Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS components) and sensors based on them
MEMS components (Russian MEMS) — means microelectromechanical systems. The main distinguishing feature in them is that they contain a movable 3D structure. It moves due to external influences. Therefore, not only electrons move in MEMS components, but also in the constituent parts.
MEMS components are one of the elements of microelectronics and micromechanics, often manufactured on a silicon substrate. In structure, they resemble single-chip integrated circuits. Typically, these MEMS mechanical parts range in size from units to hundreds of micrometers, and the crystal itself is from 20 μm to 1 mm.
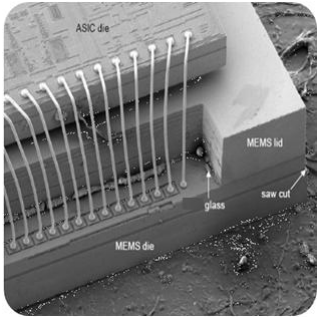
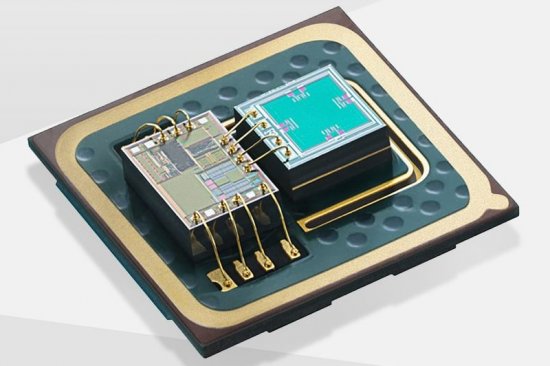
Figure 1 is an example of a MEMS structure
Usage examples:
1. Production of various microcircuits.
2. MEMS oscillators are sometimes replaced quartz resonators.
3. Production of sensors, including:
-
accelerometer;
-
gyroscope
-
angular velocity sensor;
-
magnetometric sensor;
-
barometers;
-
environmental analysts;
-
radio signal measuring transducers.
Materials used in MEMS structures
The main materials from which MEMS components are made include:
1. Silicon. Currently, the majority of electronic components are made of this material. It has a number of advantages, including: spread, strength, practically does not change its properties during deformation. Photolithography followed by etching is the primary fabrication method for silicon MEMS.
2. Polymers. Since silicon, although a common material, is relatively expensive, in some cases polymers can be used to replace it. They are produced industrially in large volumes and with different characteristics. The main manufacturing methods for polymer MEMS are injection molding, stamping, and stereolithography.
Production volumes based on the example of a large manufacturer
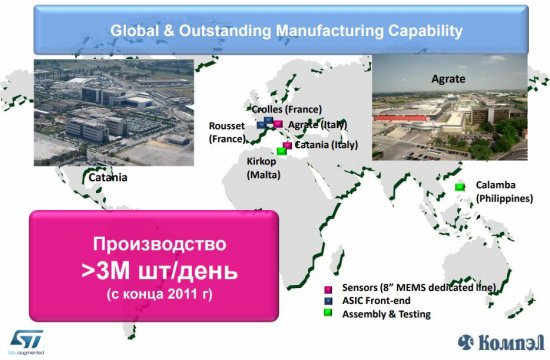
For an example of the demand for these components, let's take ST Microelectronics. It makes a big investment in MEMS technology, its factories and plants produce up to 3,000,000 elements per day.
Figure 2 — Production facilities of a company developing MEMS components
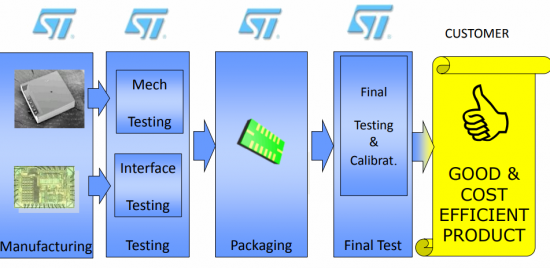
The production cycle is divided into 5 main main stages:
1. Production of chips.
2. Testing.
3. Packing in cases.
4. Final testing.
5. Delivery to dealers.
Figure 3 — production cycle
Examples of MEMS sensors of different types
Let's take a look at some of the popular MEMS sensors.
