The influence of external factors on the operation of circuit breakers
Operating parameters of circuit breakers, the principle of operation of which is based on deformation during heating contact bimetallic plate The current flowing through it is very dependent on external factors. External factors affecting the current temperature of the protective device, such as: ambient air temperature, altitude, atmospheric conditions, the location of several devices next to each other, lead to a deviation in the value of the operating current of the circuit breaker from the nominal value corresponding to a certain model.
For example, the typical average deviation from the rated operating current when the temperature of the device changes by 1 ° C is approximately 1.2%. That is, if there are no special instructions from the manufacturer, it is necessary to make corrections in the calculations regarding the operating current.
The rated operating current of the machine is determined at a temperature of 30 ° C, which means that at a device temperature of 20 ° C, the operating current will change upwards and be equal to 1.12 of the nominal.If the temperature of the device (environment) is 40 ° C, then the operating current of the machine will decrease by 12% and will be 0.88 of the nominal value. This is due to the well-defined heat capacity of the bimetal from which the plate is made.
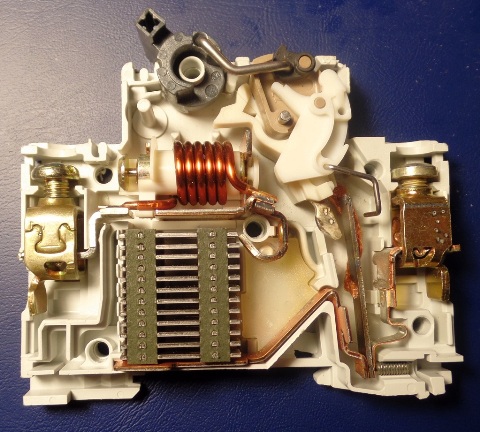
And if there is an automatic machine with a tripping characteristic C, for example C50, then at an ambient temperature of 20 ° C, the tripping current will be 56 amperes. The original limits were 250 and 500 amps, which corresponds to 5 and 10 in terms of the nominal 50 amps, but now the multiples will change to 250/56 = 4.46 and 500/56 = 8.92. If the ambient temperature continues to decrease, the machine will approach the shutdown characteristic of the B50 machine, and with an increase above 40 ° C — to D50.
It is obvious that all circuit breakers containing a combination thermoelectric circuit breaker and equipped with temperature sensitive bimetallic plates have temperature dependent time current characteristics.
According to GOST R 50345-99, the normal temperature regime for the operation of circuit breakers should be such that the average daily ambient temperature is 35 ° C and does not exceed 40 ° C. The minimum temperature should not be below 5 ° C. For other operating conditions require special switches or it is necessary to ensure the environmental conditions specified in the manufacturer's documentation.
Altitude is an important factor for circuit breakers. If the altitude is more than 2 km above sea level, the insulating and cooling properties of the air are different and must be taken into account. Thus, the air at altitude becomes more expelled, less thermally conductive, and the probability of overheating of the machine increases accordingly.But at the same time, at a higher altitude, the air temperature is usually lower, which means that the operating current increases.
Thus, if the machine is to operate at an altitude above 2000 meters, then the machine of such a model must be specially designed for these conditions — the user must compare his requirements with the manufacturer's data.
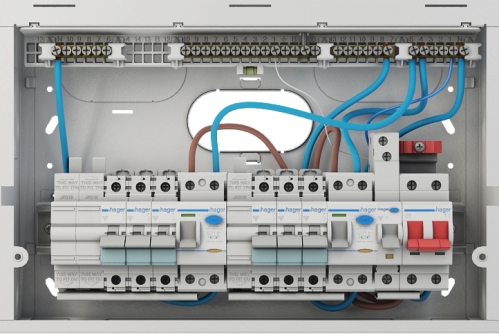
When several machines or automatic machine and other modular devices are placed close to each other on the same DIN rail, then the transfer of heat to the surrounding air is difficult, the devices heat each other and the modules located on the sides are cooled better than those , which stand between the other modules... The modules in the center get the worst cooling, so they get hotter than the others.
As a rule, the manufacturer indicates the installation conditions in its documentation. In practice, it can be assumed that each additional installed module, when it comes to circuit breakers, contributes to a reduction of the rated operating current by approximately 2.25%, and when installing 9 pieces , the correction factor will be 0.8, and with an even larger number it will easily reach 0.5.
