Time relay operation algorithms
 Each time relay is characterized by its own parameters. The most important parameter is the relay operation algorithm, i.e. the logic of the sequence of her work. The algorithm for the operation of the time relay is graphically shown in the functional diagram. Let's look at the most common algorithms:
Each time relay is characterized by its own parameters. The most important parameter is the relay operation algorithm, i.e. the logic of the sequence of her work. The algorithm for the operation of the time relay is graphically shown in the functional diagram. Let's look at the most common algorithms:
-
a — switch-on delay — after switching on the relay, the output signal appears after the set time has elapsed,
-
b — the formation of a pulse when switching on, i.e. the output signal appears when the relay is energized and disappears after a set time,
-
c — formation of a pulse after removal of the control signal, i.e. after switching on the relay, the output signal appears at the moment when the control signal is removed and disappears after a set time,
-
d — shutdown delay after removal of the supply voltage, i.e. the output signal appears at the moment of switching on the time relay and disappears after a set time after removing the supply voltage,
-
e — cyclic operation (with pause) — after supplying power to the relay, the output signal appears after the set pause time (T1). a pulse time delay (T2) occurs and the output signal disappears, the pause time delay (T1) occurs, the output signal occurs and a pulse time delay (T2) occurs, etc. before turning off the power.
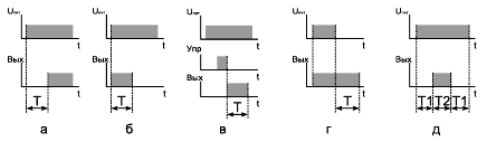
Rice. 1. The most common time relay algorithms
The described algorithms are the simplest, basic ones; more complex algorithms are built on their basis. Modern electronic relays can provide a large number of complex algorithms for operation.
Examples of functional diagrams of the most common time relays:
1) Time relay with power supply:
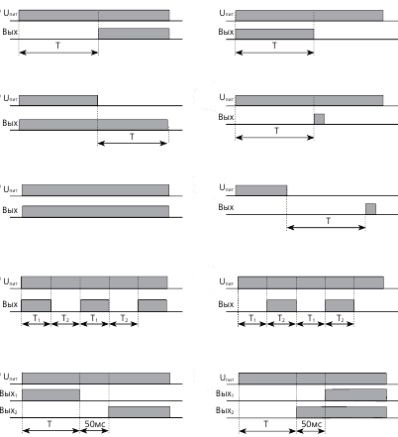
2) Time relay with external control signal:

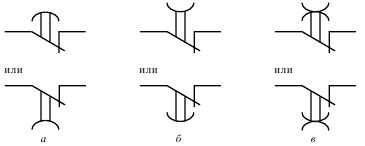
Designation of the closing contacts of the time relay:
Conventional graphic designations of the closing contacts of the time relay: a — with a delay on actuation, b — with a delay on release, c — with a delay on actuation and release
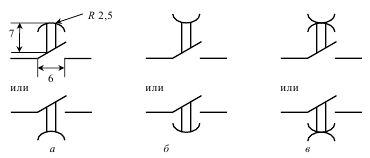
Time Relay Break Contact Symbols:
Conventional graphic symbols of the opening contacts of the time relay: a — with a delay on actuation, b — with a delay on release, c — with a delay on actuation and release