Tubular electric heaters — heating elements: device, selection, operation, connection of heating elements
 Each electric resistance heater is a high-resistance resistance (heating element) equipped with auxiliary devices for supplying current, electrical insulation, protection against mechanical damage and fastening.
Each electric resistance heater is a high-resistance resistance (heating element) equipped with auxiliary devices for supplying current, electrical insulation, protection against mechanical damage and fastening.
Tubular electric heaters (heating elements) are the most common electrothermal devices for low and medium temperature heating installations. They are completely protected from external influences, including access to air.
A device with a heating element
 Usually, the heating element consists of a thin-walled (0.8 — 1.2 mm) metal tube (sheath) in which a spiral of high-resistance wire is placed. The ends of the coil are connected to a contact rod, the outer wires of which are used to connect the heater to the power supply.The tube material may be carbon steel if the surface temperature of the heating element in operation does not exceed 450 g. C and stainless steel at higher temperatures or when the heating element operates in corrosive environments.
Usually, the heating element consists of a thin-walled (0.8 — 1.2 mm) metal tube (sheath) in which a spiral of high-resistance wire is placed. The ends of the coil are connected to a contact rod, the outer wires of which are used to connect the heater to the power supply.The tube material may be carbon steel if the surface temperature of the heating element in operation does not exceed 450 g. C and stainless steel at higher temperatures or when the heating element operates in corrosive environments.
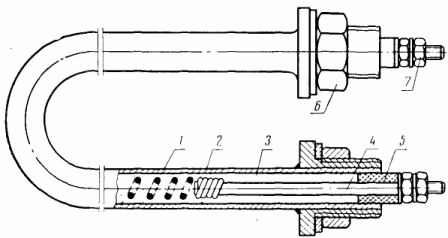
A device with a heating element. Tubular electric heater (TEN) with a hermetic design: 1 — nichrome spiral, 2 — pipe, 3 — filler, 4 — lead pin, 5 — sealing sealing sleeve, 6 — fastening nut, 7 — terminals.
The spiral is insulated from the pipe with a filler with high electrical insulation properties and good thermal conductivity. Most often, periclase (a crystalline mixture of magnesium) is used as a filler. After filling the filling, the tubes of the heating element are pressurized. Under high pressure, the periclase turns into a monolith, which reliably fixes the spiral along the axis of the tube of the heating element. The pressed heating element can be bent to give the required shape. The contact rods of the heating element are insulated from the pipe with an insulator, the ends are sealed with moisture-resistant silicon varnish.

Advantages and disadvantages of heating elements
The advantage of heating elements is flexibility, reliability and safety of service. They can be used in contact with gaseous and liquid media. The heating elements are not afraid of vibrations and shocks, but they are not explosion-proof either. The operating temperature of the heating elements can reach 800 gr. C, which satisfies their use not only in conductive and convection heating installations, but also as emitters in radiant (infrared) heating installations.Due to the sealing of the spirals, the service life of the heating elements reaches 10 thousand hours.
Heating elements are manufactured in a variety of designs, allowing them to be incorporated into a variety of installations ranging from industrial furnaces to household electric heaters. In addition to the usual design, single-ended heating elements with a cartridge with a diameter of 6.5 to 20 mm are produced, which are characterized by a high specific surface power, as well as flat heating elements with a developed surface for heat transfer.
Disadvantages of heating elements include high consumption of metal and price due to the use of expensive materials (nichrome, stainless steel), not very high service life, impossibility of repair at burn spiral.
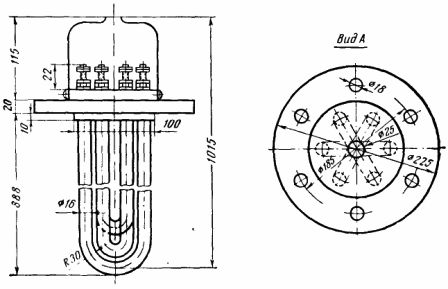
Three-element tubular electric heater NV-5.4/9.0
How to choose a heating element
TENs with a power of 15 W to 15 kW are produced in a unit with a length of 250 to 6300 mm, an outer diameter of 7 to 19 mm and a nominal voltage of 12 to 380 V in a single or three element design.
When choosing heating elements, it is necessary to take into account: the purpose of the heating element, its power, supply voltage, operating conditions (heated environment, nature of heating, heat exchange conditions, required temperature).
The force that can be removed from a unit surface of the heating element tube (specific load) depends on the operating conditions, the tube material and the filling material.
Heating elements are selected from the calculated power required to heat the medium: Pcalculation = (Kz x Ppol) / efficiency, where Kz — safety factor (1.1 — 1.3), efficiency — efficiency, taking into account power losses.
From the catalog, a heating element is found that meets the operating conditions for voltage, power. the temperature of the housing and the heated environment, as well as the shape, the possibility of placing the heating element in the working space. The number of heating elements is then determined depending on Pcalc and the unit power of the heating elements.

Working with heating elements
The main causes of failure of heating elements during work — violation of the sealing of the terminals, corrosion damage to the housing, breakage of the spiral due to overheating. These reasons are caused by excessive stress on the contact rods when connecting wires to the heating elements, the formation of a scale layer on the surface of the heating element tube.
The reliability of the operation of tubular electric heaters can be increased by following the following recommendations:
1) When connecting wires to the heating elements, do not apply excessive force to the contact rod nuts, as a result of which the tightness of the output ends of the heating element is disturbed.
2) It is necessary to turn off the operation of the heating elements without water.
3) It is necessary to clean scale from the surface of the heating elements 1 time every 2-3 months, avoiding deposits on the heating elements with a thickness of more than 2 mm.
