A brief history of robotics
Automation, robotics, fully autonomous production lines, robotic vehicles, increasingly powerful computer technologies. Machine tools, control systems, recognition systems are constantly being improved, the performance of computing units is increasing.
Man-made machines are becoming increasingly complex and pervasive in almost every branch of human activity, from manufacturing to medicine, from traffic management to the entertainment industry.
This article is about the history of robotics, a discipline that helps people solve their problems, making work easier and increasing productivity.
Nowadays, robotics is one of the most progressive technologies, which has reached unprecedented heights in its development thanks to the intellectual activity of whole generations of inventors, designers, engineers and technicians.
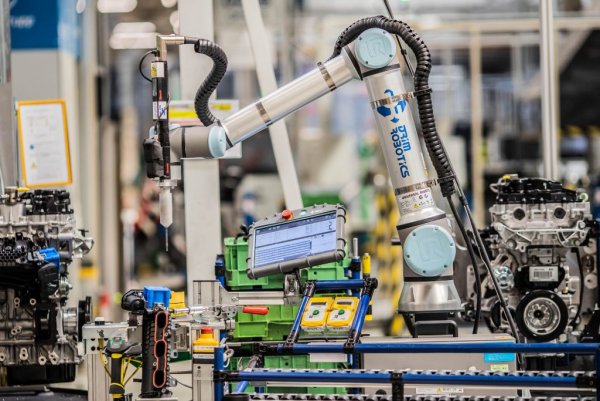
Production of a 3-cylinder engine at the Opel plant
Human and animal imitations
Looking into the past (and ultimately into the present), one cannot avoid the impression that people desperately wanted to create an artificial creature that would automatically perform boring, difficult, dangerous or undesirable actions for it.
The development of mechanization, automation and robotics is taking place gradually. As technology developed, the first imitations of humans or mechanical forms of animals appeared. Examples of mechanical imitations of animals are given in literature before the beginning of our era.
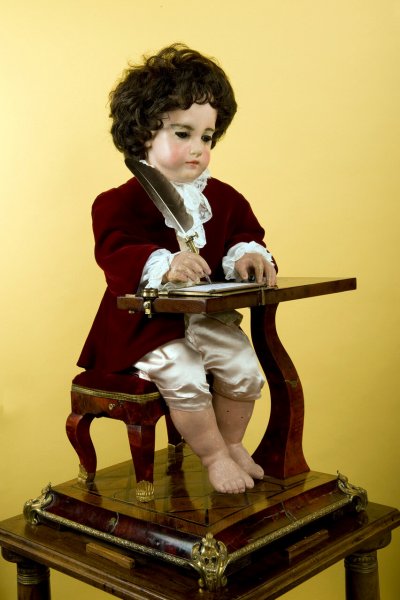
Renaissance genius Leonardo da Vinci (1495) is associated with the creation of the mechanical knight. Mechanical imitations of humans (androids) by the Swiss masters Jaquet-Droz (18th century) are also known. Their automatic scribe (calligrapher) was able to write a few sentences with a pen and mimicked a human very well.
Mechanical robot "Calligraph" by watchmaker Pierre Jacquet-Droz (1772)
After the era of mechanics, electrical engineering and then computer technology contributed to the development of robots. 1920 was a milestone in robotics.
Čapek's robots as beings with artificial intelligence
In 1920, Karel Čapek wrote a play "RUR" with the subtitle "Rossum's Universal Robots". The premiere of the play took place at the beginning of 1921 and for the first time the word "robot" was used in it, which became known in all languages of the world. The book RUR has been translated into more than thirty languages, including Esperanto.
Last year the word "robot" was 100 years old, and this year it is 100 years since Karel Čapek's first play "RUR" was performed.
Book cover of the science fiction play "RUR" written by Karel Čapek in 1920.
The word robot is perhaps the only Czech word that is used all over the world in its uncorrupted form.It gained such popularity that Karel Čapek later saw fit to claim that the real "inventor" of the word "robot" was his brother Josef.
Karel originally wanted to use the word "labor" from the English "labor" for the characters in the RUR game. So today we have the word robot used in every science fiction related to the typically Slavic word robot.
Čapek's robots are not mechanical replacements for humans, they are artificial beings created from synthetic organic matter and possessing human intelligence. In fact, they are the same as modern day androids, cyborgs and replicants.
