Effect of electric motor load on efficiency and power
Power reserve in general or under-loading the electric motor causes degradation of efficiency and power. Sometimes it is necessary to know the actual values of these coefficients in order to determine the values of the active and reactive power consumed by the electric motor from the network.
The efficiency of electric motors at loads less than nominal can be determined by the formula:
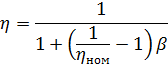
where ηnom is the nominal efficiency of the electric motor.
To determine β, use the formula:
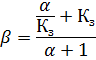
where Kz is the ratio of the actual load to the nominal (load factor);
α — coefficient assumed equal to:
• for DC motors with series excitation - from 0.5 (for low speed) to 1 (for high speed);
• for electric motors with parallel excitation - from 1 (for low speed) to 2 (for high speed);
• for asynchronous electric motors — from 0.5 to 1; for crane and synchronous electric motors — up to 2.
The values power factor induction motor depends on many factors and, strictly speaking, is different for every electric motor, even of the same type.
However, under design conditions it is sufficient to know only the approximate average values of the power factor depending on the expected loads.
From a simplified pie chart, the following relationship is obtained:
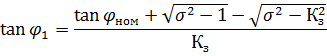
Designations — see fig. 1.
where tanφ1, is the tangent of the phase angle corresponding to the actual load of the electric motor P1, kW; tanφnom — the tangent of the phase shift angle corresponding to the nominal load of the electric motor PH0M (determined by cosφnom specified in the motor passport); σ-ratio of the overturning moment to the nominal (is within the narrow limits of 1.8-2);
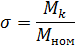
K3 — load factor.
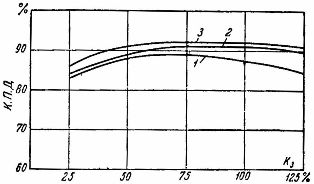
Rice. 1. Efficiency curves of asynchronous different electric motors depending on the load.
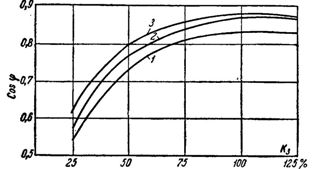
Rice. 2. Curves of the power factor of asynchronous electric motors depending on the load.
The curves of the dependence of η and cosφ on the load for the most common types of asynchronous electric motors are given in fig. 1 and 2.
