Methods for determining the location of insulation failure of the winding of electric motors from the magnetic circuit
In order to determine the location of the insulation failure of the winding of the electric motor, it is generally necessary to disconnect the phase windings and measure the insulation resistance of each phase winding of the magnetic circuit, or at least check the integrity of the insulation.
In this case, it is possible to identify the phase winding with damaged insulation. Different methods can be used to determine the place of damage to the insulation of the winding of the electric motor: the method of measuring the voltage between the ends of the winding and the magnetic circuit, the method of determining the direction of the current in parts of the winding, the method of dividing the winding into parts and "combustion" method.
In the first method for the phase winding of the motor with damaged insulation, a reduced AC or DC voltage is applied and voltmeters VI and V2 are applied, measure the voltage between the ends of the winding and the magnetic circuit.According to the ratio of these voltages, the position of the damaged winding relative to its ends can be estimated. This method does not provide sufficient accuracy at low resistance. coils.
The second method is that a constant voltage is applied to the voltage the ends of the phase winding combined in a common point and on the magnetic circuit. For the possibilities of regulation and limitation of the current in the circuit include the rheostat R. The directions of the currents in the two parts of the coil, limited by the point C of connection with the magnetic circuit will be opposite.
If you touch two millivoltmeter leads in series to the ends of each coil, the millivoltmeter needle will deflect in one direction while the millivoltmeter leads are connected to the ends of the coil group with damaged insulation. At the end of the following groups of coils, the deflection of the arrow will change to the opposite.
For a group of windings with damaged insulation, the deflection of the arrow will depend on which of the ends is closer to the location of the insulation failure; In addition, the value of the voltage at the ends of this group of coils will be less than at the rest of the groups of coils, if the insulation is not close to the ends coil group. In the same way, further determine the location of the insulation failure inside the group of coils.
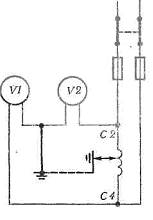 Rice. 1 Determining the location of motor insulation failure by two voltmeters
Rice. 1 Determining the location of motor insulation failure by two voltmeters
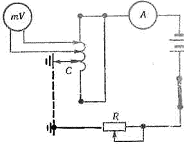 Rice. 2 Determining a winding group of an electric motor winding with damaged insulation by means of a test lamp
Rice. 2 Determining a winding group of an electric motor winding with damaged insulation by means of a test lamp
Figure 3 shows a two-layer motor winding group consisting of four windings.Leaving the switching circuit of the phase winding unchanged, measure voltage between points A — B, B — C, C — D and D — E and observe the direction of deflection of the needle of the millivoltmeter. If the insulation is damaged in the coil B — C, then the deviation of the arrow for points A — B will be opposite to its deviation for points C — D and D — E.
The direction of the current in the coil can be judged by the deflection of the magnetic needle, located sequentially above each groove with the coil being tested. During the transition through the channels in which the coil with damaged insulation is located, the direction of deflection of the magnetic needle changes in accordance with the change in the direction of the current when the coil is turned on according to the diagram in Figure 2. To perform In this study, the electric motor must be disassembled.
The listed methods give reliable results only in the case of stable contact of the winding wires with the magnetic wire.
The method of dividing the winding into parts is that the phase winding has a connection with the magnetic core, half by soldering the inter-coil connections, and then with a megohmmeter or a test lamp determine a part of the winding has a connection with the magnetic circuit. This division continues until a damaged coil is found. If the phase winding with damaged insulation and connect the magnetic circuit to a source of reduced voltage, for example, to a welding generator or transformer, then due to significant heating of the contact point of the windings and the magnetic circuit, smoke appears, and sometimes sparks (the insulation "burns" ') .
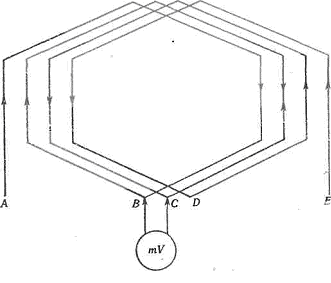 Rice. 3. Determination of the coil of an electric motor winding with damaged insulation
Rice. 3. Determination of the coil of an electric motor winding with damaged insulation
To prevent major damage due to burning of the insulation and melting of the windings, a resistance must be included in the circuit of the limiter.
In some cases, the location of the damage can be established by a relatively simple method, if the phase winding with damaged insulation and the magnetic circuit are connected to a 220 V network by means of a test lamp and a wooden lever to displace the ends of the windings. When displacing a coil with damaged insulation, the test lamp will flash.
If a coil with damaged insulation is found, it must be replaced. Limited damage removal is possible when the general condition of the insulation is satisfactory.
If it is not possible to repair the damaged insulation and the electric motor cannot be stopped to repair the winding, then disconnect the damaged winding, i.e. separate the ends of this and the adjacent coils, and then connect the ends of the entire coil. If, in addition to the insulation of the coil from the magnetic circuit, the coil is also damaged insulation, then such a coil must be disconnected and cut to eliminate a short circuit. The number of disconnected turns should not exceed 10% of the total number of turns of the phase winding.
In the presence of parallel branches or when connecting phase windings of the delta motor, disconnection of the winding can cause large equalizing currents and therefore the windings in other parallel branches (or phase windings).
