Selection of cross-sections of SIP insulated wires
 Cross-sectional insulated wires SIP up to 1 kV is selected according to the economic current density and heating, when the number of hours of use of the maximum load is more than 4000 — 5000, with a shorter duration of the maximum load — according to the heating. If the cross-section of the conductor determined by these conditions is less than the cross-section required by other technical conditions (mechanical strength, thermal resistance at short-circuit currents, voltage losses), then it is necessary to take the largest transverse stress section required by these specifications.
Cross-sectional insulated wires SIP up to 1 kV is selected according to the economic current density and heating, when the number of hours of use of the maximum load is more than 4000 — 5000, with a shorter duration of the maximum load — according to the heating. If the cross-section of the conductor determined by these conditions is less than the cross-section required by other technical conditions (mechanical strength, thermal resistance at short-circuit currents, voltage losses), then it is necessary to take the largest transverse stress section required by these specifications.
When choosing cross-sections of a self-supporting insulated heating wire, the material of the wire insulation should be taken into account: thermoplastic or cross-linked polyethylene. The permissible temperatures of wires with wires of different insulation for different operating modes are given in a table. 1.
Table 1. Design features and cost of insulated wires
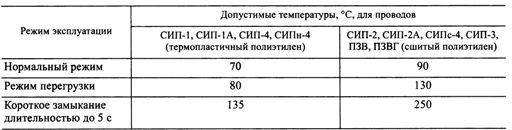
XLPE insulation is more heat resistant than thermoplastic polyethylene.In normal operation, the temperature of the core with thermoplastic polyethylene insulation is limited to 70 ° C, and with XLPE insulation - 90 ° C.
Self-supporting overload mode with insulated wire is allowed up to 8 hours per day, no more than 100 hours per year and no more than 1000 hours for the entire service life of the wire.
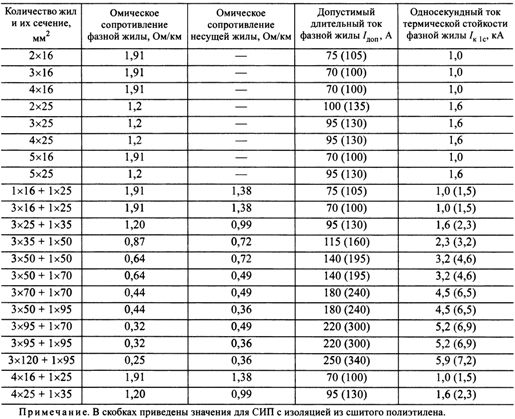
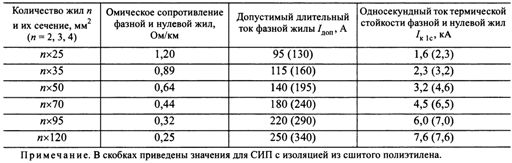
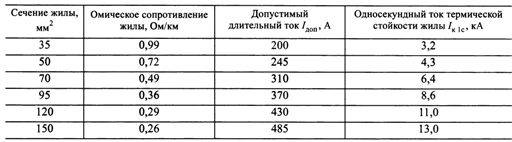
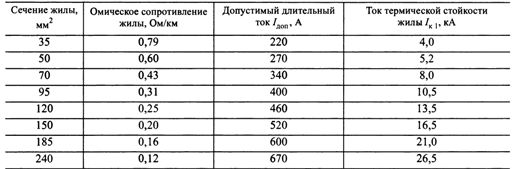
The permissible continuous currents Ipert corresponding to the permissible temperature for various designs of self-supporting insulated conductors are given in a table. 2 and 3. The ohmic resistances of phase and neutral conductors and the limiting one-second thermal stability currents are also specified here.
Section. 2. Electrical parameters of wires SIP-1, SIP-1A (SIP-2, SIP-2A)
Section. 3. Electrical parameters of SIP-4 wires
Section. 4. Permissible continuous currents of insulated conductors

For comparison in tab. 4 shows the permissible continuous currents of bare wires. SIP wires with a voltage of up to 1 kV allow lower current loads than bare wires. SIP wires are less effectively air-cooled because they are insulated and twisted into a bundle.
XLPE insulated wires are 1.15 - 1.2 times more expensive than thermoplastic polyethylene insulated wires. However, as can be seen from the table. 2 and 3, XLPE-insulated SIPs have 1.3 — 1.4 times greater load-carrying capacity than wires of the same cross-section with thermoplastic polyethylene insulation. Obviously, the choice of the cross-section of the self-supporting insulated conductor must be made on the basis of a technical and economic comparison of the options with different insulation.