Accelerometer This is a device that measures linear acceleration. It is used to determine the location or movement of an object. It is used in mobile technology, cars and more.
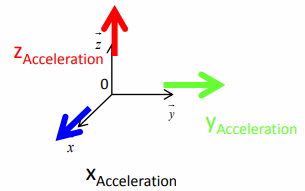
Figure 4 — Three axes recognized by the accelerometer
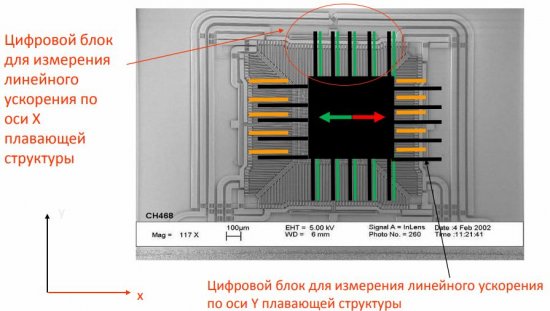
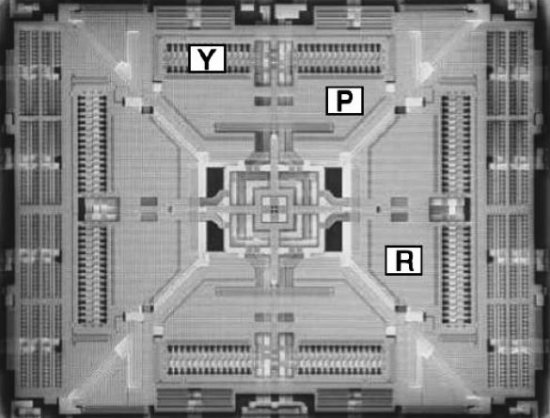
Figure 5 — Internal structure of the MEMS accelerometer
Figure 6 — Accelerometer structure explained
Accelerometer features using the LIS3DH component example:
1.3 -axis accelerometer.
2. Works with SPI and I2C interfaces.
3. Measurement on 4 scales: ± 2, 4, 8 and 16g.
4. High resolution (up to 12 bits).
5. Low consumption: 2 µA in low power mode (1Hz), 11 µA in normal mode (50Hz) and 5 µA in shutdown mode.
6. Work flexibility:
-
8 ODR: 1/10/25/50/100/400/1600/5000 Hz;
-
Bandwidth up to 2.5 kHz;
-
32-level FIFO (16-bit);
-
3 ADC inputs;
-
Temperature sensor;
-
1.71 to 3.6 V power supply;
-
Self-diagnosis function;
-
Case 3 x 3 x 1 mm. 2.
Gyroscope It is a device that measures angular displacement. It can be used to measure the angle of rotation about the axis. Such devices can be used as a navigation and flight control system for aircraft: airplanes and various UAVs, or for determining the position of mobile devices.
Figure 7 — Data measured with a gyroscope
Figure 8 — Internal structure
For example, consider the characteristics of the L3G3250A MEMS gyroscope:
-
3-axis analog gyroscope;
-
Immunity to analog noise and vibration;
-
2 measuring scales: ± 625 ° / s and ± 2500 ° / s;
-
Shutdown and sleep modes;
-
Self-diagnosis function;
-
factory calibration;
-
High sensitivity: 2 mV / ° / s at 625 ° / s
-
Built-in low-pass filter
-
Stability at high temperature (0.08 ° / s / ° C)
-
High impact state: 10000g in 0.1ms
-
Temperature range -40 to 85 °C
-
Supply voltage: 2.4 — 3.6V
-
Consumption: 6.3 mA in normal mode, 2 mA in sleep mode and 5 μA in shutdown modes
-
Case 3.5 x 3 x 1 LGA
conclusions
In the MEMS sensor market, in addition to the examples discussed in the report, there are other elements including:
-
Multi-axis (eg 9-axis) sensors
-
Compasses;
-
Sensors for measuring the environment (pressure and temperature);
-
Digital microphones and more.
Modern industrial high-precision microelectromechanical systems that are actively used in vehicles and portable wearable computers.