Types and types of supports for overhead power lines
Depending on the method of suspension of the wires, the supports of overhead lines (overhead lines) are divided into two main groups:
a) intermediate supports on which the conductors are fixed in supporting brackets,
b) anchor-type supports serving to tension the wires. On these supports, the wires are fixed in tension clamps.
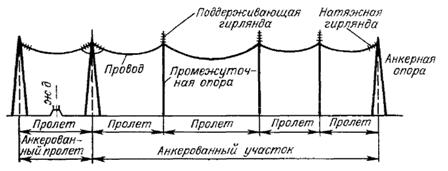
Distance between supports overhead power lines (Power line) is called a span, and the distance between anchor-type supports is an anchored area (Fig. 1).
In accordance with PUE requirements crossings of some engineering structures, for example, public railways, must be carried out on anchor-type supports. At the angles of rotation of the line, corner supports are installed, on which the wires can be suspended in supporting or tension brackets. Thus, the two main groups of supports are — intermediate and anchor — are divided into types with special purpose.
Rice. 1. Diagram of the anchored section of the overhead line
Intermediate straight supports installed on straight sections of the line.On intermediate supports with suspended insulators, the wires are fixed in supporting garlands suspended vertically, on intermediate supports with pin insulators, the wires are fixed with wire binding. In both cases, the intermediate supports perceive horizontal loads from the wind pressure on the wires and on the support and vertical loads from the weight of conductors, insulators, and the self-weight of the support.
In the case of continuous wires and cables, the intermediate supports do not, as a rule, perceive the horizontal load from the tension of the wires and cables in the direction of the line, and therefore can be made with a lighter design than other types of supports, for example, end supports that absorb the tension of the wires and the cables. However, to ensure reliable operation of the line, intermediate supports must withstand some loads in the direction of the line.
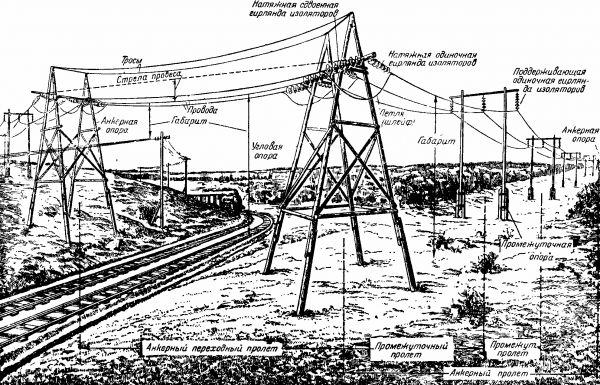
High voltage power line (drawing from a 1950s book)
Intermediate corner supports are installed at the angles of rotation of the line with suspension of wires in supporting garlands. In addition to the loads acting on the intermediate straight supports, the intermediate and anchor angle supports also perceive the loads from the transverse components of the tension of wires and cables.
At angles of rotation of the power line above 20 °, the weight of the intermediate corner supports increases significantly. Therefore, intermediate corner supports are used for angles up to 10 — 20 °. At large angles of rotation, anchor corner supports.
Rice. 2. Intermediate supports of overhead lines
Anchor supports... On lines with suspended insulators, the conductors are fixed in the clamps of the tension strings. These garlands are like an extension of the wire and transfer its tension to the support.On lines with pin insulators, the conductors are fixed on anchor supports with reinforced viscous or special clamps, which transfer the full tension of the conductor to the support through the pin insulators.
When installing anchor supports on straight sections of the route and suspending wires on both sides of the support with the same stresses, the horizontal longitudinal loads from the wires are balanced and the anchor support works in the same way as the intermediate one, i.e. horizontal transverse and vertical loads only.
Rice. 3. Anchor-type overhead line supports
If necessary, the wires on one side and the other side of the anchor support can be pulled with different tension, then the anchor support will perceive the difference in the tension of the wires. In this case, in addition to horizontal transverse and vertical loads, the support will also be affected by a horizontal longitudinal load. When installing anchor supports in the corners (at the turning points of the line), the anchor corner supports also perceive the load from the transverse components of the tension of wires and cables.
End supports installed at the ends of the line. From these supports there are wires suspended from substation portals. When suspending conductors on the line before the end of substation construction, the end supports assume full one-sided tension wires and cables overhead lines.
