Moisture meters for moisture control of bulk materials
 Moisture meters are measuring devices designed to determine moisture content. All methods of measuring humidity are usually divided into direct and indirect.
Moisture meters are measuring devices designed to determine moisture content. All methods of measuring humidity are usually divided into direct and indirect.
When direct moisture control methods are used, a direct separation of the test material into dry matter and moisture is performed.
In laboratory tests and for the control of automatic devices, the weight (direct) method is used. The essence of the method is that a sample of the test material (moulding sand, sand, etc.) is placed in a laboratory bottle and, after careful weighing, is placed in an oven at a temperature of 103 — 105 OS and dried to a constant weight.
The dried material was then placed in a desiccator, cooled in the presence of silica gel, and reweighed on the same balance. Based on the results of the weighing, the moisture content of the materials is determined. The described method provides high accuracy, but is carried out over a long period of time (2-3 hours).
Recently, indirect physical methods for measuring the moisture content of bulk materials are becoming more common. They are based on the conversion of moisture into any physical quantity that is convenient for measurement or further conversion using measuring transducers.
Depending on the nature of the measured parameter, indirect methods are divided into electrical and non-electrical. Electrical methods for measuring humidity are based on direct measurement of the electrical parameters of the studied material. Using non-electrical methods, a physical quantity is determined, which is then converted into an electrical signal. Among the electrical methods for measuring the moisture content in bulk materials, conductometric and dielectric (capacitive) methods are most widely used.
A conductometric method of moisture control based on the measurement of the electrical resistance of the material, which changes depending on the moisture content of the material. When measuring humidity by this method, a sample of substance 1 is placed between the flat electrodes 2 of the primary transducer (Fig. 1).
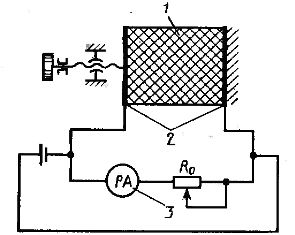
Rice. 1. Schematic of a conductometric moisture meter
The amperage measured by device 3 will depend on the moisture content of the sample. Resistor Ro is used to adjust the zero of the device. The conductometric method allows you to determine the moisture content of bulk materials in the range 2 — 20%. The upper limit is limited by the decrease in sensitivity with increasing humidity, and the lower limit is due to the difficulties in measuring high electrical resistances.
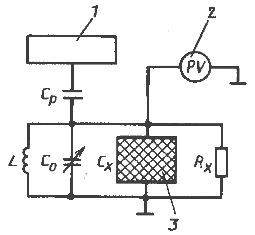
In the measuring circuit of a capacitive moisture meter (Fig. 2), operating on the principle of determining dielectric losses, the capacitance of the capacitor converter is determined using a resonant circuit consisting of an inductance L and a variable capacitance Cx. The resonance of the circuit is ensured by adjusting the capacitor Co.
Rice. 2. Scheme of a capacitive hygrometer
A voltmeter 2 is used as a resonant indicator. The circuit is separated from the generator 1 by a separating capacitor Cp. As the humidity of test sample 3 increases, the capacitance of the transducer changes. To restore symmetry, it is necessary to change the capacitance of the capacitor Co so that the total capacitance of the circuit becomes original again. The change in the position of the handle of the capacitor Co is an indicator of humidity.
The disadvantage of this method is the dependence of the capacity of the material not only on humidity, but also on the chemical composition. Therefore, capacitive methods of moisture control are used only with special devices for each specific material.