Microwave oven: history, device and principle of operation, performance regulation, aspects of safe use
History of the microwave oven
Percy Spencer was 50 years old when he worked as an engineer at the American military-industrial company Raytheon, which was engaged in the production of radar equipment.
It was 1945, then Percy accidentally discovered a phenomenon that two years later would be the basis of the first microwave oven: during another experiment with the magnetron, a piece of chocolate in Spencer's pocket suddenly began to melt for no apparent reason.
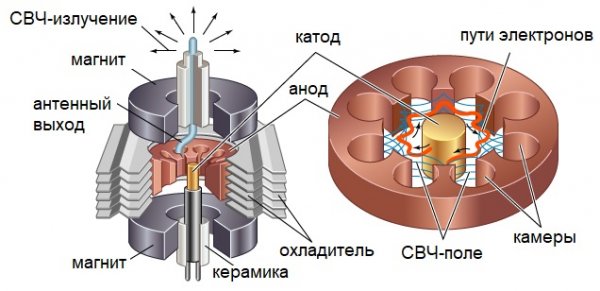
Magnetron is a device that emits electromagnetic energy in the form of microwaves. Originally used for radar technology.
It turned out that ultra-high-frequency (microwave) radiation can effectively heat food... As early as October 8, 1945, Percy Spencer received a patent for the world's first microwave oven designed for rapid defrosting of food.
In 1947the first microwave defroster under the Radarange brand was built (it can now be said to have left the assembly line). It was a unit about the size of a large modern refrigerator that weighed 340 kg with a power of 3 kW.
The first mass shipments of Radarange microwave ovens for defrosting food were sent to the chairs of military hospitals and the chairs of American soldiers. Since 1949, mass production of these ovens began, so anyone who could afford such a purchase had the opportunity to purchase a microwave oven for defrosting for only $ 3,000.
The origin of the idea of producing household microwave ovens for heating food dates back to October 25, 1955, when the first microwave oven for home use was presented by the American company «Tappan Company». Serial production of home microwave ovens began in 1962 by the Japanese company Sharp, but the demand for such an exotic household product was not great.
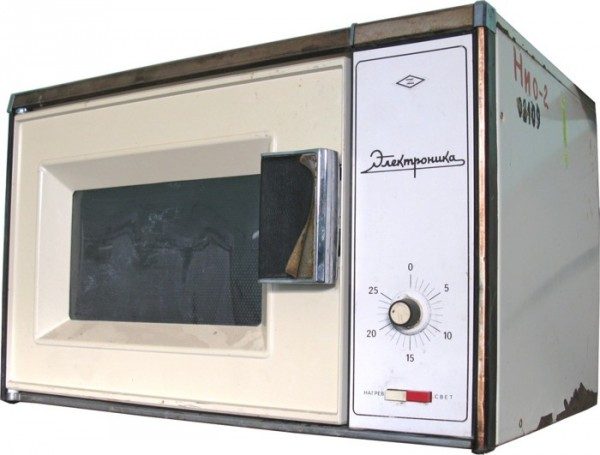 In the USSR, microwave ovens «ZIL», «Elektronika» and «Maria MV» began to be produced in the 80s. In 1990, the microwave oven "Dneprianka-1" with a volume of 32 liters, with a power of 1.3 kW at a microwave power of 600 W was produced on the M-105-1 magnetron.
In the USSR, microwave ovens «ZIL», «Elektronika» and «Maria MV» began to be produced in the 80s. In 1990, the microwave oven "Dneprianka-1" with a volume of 32 liters, with a power of 1.3 kW at a microwave power of 600 W was produced on the M-105-1 magnetron.
Thus began the mass production of home microwave ovens, which allow you to quickly defrost food, heat it and even cook it. The main condition is that the product placed in the microwave oven contains water.
The principle of operation and the device of the microwave oven
The conclusion is that electromagnetic radiation in the decimeter range leads to acceleration of the movement of polar dielectric (water) molecules that have a certain dipole moment.
As the molecules are accelerated, their interaction takes place under the influence of microwave radiation, that is, the substance absorbs electromagnetic radiation, while the temperature of this substance rises.
The optimal dielectric absorption of electromagnetic radiation by water occurs at a frequency of 2.45 GHz, which is precisely the frequency at which the magnetrons of modern microwave ovens operate.
