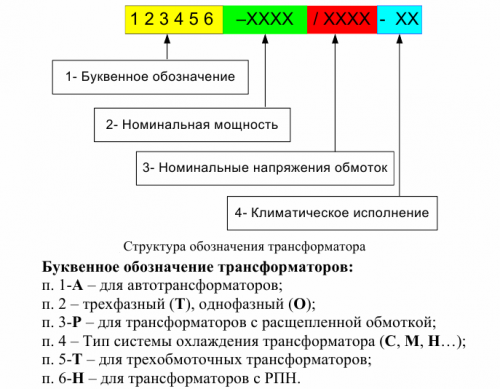
Decoding letter designations of transformers and autotransformers

Constructions power transformers are very diverse and are determined by the rated voltage, power, number of secondary windings, cooling system, etc. The structure of the symbol reflects the main design features and parameters of power transformers (Fig. 1).
According to the number of windings, two and three windings are distinguished. Three-winding transformers are produced with higher voltages up to 220 kV and autotransformers from 220 kV and above. The ratio of the rated power of the windings for high, medium and low voltage can be, respectively: 100/100/100; 100/100/67; 100/67/100. In this case, the sum of the loads on the low and medium voltage windings should not exceed the nominal.
Letter designations of transformers: TM, TS, TSZ, TD, TDTs, TMN, TDN, TC, TDG, TDTSG, OTs, ODG, ODTSG, ATDTSTNG, AOTDTSN, etc.
The first letter indicates the number of phases (T — three-phase, O — single-phase).Below is the designation of the cooling system: M — natural oil, that is, natural oil circulation, C — dry transformer with natural air cooling of an open design, D — blown oil, that is, with blowing out the tank with a fan, C — forced circulation of oil through a water cooler, DC — forced circulation of oil with blowdown.
The letter P after the number of phases in the designation indicates that the low voltage winding is represented by two (three) windings (split). The presence of the second letter T means that the transformer has three windings, with two windings there is no special designation.
The following letters indicate: H — load voltage regulation (RPN), absence — the presence of switching without excitation (PBV), G — lightning resistant. A — autotransformer (at the beginning of the symbol).
Letter designations are followed by rated power of the transformer (kVA) and by fraction — the rated voltage class of the HV winding (kV). In autotransformers, the MV winding voltage class is added as a fraction. Sometimes the year of the start of production of transformers of this design is indicated.
The scale of rated powers of three-phase power transformers and autotransformers (current state standards 1967-1974) of high-voltage networks is constructed so that there are power values in multiples of ten: 20, 25, 40, 63, 100, 160, 250 , 400, 630, 1000, 1600 kVA, etc. Some exceptions are 32000, 80000, 125000, 200000, 500000 kVA
The standard service life of household transformers is 50 years, therefore transformers manufactured before 1967and updated due to major repairs, can also be used in the electrical networks of industrial and agricultural enterprises. Their rated power scale: 5, 10, 20, 30, 50, 100, 180, 320, 560, 750, 1000, 1800, 3200, 5600, …, 31500, 40500, kVA, etc.
Cooling systems for transformers
Natural air cooling of transformers (C — dry). This cooling system is used for transformers with power up to 1600 kVA and voltage up to 15 kV. Natural oil cooling (M). With this system, there is a natural convective circulation of oil through the reservoir and radiator tubes. For transformers with a capacity up to and including 16000 kVA, the following applies:
- Oil cooling with blowing and natural oil circulation (D). In this system, coolers are used to enhance the cooling of the radiator tubes. This cooling system is used for transformers up to 100,000 kVA.
- Blast oil cooling and forced oil circulation (DC) are used for transformers 63000 kVA and above. To enhance cooling, fans and oil pumps are used for forced oil circulation. As a rule, several groups of coolers (including pumps and fans) are used, which are switched on depending on the load and oil temperature.
- Oil-water cooling with forced oil circulation (C) is used for high-power transformers in hydroelectric power plants.
See here for more details: Cooling systems for transformers
Examples of designation of transformer types:
- TM-250/10 - three-phase two-winding with natural oil cooling, voltage change using a power supply unit, rated power 250 kVA, HV winding voltage class 10 kV.
- TDTN-25000/110 - three-phase three-winding oil-cooled step-down transformer with load switch, rated power 25000 kVA, winding voltage class HV 110 kV.
- OC-533000/500 - single-phase two-winding step-up transformer, oil-cooled with forced oil circulation, with a capacity of 533,000 kVA, connected to a 500 kV network.
- TDTSTGA-120000 /220 / 110-60 — three-phase transformer with three windings, the main mode of which is gain (A), with transformations LV-HV and LV-CH, design 1960
- TMG-100/10 (three-phase transformer, oil-free cooling, under pressure, power 100 kVA, voltage 10 kV).
- ATDTsTN-250000 /500 / 110-85 - three-phase autotransformer with three windings, oil cooling with blowing and circulation, with load switch, rated power 250 MVA, step down, operating according to the autotransformer circuit between networks 500 kV and 110 kV ( HV-MV transformation, LV winding is auxiliary), project 1985.
- ATDTSTN-125000/220/110/10 (autotransformer, three-phase, air-blast cooling and forced oil circulation, three windings, with load switch, rated power-125 MVA, rated voltages-220, 110, 10 kV).