Non-contact magnetic bearings: device, capabilities, advantages and disadvantages
Speaking of magnetic bearings or non-contact suspensions, we cannot fail to note their remarkable qualities: no lubrication required, no rubbing parts, therefore no frictional losses, extremely low vibration level, high relative speed, low energy consumption, automatic control and bearing monitoring system, sealing capability.
All these advantages make magnetic bearings the best solutions for many applications: for gas turbines, for cryogenic technology, in high-speed electric generators, for vacuum devices, for various metal-cutting machines and other equipment, including high-precision and high-speed (about 100,000 rpm ), where the absence of mechanical losses, disturbances and errors is important.
Basically, magnetic bearings are classified into two types: passive and active magnetic bearings. Passive magnetic bearings are manufactured based on permanent magnets, but this approach is far from ideal, so it is rarely used.More flexible and wider technical possibilities are opened with active bearings, in which a magnetic field is created by alternating currents in the wire windings.
How the non-contact magnetic bearing works

The operation of an active magnetic suspension or bearing is based on the principle of electromagnetic levitation — levitation using electric and magnetic fields. Here, the rotation of the shaft in the bearing occurs without physical contact of the surfaces with each other. For this reason, lubrication is completely excluded and mechanical wear is still absent. This increases the reliability and efficiency of the machines.
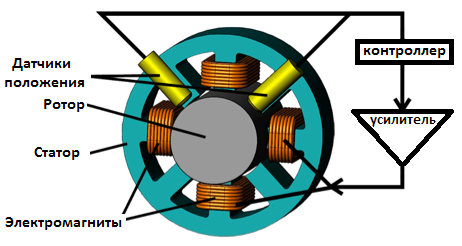
Experts also note the importance of monitoring the position of the rotor shaft. The sensor system continuously monitors the position of the shaft and provides signals to the automatic control system for precise positioning by adjusting the positioning magnetic field of the stator - the attraction force on the desired side of the shaft is strengthened or weakened by adjusting the current in the stator windings of the active bearings .
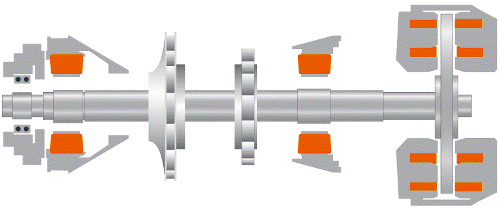
Two tapered active bearings or two radial and one axial active bearing allow the rotor to be suspended without contact literally in the air. The gimbal control system works continuously, it can be digital or analog. This provides high retention strength, high load capacity and adjustable stiffness and shock absorption. This technology allows the bearings to work at low and high temperatures, in vacuum, at high speeds and in conditions of increased requirements for sterility.
Active non-contact magnetic bearing device
From the above it is clear that the main parts of the active magnetic suspension system are: magnetic bearing and automatic electronic control system. The electromagnets all the time act on the rotor from different sides and their action is subordinated to an electronic control system.

The radial magnetic bearing rotor is equipped with ferromagnetic plates, which are acted upon by a retentive magnetic field from the stator windings, as a result of which the rotor is suspended in the center of the stator without touching it. Inductive sensors monitor the position of the rotor at all times . Any deviation from the correct position results in a signal that is sent to the controller to return the rotor to the desired position. The radial clearance can be between 0.5 and 1 mm.
A magnetic support bearing functions in a similar way. Ring-shaped electromagnets are attached to the traction disc shaft. The electromagnets are located on the stator. Axial sensors are located at the ends of the shaft.
To reliably retain the rotor of the machine during its stop or at the time of failure of the retention system, safety ball bearings are used, which are fixed so that the gap between them and the shaft is set equal to half that of the magnetic bearing.
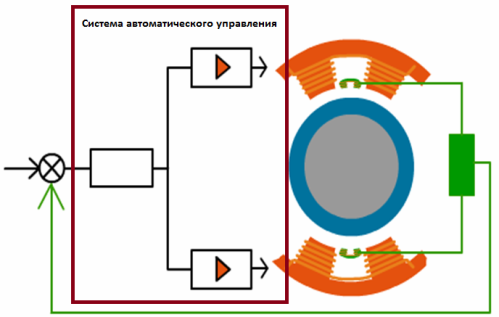
The automatic control system is located in the cabinet and is responsible for the correct modulation of the current flowing through the electromagnets in accordance with the signals from the rotor position sensors. The power of the amplifiers is related to the maximum strength of the electromagnets, the size of the air gap and the reaction time of the system to a change in the position of the rotor.
Possibilities for non-contact magnetic bearings
The maximum possible rotor speed in a radial magnetic bearing is limited only by the ability of the ferromagnetic rotor plates to resist the centrifugal force. Usually the limit for peripheral speed is 200 m / s, while for axial magnetic bearings the limit is limited by the resistance of the cast steel of the stop — 350 m / s with ordinary materials.
The applied ferromagnets also determine the maximum load that a bearing can withstand with the corresponding bearing stator diameter and length. For standard materials, the maximum pressure is 0.9 N / cm2, which is less than that of conventional contact bearings, but the load loss can be compensated by high peripheral speed with increased shaft diameter.
The power consumption of the active magnetic bearing is not very high. The biggest losses in the bearing are due to eddy currents, but this is ten times less than the energy that is lost when using conventional bearings in machines. Excluding couplings, thermal barriers and other devices, the bearings work effectively in vacuum, helium, oxygen, seawater and more. The temperature range is from -253 ° C to + 450 ° C.
Relative disadvantages of magnetic bearings
Meanwhile, magnetic bearings also have disadvantages.
First of all, it is necessary to use auxiliary safety rolling bearings, which can withstand a maximum of two failures, after which they must be replaced with new ones.
Second, the complexity of the automatic control system, which, if it fails, will require complex repairs.
Third, the temperature of the bearing stator winding rises at high currents — the windings heat up and they need their own cooling, preferably liquid cooling.
Finally, the material consumption of a non-contact bearing is high because the bearing surface must be large to support sufficient magnetic force—the stator core of the bearing is large and heavy. Plus the phenomenon of magnetic saturation.

But despite the apparent disadvantages, magnetic bearings are now widely used, including in high-precision optical systems and in laser installations. One way or another, since the middle of the last century, magnetic bearings have been improving all the time.