Types of electric discharge in gases
 Electric discharge in gases includes all cases of movement in gases under the action of an electric field of charged particles (electrons and ions) as a result of ionization processes... A prerequisite for the occurrence of a discharge in gases is the presence of free charges in it - electrons and ions.
Electric discharge in gases includes all cases of movement in gases under the action of an electric field of charged particles (electrons and ions) as a result of ionization processes... A prerequisite for the occurrence of a discharge in gases is the presence of free charges in it - electrons and ions.
A gas consisting only of neutral molecules does not conduct an electric current at all, i.e. an ideal dielectric... In real conditions, due to the action of natural ionizers (ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, cosmic rays, radioactive radiation from the Earth, etc.), the gas always contains a certain amount of free charges — ions and electrons, which give it a certain electrical conductivity.
The power of natural ionizers is very low: as a result of their action, about one pair of charges is formed in the air every second in every cubic centimeter, which corresponds to an increase in the volume density of charges po = 1.6-19 CL / (cm3 x in ). The same amount of charges undergoes recombination every second. The number of charges in 1 cm3 of air at the same time remains constant and equal to 500-1000 pairs of ions.
Thus, if a voltage is applied to the plates of a flat air capacitor with a distance S between the electrodes, then a current will be established in the circuit, the density of which is J= 2poS = 3.2×10-19 S A / cm2.
The use of artificial ionizers increases many times the current density in the gas. For example, when the gas gap is illuminated with a mercury-quartz lamp, the current density in the gas increases to 10 — 12 A / cm2; in the presence of a sincere discharge near the ionized volume, currents of the order of 10-10 A / cm2, etc.
Consider the dependence of the current passing through a gas gap with a uniform electric field on the value of the applied voltage i (Fig. 1).
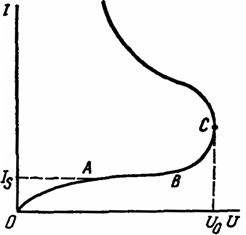
Rice. 1. Current-voltage characteristics of the gas discharge
Initially, as the voltage increases, the current in the gap increases due to the fact that the increasing amount of charges falls under the action of an electric field on the electrodes (section OA). In section AB, the current practically does not change, since all the charges formed due to external ionizers fall on the electrodes. The saturation current Is is determined by the intensity of the ionizer acting on the gap.
With a further increase in voltage, the current sharply increases (section BC), which indicates the intensive development of gas ionization processes under the action of an electric field. At voltage U0, a sharp increase in the current in the gap is observed, which in this case loses its dielectric properties and turns into a conductor.
The phenomenon in which a high-conductivity channel appears between the electrodes of the gas gap is called electrical breakdown (breakdown in a gas is often called electrical discharge, which means the entire process of breakdown formation).
The electric discharge corresponding to the section of the OABS characteristic is called dependent, since in this section the current in the gas gap is determined by the intensity of the active ionizer. The discharge in the section after point C is called independent, since the discharge current in this section depends only on the parameters of the electric circuit itself (its resistance and the power of the power source) and for its maintenance, the formation of charged particles due to external ionizers is not required. The voltage Wo at which self-discharge begins is called the initial voltage.
Forms of self-dissolution into gases depending on the conditions under which the discharge takes place, they can be different.
At low pressure, when due to the small number of gas molecules per unit volume, the gap cannot acquire high conductivity, and a glow discharge... The current density in a glow discharge is low (1-5 mA / cm2), the discharge covers the entire space between the electrodes.

Rice. 2. Glow discharge in gas
At gas pressure close to atmospheric and higher, if the power of the power source is low or the voltage is applied to the gap for a short time, there is a spark discharge... An example of a spark discharge is the discharge in the form of lightning… With prolonged exposure to voltage, the spark discharge takes the form of sparks that appear alternately between the electrodes.
Rice. 3. Sincere discharge
In the case of significant power of the energy source, the spark discharge turns into an arc, in which a current can flow through the gap, reaching hundreds and thousands of amperes. Such a current contributes to heating the discharge channel, increasing its conductivity, and as a result, a further increase in current is obtained. Since this process takes some time to complete, then with a short-term application of voltage, the spark discharge does not turn into an arc discharge.

Rice. 4. Arc discharge
In highly inhomogeneous fields, self-discharge always starts in the form of corona discharge, which develops only in that part of the gas gap where the field strength is the highest (near the sharp edges of the electrodes). In the case of corona discharge, high conductivity through a channel does not occur between the electrodes, i.e. the space retains its insulating properties. As the applied voltage is further increased, the corona discharge transforms into a bona fide or arc discharge.
Corona discharge — the type of stationary electric discharge in a gas of sufficient density, occurring in a strong inhomogeneous electric field. Ionization and excitation of neutral gas particles by electron avalanches are localized in a limited amount of zone (corona cap or ionization zone) of a strong electric field near an electrode with a small radius of curvature. The pale blue or violet glow of the gas inside the ionization zone, by analogy with the halo of the solar corona, gave rise to the name of this type of discharge.
In addition to radiation in the visible, ultraviolet (mainly), as well as in the shorter wavelengths of the spectrum, the corona discharge is accompanied by the movement of gas particles from the corona electrode — the so-called "Electric wind", hum, sometimes radio emission, chemistry, reactions (for example, the formation of ozone and nitrogen oxides in the air).
Rice. 5. Corona discharge into gas
The regularities of the appearance of electric discharge in different gases are the same, the difference lies in the values of the coefficients characterizing the process.