In addition to the listed types of supports, special supports are also used on the lines: transposition serves to change the order of the wires of the supports, branching — to make branches from the main line, support large crossings over rivers and water bodies, etc.
The main type of overhead line supports are intermediate, the number of which is usually 85-90% of the total number of supports.
By design, supports can be divided into freestanding and subordinate supports... Guys are usually made of steel ropes. Wooden, steel and reinforced concrete supports are used on overhead lines. Support structures made of aluminum alloys have also been developed.
Support structures for overhead lines
- Wooden support LOP 6 kV (Fig. 4) — single-column, intermediate. It is made of pine, sometimes larch. The stepson is made of impregnated pine. For 35-110 kV lines, wooden U-shaped two-pole supports are used. Additional structural elements of the support: hanging garland with hanging bracket, traverse, brackets.
- Reinforced concrete supports are single-column, free-standing, without guys or with guys to the ground. The support consists of a rack (trunk) made of centrifuged reinforced concrete, a traverse, a lightning protection cable with a grounded electrode on each support (for linear lightning protection). With the help of a grounding rod, the cable is connected to the grounding conductor (a conductor in the form of a pipe driven into the ground next to the support). The cable serves to protect the lines from direct lightning strikes. Other items: rack (trunk), towbar, traverse, cable resistant.
- Metal (steel) supports (Fig. 5) are used at a voltage of 220 kV or more.
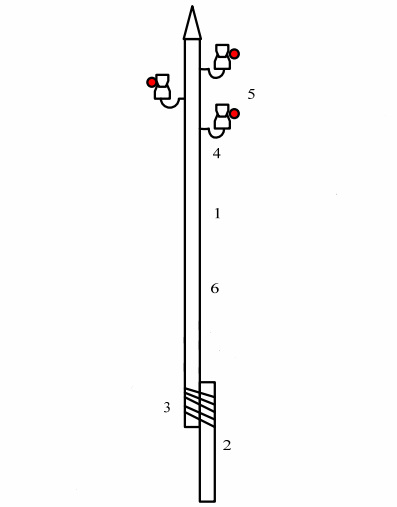
Rice. 4. Wooden single-post intermediate supports of 6 kV power lines: 1 — supports, 2 — step, 3 — bandage, 4 — hook, 5 — pin insulators, 6 — conductors
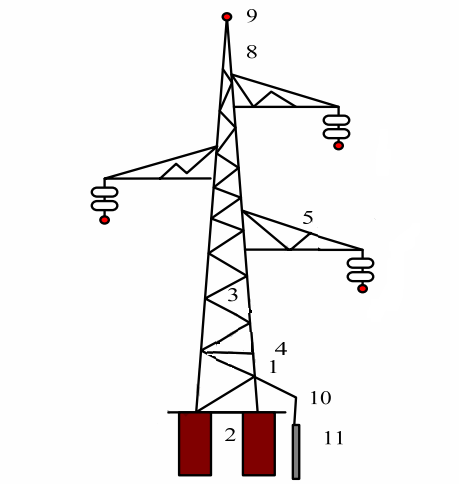
Rice. 5.Metal support for power lines 220-330 kV: 1 — support (trunk) of the support, 2 — prefabricated reinforced concrete or monolithic base, 3 — clamps, 4 — support belt, 5 — traverse (traverse and traverse belt), 6 — tension insulators or suspended, depending on the purpose of the support, 7 — wire, S — wire rope, 9 — lightning protection cable, 10 — ground electrode, 11 — grounding
On the first 110-500 kV overhead lines, metal welded support structures mounted on monolithic, rammed or metal footings were widespread. At the moment, metal supports with anti-corrosion protection of metal by hot-dip galvanization, mounted on prefabricated reinforced concrete foundations, are widely used on such overhead lines.

No less important in the reconstruction, modernization and construction of lines are the issues of reducing the transport weight of the supports, ease of installation, high specific strength of the supports, durability, resistance to vandals, resistance to climatic loads, environmental friendliness. Therefore, at the current stage, it is necessary to actively work on the implementation of the introduction of new forms of supports and the modification of existing structures of supports and their elements with the help of new materials and technologies.
Composite poles of overhead lines
Composite poles of overhead lines are a modular structure of consecutively assembled composite modules with a conical shape based on fiberglass (glass roving) and are used for single-circuit and double-circuit intermediate poles of power lines with a voltage of 110 and 330 kV. Insulated crossheads are recommended for composite supports.