Dryer insulation of windings of electrical machines
 Electrical machines dry out when the insulation of the windings and other live parts becomes wet, for example during transport, storage, installation and repair, as well as when the unit is switched off for a long time.
Electrical machines dry out when the insulation of the windings and other live parts becomes wet, for example during transport, storage, installation and repair, as well as when the unit is switched off for a long time.
Drying the insulation of the windings of electrical machines without a special need causes additional unjustified costs, and if the drying mode is not maintained correctly, in addition, damage to the winding occurs.
The purpose of drying is to remove moisture from the insulation of the windings and increase the resistance to a value where the electrical machine can be powered. The absolute resistance, MΩ, of the insulation for electric machines that have undergone major repair must be at least 0.5 MΩ at a temperature of 10 — 30 ° C.
 For newly installed electrical machines, this value should not be lower than the values given in the table. 2, and for electric motors with a voltage of more than 2 kV or more than 1000 kW, in addition, it is necessary to determine with a megohmmeter absorption coefficient ratio ka6c or R60 / R15.
For newly installed electrical machines, this value should not be lower than the values given in the table. 2, and for electric motors with a voltage of more than 2 kV or more than 1000 kW, in addition, it is necessary to determine with a megohmmeter absorption coefficient ratio ka6c or R60 / R15.
If the data obtained show an unsatisfactory condition of the insulation, the electrical machines are dried.
The removal of moisture from the insulation of an electrical machine winding occurs due to diffusion, which causes moisture to move in the direction of heat flow from the warmer part of the winding to the colder part.
The movement of moisture is due to the difference in moisture in the different layers of insulation, from layers with a higher moisture content moisture moves to layers with a lower moisture content. The decrease in humidity, in turn, is due to the decrease in temperature. The greater the temperature difference, the more intense the drying of the insulation. For example, by heating the inner parts of the coil with current, it is possible to create a temperature difference between the inner and outer layers of insulation and thus speed up the drying process.
To accelerate drying, coils heated to the limit temperature must be periodically cooled to ambient temperature. Therefore, the efficiency of thermal diffusion is greater, the faster the surface layers of the insulation are cooled.
Section. 1. Approximate drying time for electric machines
Electric cars Minimum time, h, to reach the temperature Drying time, h 50 ° C 70 ° C general minimum after reaching a stable insulation resistance, MOhm Small and medium power 2 — 3 5 — 7 15 — 20
3 — 5
High power open design 10 — 16 15 — 25 40 — 60 5 — 10 High power closed design 20 — 30 25 — 50 70-100
10 — 15
During the drying process, the coils and steel must be heated gradually, because with rapid heating the temperature of the internal parts of the machine can reach a dangerous value, while the heating of the external parts will still be negligible.
 The rate of increase in the temperature of the coil during drying should not exceed 4 — 5 ° C per hour. According to the PTE of consumer electrical installations, the measurement of the insulation resistance to the machine body and between the windings is carried out for windings of electrical machines with a voltage of up to and including 660 V megohmmeter with 1000 V, and for electric machines the voltage is higher than 660 V — with a megohmmeter at 2500 V.
The rate of increase in the temperature of the coil during drying should not exceed 4 — 5 ° C per hour. According to the PTE of consumer electrical installations, the measurement of the insulation resistance to the machine body and between the windings is carried out for windings of electrical machines with a voltage of up to and including 660 V megohmmeter with 1000 V, and for electric machines the voltage is higher than 660 V — with a megohmmeter at 2500 V.
However, according to GOST 11828 — 75, the resistance of the windings of electrical machines for a rated voltage of up to 500 V inclusive is measured with a megohmmeter designed for 500 V, of the windings of electrical machines for a rated voltage of more than 500 V — with a megohmmeter for 1000 V. Therefore, PTEs somewhat tighten the requirements for testing insulation with a megohmmeter.
Insulation resistance measurement produced at a winding temperature of 75 ° C. If the insulation resistance of the windings is measured at a different temperature, but not lower than 10 ° C, it can be converted to a temperature of 75 ° C.
