3 Tasks for Power Metering Tools in a Modern UPS
The purpose of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) is to protect critical equipment during a major power outage with battery backup. At the same time, the function of measuring energy consumption is only one of many available in modern enterprise-class UPSs.
Why does it deserve a separate article? Let's take a look—and find out how many emergencies can be prevented by constantly measuring the power consumption of each UPS outlet.
Measurement results: on the screen, in the local network and in the cloud
First, let's clarify how users—and in organizations, this is an operations engineer or system administrator—can read the load readings on the UPS outputs.
The source can display these values to the user in three ways: display them on the built-in monitor (all enterprise-class UPS are equipped with small service monitors), transmit them over the local network, or display them on a special website of the UPS manufacturer. The latter is called cloud monitoring.
The first method is used quite rarely — except at the time of initial connection of the load to the UPS: we connected a computer, printer, network equipment, etc., looked at the monitor — if the power consumption is normal, we went about our business.
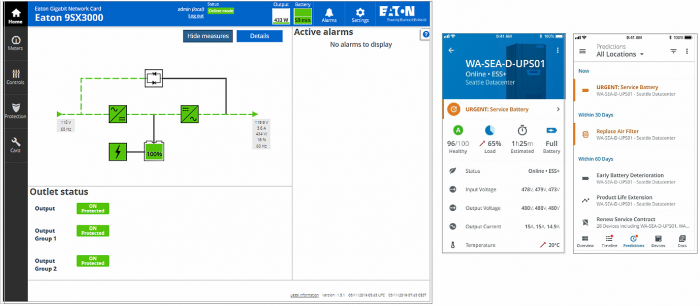
Pictured: example of UPS remote monitoring screens on desktop and mobile devices.
In addition, the task of monitoring the load's energy consumption passes to special software (software) that automatically reports critical power events via email, SMS or push messages. For this purpose, the UPS is equipped with a network card and is connected to the local network of the enterprise.
Eaton's Intelligent Power Manager is an example of such software. By the way, almost all UPS manufacturers have software tools for remote monitoring of energy consumption, and such software has been available on the market for more than a decade.
Among the new products that the pandemic brought in 2020 is cloud-based monitoring of energy consumption and the status of all UPSs in the corporate network.
The idea is simple: a remote system administrator can't walk around the facility checking UPS monitors—and often can't even come to his office unless absolutely necessary. But using the Internet of Things (IoT) technology, it is possible to display the UPS readings on a special website, where the system administrator can watch at any time from a computer or smartphone (or view this information through a mobile application).
Cloud monitoring software, in addition to displaying readings from UPS, temperature sensors and other "smart" devices, can send emergency messages about malfunctions and accidents, as well as display advanced data analytics — on the battery status of all UPS, total energy consumption, mains voltage, temperature inside the UPS and office areas, etc.
Cloud monitoring is currently only provided by leading enterprise-class UPS manufacturers—for example, Eaton's PredictPulse and Schneider Electric's APC SmartConnect.
Now let's go directly to the tasks that are solved by continuously measuring the energy consumption of UPS loads.
Task number 1: calculate the backup power time
If you drive a car, you are probably familiar with such a parameter on the dashboard as the estimated distance that can be traveled with the remaining fuel in the tank. Sometimes these numbers are critical — for example, if you need to get to a gas station in an area with few gas stations.
A similar task is performed by the UPS power consumption measurement function — it summarizes the load on each outlet and tells the user how long a computer connected to the UPS or, for example, medical or industrial equipment can operate on battery power in the event of an interruption of the external power supply. Additionally, this calculation will be made as accurately as possible based on the current UPS battery charge level.
Battery UPS operating time directly depends on load power consumption. In general, when the workload is halved, the operating time triples.
Many enterprise-class UPSs allow you to connect additional battery modules to the device, but there is an important feature: adding batteries to the UPS can increase the duration of the battery load, but does not increase the rated power of the UPS - it is set according to the characteristics of the electronic by blocks, not by battery capacity.
