Armature reaction in DC machines
 The magnetic flux in a DC machine is created by all of its current-carrying windings. In idle mode, no current flows through the armature winding of the generator, but an idle current of small value flows through the armature winding of the motor. Therefore, in the machine there is only the main magnetic flux Ф0, created by the excitation coil of the poles and symmetrical around their center line (Fig. 1, a).
The magnetic flux in a DC machine is created by all of its current-carrying windings. In idle mode, no current flows through the armature winding of the generator, but an idle current of small value flows through the armature winding of the motor. Therefore, in the machine there is only the main magnetic flux Ф0, created by the excitation coil of the poles and symmetrical around their center line (Fig. 1, a).
In fig. 1, and (the collector is not shown) the brushes are located next to the wires of the armature winding, from which there are taps to these collector plateswith which the brushes are currently connected. This position of the brushes is called the position of geometric neutrality, that is, the line passing through the center of the armature and the winding wires, where the EMF induced by the main magnetic flux. etc. s. is zero. Geometric neutrality is perpendicular to the center line of the poles.
When a load Rn is connected to the armature winding of the generator or when the braking torque acts on the motor shaft, the armature current 1R flows through the winding, which creates an armature magnetic flux Fya (Fig.1, b). The magnetic flux of the armature is directed along the line on which the brushes are located. If the brushes are located on the geometric neutral, then the armature flux is directed perpendicular to the main magnetic flux and is therefore called transverse magnetic flux.
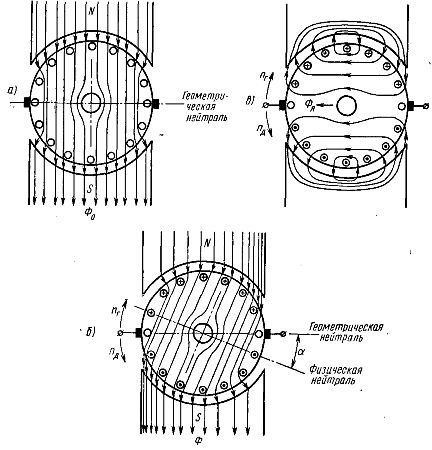
Rice. 1. Magnetic fluxes in a DC machine: a — magnetic flux from poles; b — magnetic flux of the armature winding; c — the resulting magnetic flux
The influence of armature magnetic flux on the main magnetic flux is called armature reaction. In the direct current generator, under the "running" edge of the pole, the magnetic fluxes are added, under the "running" edge they are subtracted. The opposite is true for the engine. Thus, under one edge of the pole, the resulting magnetic flux F increases compared to the main magnetic flux, under the other edge of the pole it decreases. As a result, it becomes asymmetric with respect to the central line of the poles (Fig. 1, c).
Physical neutral — a line passing through the center of the armature and the wires of the armature winding, in which induced by the resulting magnetic flux e. etc. s. equal to zero, rotates at an angle a relative to geometric neutrality (in the direction of the lead in generators, in the direction of lagging in engines). At idle, physical neutrality coincides with geometric neutrality.
As a result of the armature reaction, the magnetic induction in the machine gap becomes even more uneven. In the wires of the armature, located at the points of increased magnetic induction, a large d. with is induced, which leads to an increase in the potential difference between adjacent collector plates and to the appearance of sparks on the collector. Sometimes the arc will overlap the entire collector, creating a "circle fire".
In addition, the armature reaction leads to a decrease in e. etc. v. anchors if the machine is operating in a zone close to saturation. This is due to the fact that when the main magnetic flux Ф0 creates a saturated state of the magnetic circuit, then the increase in magnetic flux by + ΔФ below one edge of the pole will be less than the decrease by –ΔФ below the other ( Fig. 2). This leads to a decrease in the total pole flux and e. etc. v. anchors since then
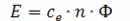
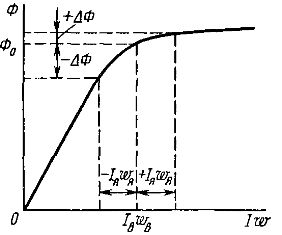
The negative impact of the armature reaction can be reduced by moving the brushes to physical neutrality. In this case, the armature flux is rotated through an angle α and the countercurrent under the falling edge of the generator pole decreases. Brushes are moved in the generator in the direction of rotation of the armature, and in the motor - against the direction of rotation of the armature. The angle α changes with a change in the armature current Iia. In practice, brushes are usually placed at a moderate angle.
Rice. 2. Influence of the degree of magnetization on the resulting magnetic flux (Iw • ww — ppm from the excitation winding; Iya • wя — ppm from the armature winding).
In machines of medium and high power, a compensating winding is used, located in the grooves of the main poles and connected in series with the armature winding, so that its magnetic flux Fk is opposite to the magnetic flux Fya. If at the same time Fk = Fya, then the magnetic flux in the air gap is practically not distorted due to the armature reaction.