Before drying the insulation of the windings of electrical machines, the room must be cleaned of debris, dust and dirt. Electrical machines must be carefully inspected and blown with compressed air. During drying, measure the insulation resistance of each winding of the electrical machine to the grounded body of the machine and between the windings (Fig. 1).
Every time before the measurement it is necessary to remove the residual charges in the insulation; for this the winding is earthed to the housing for 3 — 4 minutes. In addition, when drying the windings of electrical machines, it is necessary to measure the temperature of the windings, the ambient air and the drying current. In practice, as a result of drying out the windings of electrical machines, the insulation resistance at a temperature of 750 ° C should not be lower than the data in the table. 2.
Section. 2. The smallest permissible insulation resistance of the windings of electrical machines after drying
Machines or parts thereof The smallest permissible insulation resistance Stators of an alternating current machine with a working voltage: over 1000 V 1 megohm at 1 kV working voltage up to 1000 V 0.5 MOhm at 1 kV Armatures of DC machines with a voltage up to 750 V including 1 MOhm for 1 kV Rotors of asynchronous and synchronous electric motors (including the entire excitation circuit) 1 MΩ per 1 kV, but not less than 0.2 — 0.5 MΩ Electric motors with a voltage of 3000 V and more: stators 1 MOhm at 1 kV rotors 0.2 MOhm at 1 kV 
Drying of windings of electrical machines by the method of induction losses in steel
In recent years, rational methods have been introduced for drying electric motors through induction losses in the stator steel with stationary machines, which are not related to the passage of current directly into the windings. In this drying method, there are two types: losses in the active steel of the stator and losses in the stator housing.
Heating of electric motors is done by losses due to magnetization reversal and eddy currents in the active steel of the stator of an AC electric motor or the inductor of a DC machine from the alternating magnetic flux generated in machines in the stator core and machine casing.
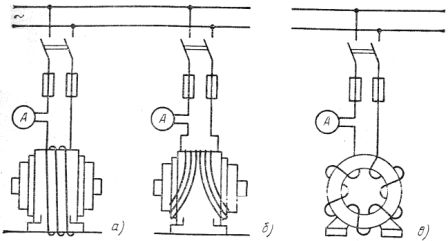
Variable magnetic flux is created by a special magnetizing coil wound on the body of the machine on its outer surface by pulling the wires under the frame (Fig. 1, a) or on the body and bearing shields (Fig. 1, b), the alternating magnetic flux can be created and from induction losses in the active steel of the stator and the body of the electric machine (Fig. 1, c).
The rotor of an induction or synchronous machine must be removed in order to wind the magnetizing turns of the stator.
Rice. 1. Drying of electric machines due to induction losses in steel: o -in the machine housing, b — in the housing and bearing shields, c — in the housing and active steel of the stator
The magnetizing coil is made with an insulated wire, the cross section and the number of turns are determined by the corresponding calculation.
In the drying process, the insulation resistance of the windings of electrical machines during the first drying period decreases, then increases and, reaching a certain value, becomes constant. At the beginning of drying, the insulation resistance is measured every 30 minutes, and when steady-state temperature is reached, every hour.
The results are recorded in the drying diary and at the same time curves are drawn (Fig. 2) for the dependence of the insulation resistance and temperature of the windings on the drying time.Measurements of insulation resistance, winding temperature and ambient temperature continue until the electric machine has completely cooled down.
The drying of the windings of an electric machine is stopped after the insulation resistance practically does not change at a constant temperature for 3 to 5 hours and ka6c is at least 1.3.
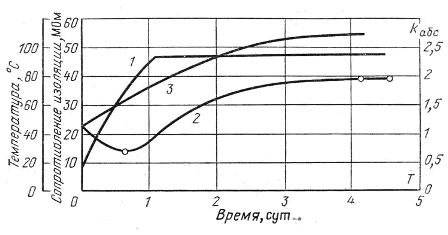
Rice. 2. Curves of the dependence of the insulation resistance 2, the absorption coefficient 3 and the temperature of the winding 1 of the electric machine on the duration of drying
Drying the insulation of the windings of electric motors in a drying oven