Load relay with priority
 The load priority relay (or load control relay) serves as a means of automatically tripping non-priority loads if the maximum allowable total current begins to be exceeded. This means that this device limits the electrical energy consumed by the network by disconnecting priority loads from the network when necessary and leaving only those connected with priority. Such relays are the basis of automatic load control systems.
The load priority relay (or load control relay) serves as a means of automatically tripping non-priority loads if the maximum allowable total current begins to be exceeded. This means that this device limits the electrical energy consumed by the network by disconnecting priority loads from the network when necessary and leaving only those connected with priority. Such relays are the basis of automatic load control systems.
Normally, the priority relay works as follows. A current transformer is installed on the common line and after it the loads are connected and the priority loads are switched on first, these are those consumers which are not switched off under any conditions, respectively have the highest priority.
Then a load priority relay is connected, through which groups of non-priority loads are connected, that is, groups of consumers that will be disconnected in a certain sequence in accordance with the degree of priority of each of the groups, if the maximum permissible current is exceeded.

The signal from the current sensor is processed using a comparator built into the module, and the input signal is compared with the reference voltage. The reference voltage is set by the switch settings, and the relay setting determines at what current the comparator will operate and, accordingly, at what point the internal contactor will switch off the lowest priority load group, thus the total current drawn from the mains will be lower.
After some time, for example after 5 minutes, an attempt will be made to reconnect non-priority loads to the network, starting from the highest priority of the disconnected ones.

These relays are three-phase and single-phase, single-channel and multi-channel. Multi-channel priority relays have multiple low-priority lines that are switched off in sequence, starting with the lowest priority. The switch is done the other way around — from the highest priority.
The use of such relays allows you to connect equipment to the network without resorting to the purchase of additional electrical energy, which is sometimes very appropriate on an enterprise scale and provides significant savings.
Or in the case of an apartment. An automatic machine for 25A is installed at the entrance, then there is a counter, and then there are several circuit breakers. Boiler, air conditioner, washing machine, kitchen appliances, TV, lighting, etc.
If you have to turn everything on at the same time, then the machine at the entrance can easily work, the one in the floor electrical panel and it will be dark in the apartment, the washing machine will stop washing, etc. Thermal protection will work and the machine will disconnect the apartment from the network.We will need to turn on the machine, having previously understood which of the devices caused the overload.
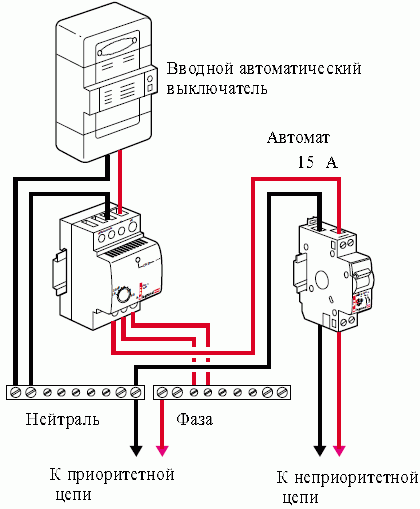
If in this case we use a priority relay, the contactors in which are designed for currents up to 16A, there will be no problem, you can make the washing machine, light and some contacts priority and include several priority groups through the relay module, then the smallest device will turn off on overload, at the discretion of the owners, and everything will be fine.
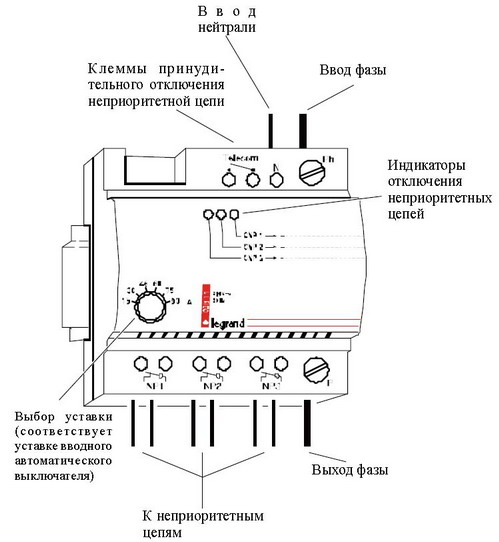
Limiting the maximum current due to economic reasons, either due to the small cross-section of the wires or depending on the restrictions imposed by the electricity supplier - in any case, the priority relay will prevent a total power failure, limiting the current painlessly for the user.
It is also possible to use a priority relay in relay protection circuits to prevent production accidents associated with the use of a large number of different electrical machines, transformers and other equipment where short circuits and overloads are unacceptable.
