Using a capacitor as resistance
It is known that a capacitor installed in an alternating current circuit has a frequency-dependent resistance and is called reactive... Using it, you can also extinguish the excess network voltage, and the power of the reactive resistance is not released, which is a big advantage of the capacitor over the damping resistor. To determine it, it is easier to use the nonogram shown in the figure.
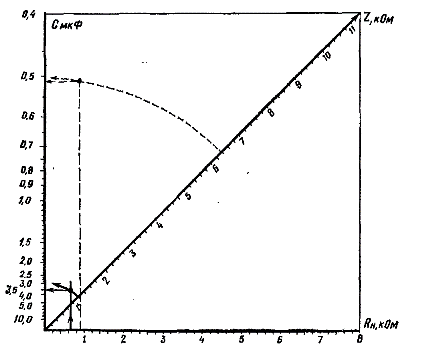
On the nomogram, the abscissa shows the resistances Rn in kΩ, the ordinate shows the capacity C of the quenching capacitors in μF and along the axis drawn at an angle of 45 ° to the axis of the abscissa - impedances Z of the circuit in kOhm.
To use a nonogram, you must first determine by Ohm's law or the power formula Rn and Z. On the abscissa axis of the nonogram, the calculated value of Rn is located, and from this point a vertical line is drawn parallel to the ordinate axis. Then, along the inclined axis, a predetermined value Z is sought. From the starting point, an arc is drawn through the point Z, which must intersect a line drawn parallel to the ordinate axis.A line parallel to the abscissa axis is drawn from the point of intersection. The point where this line meets the y-axis will indicate the desired capacity of the cooling condenser.
An example. Determine the capacitance of the capacitor that must be connected in series with a 127 V, 25 W electric soldering iron so that it can be connected to a 220 V AC network. Find Rn. Rn = U NS U / P = 127 NS127/25=645 ohms, where U is the voltage for which the electric soldering iron is designed, P is the power of the electric soldering iron.
To determine Z, you need to know the current Azflowing in the circuit: Then Z is equal to: Az= P / U = 25/127 = 1100 ohms. How to find the capacity of the cooling condenser using the calculated preliminary data is shown in the nomogram with bold lines.
See also: Calculation of capacitor capacitance
