Maintenance of relay protection and automation devices
In three-phase electrical networks, damage to electrical equipment and difficult operating modes are possible. Damage associated with insulation failure, breakage of wires and cables of power lines, personnel errors during switching, lead to phase failures to each other and to the ground.
Short circuit, a large current appears in a closed loop, the voltage drop on the equipment elements increases, which leads to a general decrease in voltage at all points of the network and disruption of the work of consumers.
 In order to ensure normal operating conditions of electrical networks and to prevent the development of accidents, it is necessary to quickly react to changes in the operating mode, immediately separate the damaged equipment from the working one and, if necessary, turn on a backup power source to users. These functions are performed by devices a B C) relay protection and automation. (RPA).
In order to ensure normal operating conditions of electrical networks and to prevent the development of accidents, it is necessary to quickly react to changes in the operating mode, immediately separate the damaged equipment from the working one and, if necessary, turn on a backup power source to users. These functions are performed by devices a B C) relay protection and automation. (RPA).
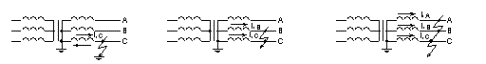
Rice.Fault in an electrical network with grounded neutral A, b, c, -one -, two -, three-phase short circuit, respectively.
Relay protection in the event of an emergency shuts down the damaged sections of the network and equipment.
Relay Protection and Automation (RPA) device checks
 Relay protection and automation devices are managed by local relay protection, automation and telemetry offices. Therefore, the operational staff checks these devices, checks their operability and readiness for action at least once a month, if there is a tele-signaling of a malfunction of the device. If they are absent, checks are carried out at least weekly when servicing substations OVB (Operational Field Teams).
Relay protection and automation devices are managed by local relay protection, automation and telemetry offices. Therefore, the operational staff checks these devices, checks their operability and readiness for action at least once a month, if there is a tele-signaling of a malfunction of the device. If they are absent, checks are carried out at least weekly when servicing substations OVB (Operational Field Teams).
When inspecting relay protection, automation and metering devices, maintenance personnel check the relay protection log entries or relay protection cards for all work done since the last inspection, changes to settings, circuits, relay protection devices, introduced or decommissioned as well as entries in the operational log.
Then it checks the operability of the emergency and warning signaling, signaling the position of the switches, the presence of voltage in the working current buses, all sources of direct and alternating current and the mode of operation of the chargers.
 For stationary devices, it controls the insulation resistance of the operating current circuits.By signaling, they check the operability of the control circuits of switches and other switching devices, the presence of operating current in all devices and circuits of relay protection and automation, control, serviceability of fuses and automatic switches of sources of operating current, the correct position of circuit breakers, circuit breakers and other switching devices in the circuit of the automatic transfer switch and the correspondence of their positions to the main diagram. Installed measuring devices monitor the health of voltage transformer circuits and fuses.
For stationary devices, it controls the insulation resistance of the operating current circuits.By signaling, they check the operability of the control circuits of switches and other switching devices, the presence of operating current in all devices and circuits of relay protection and automation, control, serviceability of fuses and automatic switches of sources of operating current, the correct position of circuit breakers, circuit breakers and other switching devices in the circuit of the automatic transfer switch and the correspondence of their positions to the main diagram. Installed measuring devices monitor the health of voltage transformer circuits and fuses.
Check all protection and automation devices on the control panel, relay board, in the corridors of the switchgear, the switchgear. Indicator relays triggered by accidental causes (eg shocks) return to their initial position. Check and check the readiness for action of the fixing devices.
All malfunctions identified during the inspection are recorded in the relay register and immediately reported to the PES dispatcher and the management of the local relay protection and automation service.

Some malfunctions can be fixed by the operating personnel themselves, including:
-
 Switching on circuit breakers or replacing fuses in VT circuits or powering relay protection devices.
Switching on circuit breakers or replacing fuses in VT circuits or powering relay protection devices. -
Deactivation of all devices for relay protection and automation in case of breakage of the breaker or other switching device, with subsequent implementation by the dispatcher of the measures provided for the connection, completely excluded from the relay protection;
-
Determining the location of the fault in the event of an earth fault in the working current circuits;
-
Disconnection of devices acting on the automatic closing of the circuit breaker in case of failure of the rectifiers supplying the switching circuits of electromagnetic drives.
All work in relay protection and automation devices, as a rule, is carried out by relay service personnel of relay protection and automation equipment according to previously issued applications.