WABOT-HOUSE PROJECT (2002)
Definition of robot and robotics
As is usual in science and technology, it is necessary to define the meaning of the word robot. Originally a robot was understood as a simple machine, see for example the 1947 Encyclopedia Britannica which gives a gyroscopic stabilizer for the course of an airplane or a ship as an example of a robot .
In 1941, the writer Isaac Asimov first used the word robotics and formulated three basic laws of robotics that represent the basic requirements for the development and use of robots.
Isaac Asimov's Laws of Robotics
A robot is most often understood as a computer-controlled integrated system capable of autonomously and purposefully interacting with a real environment in accordance with human instructions.
This definition is supplemented by other conditions that determine the definition of a robot, for example, the ability to perceive and recognize the environment, communicate with humans in artificial or natural language, etc.
Robotics as a scientific and technical discipline is the science of robots, their design, manufacture and application.Robotics is closely related to electronics, mechanics and software.
Terms and definitions: Robots and robotic devices
It seems that the ultimate goal of robotics is indeed to build a machine that will almost replace humans, including their intelligence.
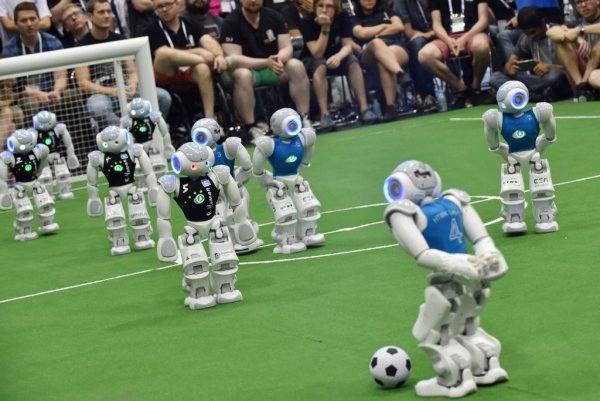
In 1997, a computer defeated the reigning world chess champion. In the same year, the international competition RoboCup was created with the following goal (dream) in the preamble: "By the middle of the 21st century, eleven fully autonomous humanoids will defeat the reigning football champion according to the official rules of FIFA." The goal seems silly, but, as in the case of conquering the moon, the path to this goal can have a number of "secondary" but significant results.
RoboCup (2017)
The ASIMO humanoid robot is primarily used for advertising purposes and to promote robotics
A humanoid robot (android) is a robot with a human form. Since many robots in science fiction look human, a humanoid robot may be the default robot for most people.
On the other hand, it cannot be argued that all robots that have to perform some tasks in the real world must necessarily be humanoid robots, for example airplanes do not look like birds either. The required functions for the robot should determine its optimal appearance.
Industrial robots
One of these results, without which, in particular, it is already impossible to imagine the production of cars, are industrial robots, the definition of which has already been given, ISO 8373: 2012, in general translation: "industrial robot: Automatic control, reprogrammed, a reconfigurable manipulator programmable in three or more degrees of motion that can be either permanently installed or moved for industrial automation applications. «
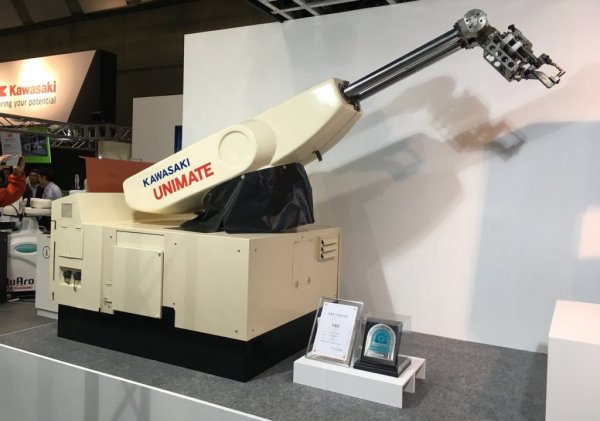
The first industrial robots, Unimate and Versatran, were built and put into service in the US between 1960 and 1962. These were relatively heavy machines with a small number of controlled axes with hydraulic and electro-hydraulic drives. Their programming and control were based on analog technology.
