Design parameters of overhead power lines
 The main design parameters of the overhead line (OL) is the length of the distance, the sag of the wires, the distance from the wires to the ground, to the covering of roads and other engineering structures crossed by the line (dimensions).
The main design parameters of the overhead line (OL) is the length of the distance, the sag of the wires, the distance from the wires to the ground, to the covering of roads and other engineering structures crossed by the line (dimensions).
Intermediate span length referred to as the linear distance between two adjacent intermediate supports. The length of the section of the 0.4 kV overhead line varies from 30 to 50 m and depends on the type of supports, the brand, the cross-section of the conductor, as well as the climatic conditions of the area.
Arrow sag of the wires called the vertical distance between an imaginary straight line connecting the points of attachment of the wires of two adjacent supports and the lowest point of their sag in the distance. The drooping arrow depends on the same factors as the span length.
Dimensions of the overhead line is called the smallest vertical distance from wires to the surface of the earth, rivers, lakes, communication lines, highways and railways, etc. Airline dimensions regulated by PUE and it depends on the stress and the people who visit the area.
To ensure normal operation and safe maintenance of overhead lines, the distances from them to various structures must meet the standards established by PUE. So the distance from the wires to the ground vertically with the largest arrow of sag should be at least 6 m in a populated area, the distance from the wires to the ground can be reduced in hard-to-reach areas to 3.5 m and in inaccessible areas to 1 m. Distance 4 along the horizontal line from the overhead lines to balconies, terraces, windows of buildings should be at least 1.5 m, and to empty walls at least 1 m. The passage of overhead lines over buildings is not allowed.
The route of the overhead line may pass through forests and green areas. The horizontal distance from the wires to the crown of trees and bushes with the greatest sagging should be at least 1 m.
Sizes of overhead lines 0.4 — 10 kV

Crossing air lines of navigable rivers rules are not recommended. When crossing non-navigable and freezing small rivers and canals, the distance 4 from the wires of the overhead line to the highest water level should be at least 2 m, and from the surface of the ice at least 6 m. The horizontal distance from the support of the overhead line to the water should be at least power line support heights.
The angle of intersection of overhead lines with streets, squares, as well as with various structures is not standardized.The intersections of overhead lines up to 1 kV between each other are recommended to be carried out on transverse supports, and not at distances.
Crossing points of overhead lines with overhead communication and signal lines should be performed only within the range of the line, and the wires of the overhead line should be located higher.
The distance between the upper wire of the communication line and the lower overhead line must be at least 1.25 m. Special requirements are imposed on overhead line wires in the cross section: they must be multi-wire, with a cross section of at least 25 mm2 (steel and steel-aluminium) or 35 mm2 (aluminium) ) and fixed on the supports by double fastening. Supports overhead lineswhich limit the range of intersections with communication lines of I and II class must be anchored; when crossing with communication lines of other classes, intermediate supports are allowed (wooden ones must have reinforced concrete attachments).
When crossing underground cable communication and signal lines, overhead line supports should be located as far as possible from the cable (but not less than 1 m between the grounding of the support and the cable in narrow conditions).

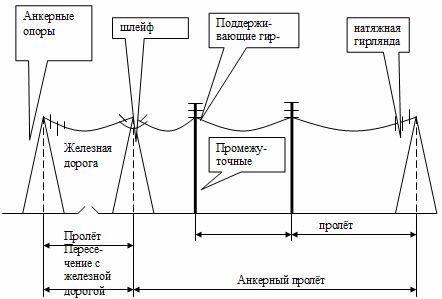
When crossing non-electrified trunk railway lines for general use, the transition supports of the overhead lines must be anchored; accessible railway tracks are allowed to cross overhead lines of intermediate ones (except for wooden ones) at an angle of at least 40 degrees. and as close to 90 degrees as possible. Electrified railways must be crossed with a cable insert in the overhead line.
Crossing overhead lines of Category I highways must be done on anchor supports, other roads can be crossed on intermediate supports. The cross-section of overhead lines passing through highways must be at least 25 (steel-aluminum and steel) and 35 mm2 (aluminum). The smallest distance from air lines there must be at least 7 m to the roadway. When crossing tram and trolleybus lines, the minimum distance from overhead wires to the ground must be at least 8 m.
The figure shows a diagram of the anchor span of the overhead line and the distance of the junction with the railway.
The vertical distance from the conductors of the line to the ground surface in an uninhabited area during normal operation should be at least 6 m for overhead lines up to 110 kV, 6.5; 7; 7.5; 8 m respectively for overhead lines 150, 220, 330, 500 kV.