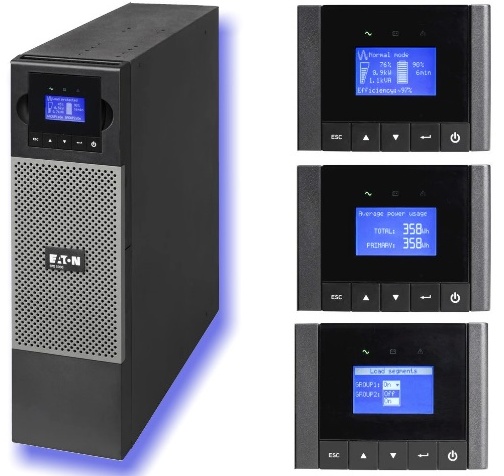

The picture shows an example of UPS screens (here: Eaton 5PX) with indication of load power, battery level and output segment selection.
The most commonly used batteries in UPS are VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) batteries, also known as maintenance. Manufacturers recommend selecting the UPS power for the load so that it is charged in terms of power by no more than 75%.
Batteries age and lose capacity over time, and cloud monitoring (such as monitoring over a local network) allows you to notice in time that the battery capacity has dropped to an unacceptably low level. The monitoring software automatically tracks such incidents and advises in advance when the battery replacement time is near.
This is important for powering servers, where a graceful shutdown of all programs requires at least a few minutes. If the battery is old, the UPS will shut down before the programs are completed and valuable data may be lost.
Modern enterprise-class UPS models, for example Eaton 5P / 5PX, allow the administrator not only to monitor the level of energy consumption in the UPS, but also to manage the load in the battery power supply from the mains, turned off mainly for non-essential equipment.
Task 2: identify overloaded and underloaded UPS
The second task of measuring power consumption is to prevent a situation where some UPSs are overloaded while others remain underloaded. UPS overload is usually caused by two reasons:
1) to protect the power supply of the load, a UPS with insufficient rated power is selected (for example, a load in the range of 700-1100 V·A is connected to a 1000 V UPS·A so that the rated power is periodically exceeded);
2) unqualified personnel connected more equipment to the UPS than originally calculated (possible case - the cleaner plugged a powerful professional vacuum cleaner into the nearest socket that he saw next to him, and this socket was from the UPS).
In the event of an overload, the enterprise-class UPS seeks to maximize the performance of the protected equipment and sends an alarm signal over the network to the system administrator's mobile device.
In addition, since the protected equipment draws more power than the UPS is designed for, the UPS transfers the load directly to the mains via an adapter called «bypass».
Then, depending on the logic in the UPS, the bypass can stay on for a while, waiting for the load to normalize. If this does not happen and the overload continues, the UPS will shut down completely and shut down the load.
The picture shows the installation of the UPS operation mode manually, through the service monitor of the source
The task of the administrator is to constantly monitor the situation in the enterprise regarding the possible overload of certain UPSs through remote monitoring.If the load on any UPS is close to the recommended maximum, then the administrator writes an application for the purchase and installation of a higher-power UPS or redistributes the load to another, less loaded UPS, while conducting explanatory work among the workers.
Task number 3: Observation of a short circuit or an open circuit in the load
As a rule, a UPS is used to protect the power supply of electronic devices that have their own power supply. Sometimes in the power supplies of such devices (servers, routers, printers, etc.) there is a malfunction and a short circuit.
In this case, the UPS immediately shuts down such load and issues an alarm, both locally with an audible signal and as a message over the local network or to a monitoring site in the cloud. When an alarm is received, actions are taken to eliminate the alarm.
Another case is the appearance of an open circuit in the load supply. In this case, the UPS will not alarm, but the administrator can see this situation on the UPS load charts in the cloud (or through the monitoring software over the local network) and also take measures to replace the damaged load power supply.
Considering that in addition to IT equipment, UPS devices are used to back up power for medical and industrial equipment, monitoring short circuits and open circuits in the load is important not only to maintain the operation of software and the safety of computer data, but also for people's health or the trouble-free execution of production processes. …
Conclusion
Thanks to remote monitoring (cloud or local network), the measurement of energy consumption in UPS output groups is of great practical importance, which allows you to respond in time to emergency situations, as well as evenly redistribute the load between UPS to achieve possible the longest battery life and increasing power reliability of critical devices...
The use of an enterprise-class UPS with high efficiency (for example -99% efficiency, as in the aforementioned Eaton 5PX) and advanced service functions: software for remote / cloud monitoring, the ability to connect additional batteries, automatic calculation of the remaining charging time from the batteries , the availability of three-level software charging batteries, which extends the life of the battery up to 50%, and informing the staff about the time of battery replacement — allows you to most effectively protect the computer, medical and industrial equipment in companies of any size and industry.