Transient processes in AC circuits, commutation laws, resonance phenomena
 Stationary modes of operation of electrical circuits are modes in which the parameters in the circuit are constant: voltage, current, resistance, etc. If, after reaching a steady state, the voltage changes, the current will also change. The transition from one steady state to another does not occur immediately, but over a period of time (Figure 1).
Stationary modes of operation of electrical circuits are modes in which the parameters in the circuit are constant: voltage, current, resistance, etc. If, after reaching a steady state, the voltage changes, the current will also change. The transition from one steady state to another does not occur immediately, but over a period of time (Figure 1).
The processes that take place in the circuits during the transition from one stationary state to another are called transient. Transients occur with any sudden change in circuit parameters. The moment of a sudden change in the mode of operation of the electric circuit is taken as the initial moment of time, relative to which the state of the circuit is characterized and the transient process itself is described.
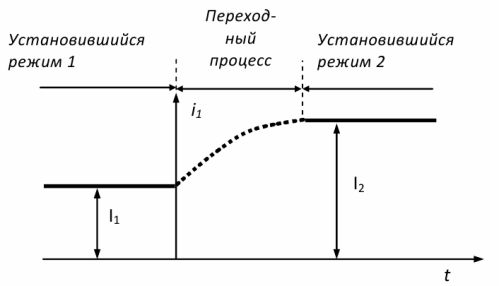
Rice. 1. Modes occurring in the AC circuit
The duration of the transient process can be very short and can be calculated in fractions of a second, but the currents and voltages or other parameters characterizing the process can reach large values.Transients are triggered by commutation in the circuit.
Commutation is the closing or opening of the contacts of switching devices. When analyzing transients, two commutation laws are used.
The first law of commutation: current. flowing through an inductor before switching is equal to the current through the same coil immediately after switching. These. the current in the inductor cannot change abruptly.
The second law of commutation: the voltage across the capacitive element before switching is equal to the voltage across the same element after switching. These. the voltage across the capacitive element cannot change abruptly. For series connection of resistor, inductor and capacitor the dependencies are valid
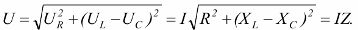
In the considered circuit with the same reactions Xl and Xc, the so-called voltage resonance... Since these resistances depend on the frequency, the resonance occurs at a certain resonance frequency ωо.
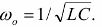
The total resistance of the circuit in this case is minimal and purely active. Z = R, and the current has a maximum value. At ω ωо the load has an active-capacitive character, with ω >ωо — active-inductive.
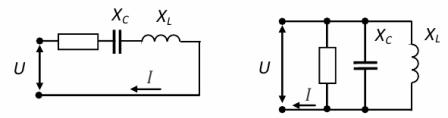
It should be noted that the sharp increase in current in the circuit at resonance corresponds to an increase in Xl and Xc. These stresses can become much larger than the voltage. U applied to the circuit terminals, therefore voltage resonance is a phenomenon that is dangerous for electrical installations.
The currents in the branches of parallel-connected circuit elements have a corresponding phase shift with respect to the total circuit voltage.Therefore, the total current of the circuit is equal to the sum of the currents of its individual branches, taking into account the phase shifts and is determined by the formula
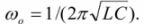
If the reactances Xl and X are equal, in a circuit with parallel connection of elements resonant currents... The resonant current reaches its maximum value and the maximum power factor (cosφ = 1). The value of the resonance frequency is determined by the formula
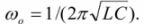
The currents in the branches containing L and C, at resonance, can be greater than the total circuit current. Inductive and capacitive currents are opposite in phase, equal in value and mutually offset with respect to the power source. These.in the circuit, energy is exchanged between the inductive coil and the capacitor.
The close-to-resonance mode of currents is widely used to increase the power factor of electricity consumers. This gives a significant economic effect due to the unloading of wires, reduction of losses, saving of materials and energy.