Let's consider a concrete example of choosing the cross-section of the self-supporting insulated wire for the rated current Icalc = 140 A.
In accordance with the original data table. 2, you can take two SIP options:
SIP-1A 3×50 + 1×70, Add = 140 A; insulation — thermoplastic polyethylene;
SIP-2A 3×35 + 1×50, Add = 160 A; insulation — cross-linked polyethylene.
Obviously, it is economically feasible to adopt SIP-2A 3×35 + 1×50 with XLPE insulation:
In this way, the replacement of the SIP-1A wire with the SIP-2A wire of smaller cross-section and lower cost is actually done. Thanks to this replacement:
-
the weight of the wire is reduced;
-
the dimensions of the wire are reduced and accordingly the loads from ice and wind on the wire are reduced;
-
the service life of VLI is increased because cross-linked polyethylene is more durable than thermoplastic polyethylene.
The technical parameters of the SIPn-4 wire correspond to the parameters of the SIP-4 wire. SIPn-4 wire with refractory insulation should be used in conditions of increased fire safety requirements:
-
for entrances to residential buildings and industrial buildings;
-
when laying on the walls of houses and buildings;
-
in areas with increased fire danger.
If the choice of the SIPn-4 conductor is determined based on fire safety requirements, then the choice between SIP-4 and SIPs-4 conductors is made by technical and economic comparison of options.
To check the cross-sections for thermal resistance at short-circuit currents in tab. 2 and 3 the permissible thermal stability currents for one second Azk1 are given.
With different short-circuit durations, the permissible thermal current is determined by multiplying the current Azk1 by the correction factor
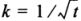
where t is the short circuit duration, s.
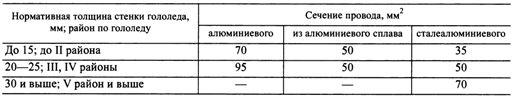
According to the conditions of mechanical strength of VLI highways, line branches and branches, wires with the minimum cross-sections specified in the table must be used at the inputs. 5. When checking the cross-sections of the self-supporting insulated conductor for the permissible voltage loss, it is necessary to know the linear parameters of the conductor. The ohmic resistances of self-supporting insulated wires are given in the table. 11 and 2, inductive resistance — in table. 6.
Section. 5. VLI wires with minimum cross-sections (example)

Section. 6. Inductive resistance of multi-core wires SIP
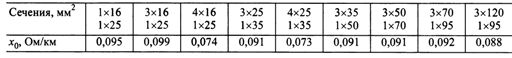
It should be noted that the inductive resistances of bare VLI wires are Xо = 0.3 Ohm / km.
Because of the lower reactances, the voltage loss in a line with self-supporting insulated wire will be less than in a line with bare conductors, under all other conditions.
The cross-sections of insulated wires with a voltage higher than 1 kV are selected according to the economic current density. The selected sections must meet the requirements for permissible heating, thermal resistance at short-circuit currents, mechanical strength, permissible voltage loss.
The permissible heating temperatures of conductors protected by insulation (SIP-3, PZV, PZVG) are given in the table. 1, the electrical parameters of these wires are tabulated. 7 and 8.
The cross-sections of insulated wires with a voltage higher than 1 kV are selected according to the economic current density. The selected sections must meet the requirements for permissible heating, thermal resistance at short-circuit currents, mechanical strength, permissible voltage loss.
Section. 7.Electrical parameters of SIP-3 wires
Section. 8. Electrical parameters of PZV and PZVG conductors
Section. 9. VLZ wires with minimum cross sections (example)
The cross-sections of insulated wires with a voltage higher than 1 kV are selected according to the economic current density. The selected sections must meet the requirements for permissible heating, thermal resistance at short-circuit currents, mechanical strength, permissible voltage loss.
The permissible continuous currents of insulated conductors are higher than those of bare conductors. This is due to the good cooling conditions for single-core insulated conductors, as well as the more favorable operating conditions for contact connections compared to contact connections for bare conductors. With VLI and VLZ all contact connections are sealed.
The thermal resistance of insulated conductors with a voltage above 1 kV is checked in the same way as insulated conductors with a voltage of up to 1 kV.
According to the conditions of mechanical strength of overhead lines, wires with the minimum cross-sections specified in the table should be used. nine.