P-41 and P-91 series engine construction
 DC electric motors have a more complex structure than asynchronous ones, which is explained by the fact that they have collector, brush mechanism, additional poles and anchor coil. In industrial enterprises, the most widespread are direct current electric motors of a P series.
DC electric motors have a more complex structure than asynchronous ones, which is explained by the fact that they have collector, brush mechanism, additional poles and anchor coil. In industrial enterprises, the most widespread are direct current electric motors of a P series.
The P-41 DC electric motor of shielded, vented construction is shown in fig. 1, a. The main parts of the machine are the frame, the coiled posts and the armature. The main poles 17 with a field coil are attached to the cast-iron frame, creating the main magnetic field of the motor, and additional poles 16 with a coil, which ensure the unobtrusive operation of the brushes on the collector. Additional poles are located between the main poles and their windings are connected in series with the armature winding 4.
The motor armature consists of a core, a winding, a shaft and a collector.The core is made of electrical steel sheets and is pressed together with two thrust washers, of which the washer on the drive side rests on the protrusion (step) of the shaft 2, and on the collector side 5 is locked with a steel clamping washer 3.
The armature coil 4 is laid in the semi-closed channels of the core mounted on the armature shaft 2 and is held in them by wedges, and in the front parts by bandages of steel wire or non-woven glass tape impregnated with an epoxy compound. The front parts of the armature winding lie on the valves of the washer 3 and the winding holder 24. The ends of the armature winding are attached to the collector 5.
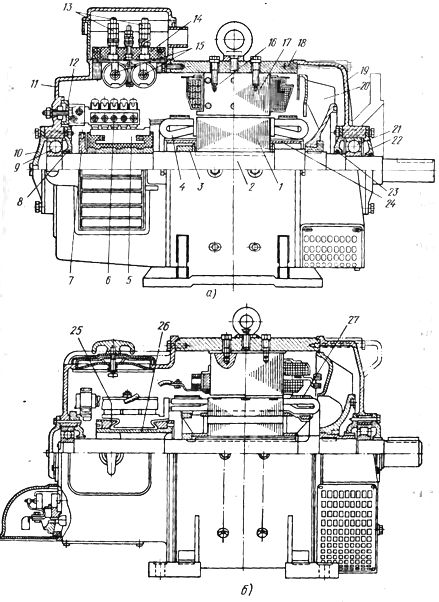
Rice. 1. DC motors P -41 (a) and P -91 (b): 1 — armature core, 2 — shaft, 3 — clamping washer, 4 — armature winding, 5 — collector, 6 — brush running part , 7 — armature balancing steel disc, 8, 23 — ball bearing inner caps, 11, 19 — front and rear end shields, 12 — cradle, 13 — terminal clamps, 14 — terminal board, 15 — capacitors for suppressing interference, 16, 17 — additional and main pole, 18 — frame, 20 — fan, 24 — coil holder, 25 — pressure cone, 26 — sleeve, 27 — wire.
The collector 5 consists of copper plates (lamellas), isolated from each other with a trapezoidal cross-section. The inside of the manifold plates have dovetail cutouts. The collector plates of the machine are molded in plastic. Inside the manifold is a steel sleeve to secure it to the armature shaft.Above the collector there is a traverse 6 of the brush holders, bolted to the front end of the shield 11, which has oval-shaped openings that allow the traverse to move around the circumference and mount the brushes on the neutral part of the motor.
The armature rotates in wide bearings 9 and 21, the outer rings of which are inserted into the holes of the end shields 11 and 19. The bearings are closed from the inside with covers 8 and 23, and from the outside with covers 10 and 22. The armature is balanced by welding balancing weights to the steel disk 7 (at the corresponding points) ... In this way, the uniform distribution of the mass of the armature along its circumference is regulated. The number, mass of the loads and their placement on the discs depend on the location and size of the imbalance. The side of the armature where the fan is located is also balanced.
During the operation of an electric motor, electromagnetic oscillations occur, which interfere with radio reception. To suppress these noises, the electric machine is equipped with a special noise suppression device consisting of capacitors 15 located under the circuit board 14 and clamps 13.
The ventilation system of the engine is axial and is carried out by air sucked in by the fan 20 through the louvers of the shield 11 at the front end and expelled through the grills of the rear shield 19. The legs are welded to the frame of the engine, with which it is attached to the frame or base .
The arrangement of the P-41 motor is typical of single P series DC machines of sizes 1 through 6. The DC motors of this large size series are slightly different in design from the motor shown in Fig. 1, a.
For example, in a 9 gauge P-91 engine (Fig.1, b), the armature core has open slots in which hard windings are embedded, and horizontal through ventilation channels that improve cooling conditions for the core and armature winding. The sealing washers pressing the sheets of the armature core are cast from cast iron in the form of three rings connected by ribs. The manifold has a cast iron sleeve 26 that rests on the shaft with three ribs. The pressure steel cones 25 of the collector are isolated from the plates by hot-pressed micanite sleeves.
The coil has bent heads only on the side of the free end of the shaft, as it is made of single-turn coils. The front and grooved parts of the armature winding are held by bandages 27, wound from steel wire. The windings are placed on additional posts, which are held on them by a stamped frame. The coils are wound with rectangular copper busbars.
The rotor rotates in rolling bearings: ball bearings on the collector side and roller bearings on the free end of the shaft. The frame of the P-91 DC motor is welded bent sheet steel with legs welded to it for mounting and securing to a foundation or frame.