Compared to conventional ovens, in a microwave oven, food is heated not only on the surface, but also in the volume of the product, because the electromagnetic wave penetrates the heated body at a depth of 1.5 to 2.5 cm, which accelerates heating, gives an average an increase in the temperature of the food equal to 0.4 ° C per second.
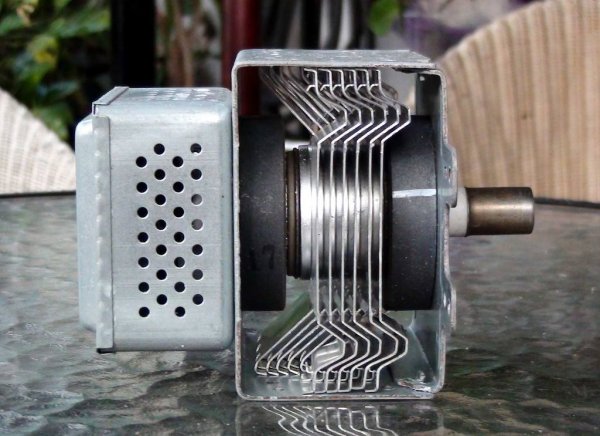
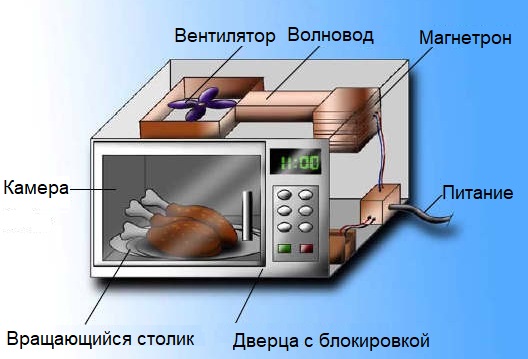
To obtain microwave radiation with a certain wavelength, a magnetron with specially calculated design parameters is used in a microwave oven. The radiation generated by the magnetron is transmitted through a waveguide and concentrated in a chamber in which a heated plate is placed.
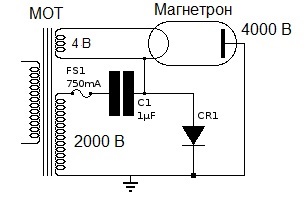
The chamber is closed with a metal door that prevents the propagation of microwave waves beyond its boundaries. The magnetron is powered traditionally from the secondary winding of a high voltage transformer (MOT) with an output voltage of 2000 volts, which is increased by a doubling circuit (consisting of a capacitor and a diode). Heating of the cathode of the magnetron is provided by a special secondary winding with a voltage of 4 volts from the same transformer.
The classic method of automatically adjusting the thermal characteristics of a microwave oven is the same as that used in irons and household heaters: the magnetron is periodically switched on and off so that the average thermal power delivered to the chamber in the form of electromagnetic waves is equal to that set by the user.

Safety aspects of microwave ovens
According to scientific data, the direct effect of microwave waves on the human body generates a noticeable heat effect, and in case of prolonged (or powerful) exposure, it can lead to local overheating and cause serious burns.
So, at a microwave power density of about 35 mW / cm 2, one feels heating. Prolonged exposure at power densities above 100 mW/cm2 causes cataracts and may lead to temporary infertility.
A microwave density level of 10 mW/cm2 is considered safe. Applied directly to microwave ovens, according to the European standard, at a distance of 5 cm from the microwave oven, the maximum power density level should not exceed 1 mW / square cm, and at a distance of 50 cm from the oven, it should not be more than 0 .01 mW / sq. Cm. cm. It is precisely these standards that meet modern microwave ovens during their production.
By the way, the open door of the oven always blocks its activation, that is, the microwave oven should never work with the door open.
Now for the effect of microwave waves on electrically conductive substances (especially metals). The wave, of course, does not penetrate metal objects, but it is able to induce induced currents in the metal, including eddy currents, which in turn strongly heat the metal.
For this reason, you will not be able to effectively heat food in a metal container using a microwave oven. What can we say about dishes with metal patterns and edges that are easily destroyed by microwave waves (from induced eddy currents) that simply spoil the dishes.