or bracket), 3 — lamp, 4 — channel, 5 — metal stand, 6 — junction box U- 409, 7 — cable.
 Machine operations… All metal cutting machines should have local lighting, which is usually included in the machine. The main object is the cutting area and the control panel. Visual tasks are related to observing the correct assembly and fastening of the workpiece and the cutting tool, reading the drawing and checking the quality of the cutting operation.
Machine operations… All metal cutting machines should have local lighting, which is usually included in the machine. The main object is the cutting area and the control panel. Visual tasks are related to observing the correct assembly and fastening of the workpiece and the cutting tool, reading the drawing and checking the quality of the cutting operation.
All lighting fixtures of the machine must withstand mechanical loads corresponding to the group of operating conditions M8 in accordance with GOST 17516-72. A specific lighting requirement for many machine tools is the need to limit reflected glare. The observed object can be in any plane, which determines the possibility of using easily movable lamps.
When using a water-based fluid to cool the cutting tool, a splash-resistant lamp design is required. For large metal-working machines, several local lighting fixtures are usually installed, for small metal-cutting machines, as well as polishing and grinding machines, it is convenient to use a small-sized lamp of type LL LKS01.
The presence of an organic glass diffuser creates low brightness at the output of the luminaire, which is important when working with glossy surfaces, and the splash-resistant design provides protection against ingress of water-based liquid into the luminaire.
Woodworking machines are characterized by the fact that the dimensions of the products processed on them are relatively large, this, as a rule, determines the rejection of local lighting and its replacement with general uniform or localized lighting. If local lighting is still needed, it is carried out using one or two lamps of the NKP type. In some cases, they are replaced by lamps that are not specifically designed for local lighting (LSP16, LSP22, LSP18, etc.).
Luminaires with LN NVP01 (built-in) and NKP01 (built-in) are used to illuminate the presses. Local illumination of small presses can be solved by attaching NKS01 illuminators fixed to absorb shocks on rubber pads.
Locksmith work... On a metal worktop, it is necessary to ensure good lighting of three working areas: the horizontal surface of the worktop (marking of parts, punching, etc.); drawing plane fixed vertically on a wall or fence; the surface of the workpiece clamped in a vise, which must be illuminated from different sides.
There are no lighting fixtures that can illuminate all three areas of the desk well at the same time. The most successful solution should be considered the simultaneous use of two lamps.
For illumination of large planes, a powerful lamp with LL (for example, ML-2×40) is installed, the second lamp provides directional illumination of the workpiece in the vise. This can be a light fixture with LN (eg NKS01).
Layout and curvature works… Visual marker work requires high visibility to detect small marks. To reduce the brightness of reflected glare when marking glossy products, lamps with a large area and low brightness of the output hole are used, i.e. LL lamps covered with light diffusing material. When localized lighting is structurally difficult or impossible, general localized lighting is created.
A feature of the marking and bending work is the need to detect the gap between the template and the part, which is provided by lighting «to the light» (by installing an additional vertical screen).
When manually feeding small items, the spotlight can be positioned low above the work surface and firmly attached to the table. The use of double lighting fixtures allows you to provide the necessary lighting.
When working with glossy products, lamps covered with light-scattering glass are used. When the products are delivered with lifting and transport mechanisms, mobile and portable lamps are used as local lighting fixtures, the number and power of which are determined by the dimensions of the plates. In the case of localized illumination of the marking plates, lines of oblique lighting fixtures located behind the worker's back are also used.
Assembly work… Depending on the dimensions of the assemblies and parts that will be assembled in the assembly area, it is necessary to create different lighting. As a rule, the assembly of small-scale products refers to high and very high precision works, the assembly of medium-sized products to medium-precision works, the assembly of large-scale products to low-precision works.
The lighting of assembly areas of medium-sized products is similar to the lighting of locksmith work. When assembling large products, the necessary lighting is usually provided by lamps with general (localized or uniform) lighting, when assembling small products, local lighting can be realized using the lamp LNP01-2×30, and in some cases (when the work is done inside the volume of the product) — with the help of lamps NKS01 ...
In electrical repair workshops, where a large share is small electrical work, local lighting can consist of one or two directional lighting fixtures with many degrees of freedom (LNP01, NKS01, NKP02). Electrical repair (electrical repair) workshops. The classification of the premises of energy repair workshops for the risk of fire and explosion is given in the norms for the technological design of energy repair workshops, in particular, in the All-Union norms for the design of workshops for machine-building enterprises (ONTP-01-78).
The names of the premises are given as one of the possible ones and are subject to change. So the disassembly and cleaning department can be called disassembly and flushing, disassembly and fault finding, etc.When organic solvents are used in certain workplaces, these areas may have an explosive or fire-hazardous environment: for example, when parts are wiped with gasoline, kerosene, white spirit, an explosive zone of class B-1a is located within a radius of 5 m from the place at work, when wiping and washing parts tetrachlorethylene zone within a radius of 3 m is fire hazard class P-1.
When combining different departments in one room, lighting of 300 Lx is taken with a common lighting system (category IIIb) and 1000 Lx — with a combined lighting system.
Woodworking workshops for repair blocks and building bases. To illuminate these workshops, a system of general uniform or general localized lighting is mainly used. Local lighting is mainly used only in the carpentry and assembly and saw-blasting departments. LL and RLVD are recommended as light sources. In woodworking shops, lamps PVLM, LSP22, LSSH8, RSSHZ, etc. are widely used. Cabling is mainly done with non-armoured cables with non-combustible sheath and insulation.
Painting departments of repair shops and construction bases. RL (lamps N4T4L, N4T5L, OWP-250, OMR-250, etc.) are mainly used as light sources. LNs can be used for small painting areas. In some cases, lighting during painting can be increased depending on the coating class of the painted products. In places where painted products are checked, the illumination is increased to 300-400 Lx. Electrical wiring, as a rule, is done with cable, starting equipment and shields are moved out of hazardous areas.