NServth real in history user interface industrial robot Unimate
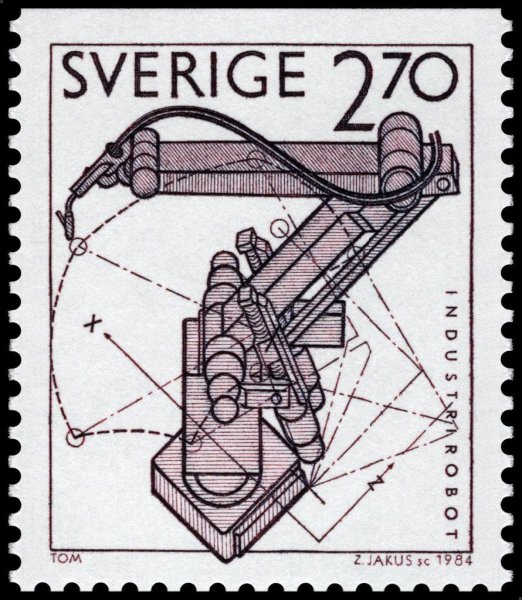
The first industrial robot using a microprocessor for control appeared in 1974. In Europe it was the successful Asea IRB 6 robot.
The robot had a manipulator in the form of an anthropomorphic arm structure, five controllable axes with electric drives and a load capacity of 6 kg. Despite the relatively simple control concept, it can also be used for arc welding and surface treatment. This robot was produced from 1975 to 1992, with a total of almost 2,000 produced.
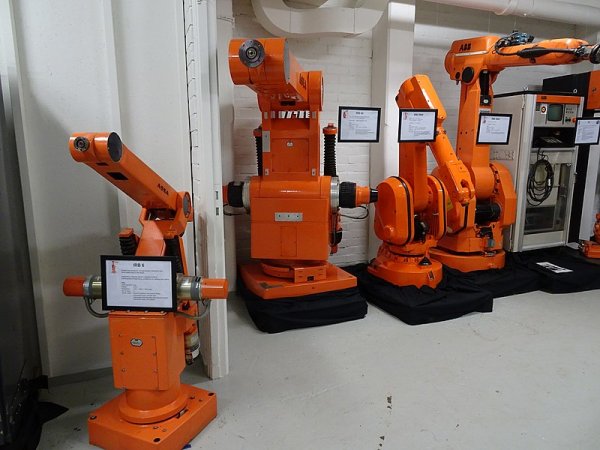
ASEA industrial robots (from left to right: IRB 6, IRB 2000, ABB IRB 3000, ABB S3 control cabinet)
ASEA IRB 6 robot on a 1984 Swedish postage stamp.
In the following years, the mechanics of industrial robots improved and the product range expanded, especially the load capacity — from robots for working with small parts to robots with a load capacity of about 1000 kg.
Industrial robots also began to be equipped with computer vision and other smart sensors. However, a major change has occurred in the way it is controlled and programmed, allowing the use of 3D CAD techniques and the programming of interactive robots.
The latest trend is collaborative industrial robots (cobots) that provide human-robot contact and respect the first law of robotics "a robot must not harm a human".A change has also occurred in the way of control and programming, which allows the use of 3D CAD methods and the programming of interactive robots.
According to statistics from the International Federation of Robotics, 76,000 new industrial robots were put into service in 2018 alone.
Modern collaborative robot Cobot UR5. Thanks to their sensors, collaborative robots (cobots) can interact directly and safely with humans.
More on modern industrial robots:
Classification of industrial robots
Ensuring safety when using industrial robots
Industrial robots and the benefits of their implementation in production, the importance of robotics
Robots and artificial intelligence
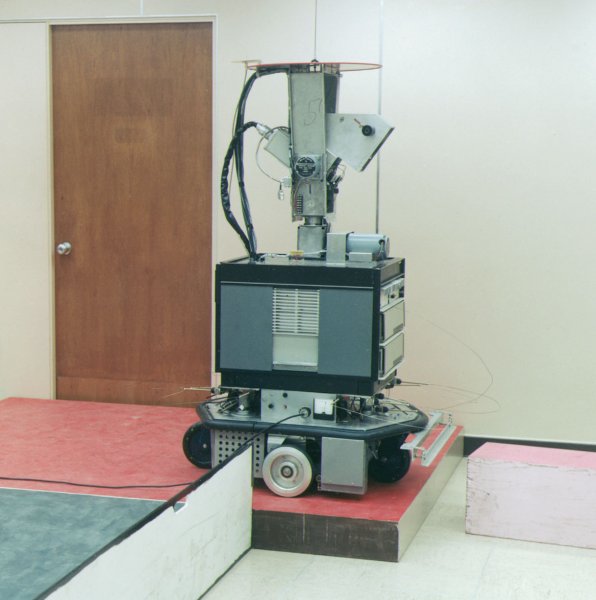
But back to our goal of replacing humans with machines. In the 1960s, the first artificial intelligence laboratories were established in American universities, and in 1968, at the Stanford Research Institute, the first intelligent mobile robot on wheels, Shakey, equipped with computer vision, which was able to recognize the environment, was created environment and to move purposefully in it.
Shakey Robot (1968)
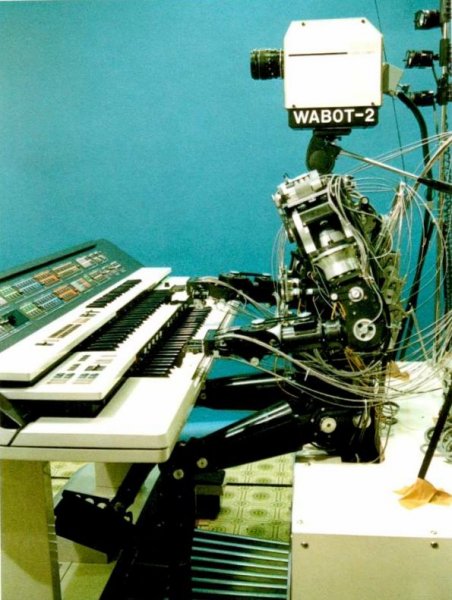
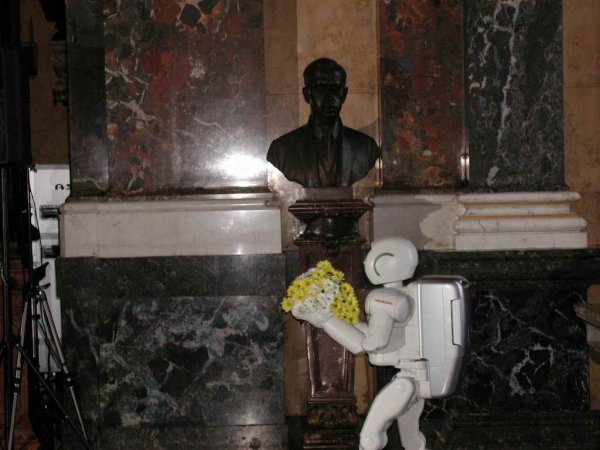
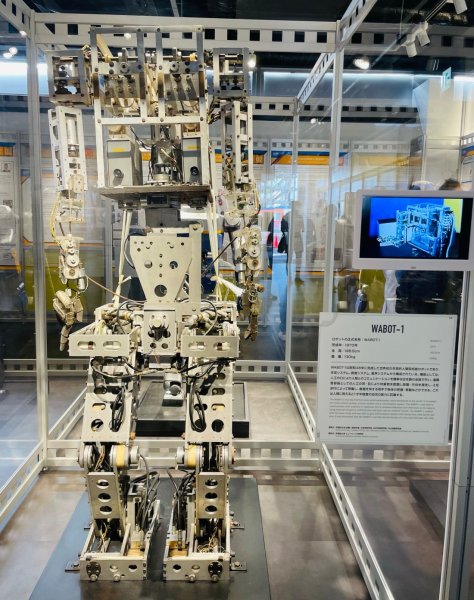
In 1973, the first modern humanoid Wabot-1 was launched in Japan at Waseda University. At Expo 85, Vabot played an electronic organ, and on August 22, 2003, the Japanese humanoid robot Asimo (ASIMO) laid flowers in Prague at the bust of Karel Čapek.
The Asimo v 2000 inch Waco Fundamental Research Center robot was created in Japan by the Honda Corporation and for a long time it was the most famous humanoid robot in the world.
Robot WABOT-1 (1973)
Robot WABOT-2 (1984)
Asimo's robot brought chrysanthemums to the bust of the creator of the word "robot", Czech writer Karel Čapek (2003)
Nowadays, there are a large number of service robots such as robotic vacuum cleaners, lawn mowers, robotic milking machines and many other devices based on the achievements of robotics.
From robotics came the interdisciplinary field of engineering - mechatronics, as many innovative solutions were first invented and implemented in the creation of robots, and then began to be used in other machines and mechanisms.
The word "mechatronics" was first used by Tekuro Mori, an engineer at the Japanese company Yaskawa, in 1969. Mechatronics is the pursuit of complete integration of mechanics, electrical machines, electronics, microprocessors, and software.
For more information on mechatronics, see here:What is mechatronics, mechatronic elements, modules, machines and systems